Why a dog does not have a heat – 9 reasons

Contents
About estrus in dogs
Puberty in dogs occurs at different ages – from 5 to 12 months. In breeds of giant size – such as, for example, Great Dane, Alabai, Caucasian Shepherd Dog, Newfoundend, longer – up to 24 months. Its onset depends on the breed, size, type of food and conditions of detention.
The entire period of the hormonal cycle can be divided into 4 phases:
Proestrus – preparation for the release of the egg. The bitch’s genitals swell, behavior changes, she flirts with relatives, but rather aggressively cuts off all contacts. Bloody discharge begins from the loop – the external genital organs. The duration of the stage is 7-10 days.
Estrus in dogs – the period of release of the egg and readiness for fertilization. Ovulation occurs on day 2-3, and this is the best time for a possible conception. Bloody discharge stops and scanty mucous membranes appear. The loop is very swollen and the female is ready for contact with males.
Metaestrus. If fertilization occurs, pregnancy occurs, if not, the body begins to return to the state before estrus. The genitals are reduced, the behavior becomes normal. On average, it lasts about 60-90 days.
Anaestrus. Lasts 4-12 months. This period is the time between estrus.
In young animals, there is a special variant of the flow of estrus – split.
The follicle matures and prepares to release an egg, and symptoms of proestrus develop. But, for some unknown reason, it decreases, and all symptoms disappear. After 10-20 days, the body “remembers” that it’s time to release the egg and starts the whole process again – the symptoms return. This is a variant of the norm, and it does not require treatment. To date, the exact reasons why this happens have not been clarified.

Reasons why dogs don’t heat
We will analyze the pathological reasons why a dog does not have estrus.
Stress
The hormonal background of the female depends on the emotional state. If she experiences prolonged stress, fear, pain, or other very intense emotions, she may not be in heat. Often such provoking factors are moving, operations, skirmishes with other dogs, hunger.
Additional symptoms: Trembling, fearfulness, aggression, unwillingness to contact.
Treatment: Sedative drugs.
Prevention: Attention and care.
Hormonal disbalance
An insufficient amount of sex hormones sometimes leads to a weak reproductive function, due to which the follicles do not mature, and the sexual cycle is impossible. Then the dog does not have a heat, and she is not able to become pregnant, because there are no eggs ready for fertilization.
Additional symptoms: As a rule, such health problems do not show other symptoms. In general, the pet feels great, the behavior does not differ from usual.
Diagnostics: Tests for progesterone, ultrasound of the ovaries, vaginal smears and other specific studies.
Treatment: It is selected individually depending on the combination of hormones.

Tumors of the genital organs
Oncological processes are always malfunctions of the body. Tumors of the uterus, vagina, ovaries can affect the hormonal background or the structure of the organ, disrupting sexual function. It is more common in older females and after taking hormonal drugs.
Additional symptoms: Discharge from the vagina of a different nature, visible lesions of the mucous membrane of the vulva (genitals), tumors of the mammary glands, changes in the general condition of the dog – lethargy, loss of appetite.
Diagnostics: Abdominal ultrasound and blood tests.
Treatment: The treatment regimen is individual, surgery, chemotherapy may be needed.
Prevention: Regular check-ups by a veterinarian for older pets.
ovarian cysts
Probably one of the most common causes of cycle disorder or lack of estrus is ovarian cysts. They interfere with the normal functioning of the ovaries, and failures occur in the cycle. There is no estrus, or vice versa, it flows more often and longer than expected. Often, cysts occur due to the use of hormonal-type drugs for contraception (Kontrseks, Sex barrier, Gestrenol, etc.). The true cause of the disease, breed or age predispositions have not been identified.
Diagnostics: Often they become an accidental finding during the examination of the dog on ultrasound, since their growth is often asymptomatic.
Treatment: It is possible by aspiration of the cyst (removal of its contents through a puncture), but this is quite dangerous, and doctors rarely resort to such a procedure. Most often, the ovaries are removed.
Wasting and an unbalanced diet
The hormonal background of the female is very dependent on the nutrients and vitamins that come with food. If the body is depleted, it cannot bear the fetus, which means that it does not need to become pregnant. As a result, the amount of sex hormones decreases, and the reproductive function is impaired.
Additional symptoms: Increased thinness, poor quality wool, low activity.
Diagnostics: Examination of the pet and collection of anamnesis (medical history).
Treatment: Improving living conditions, a balanced diet.
Prevention: Compliance with the norms of feeding, based on individual needs.

Hermaphroditism
A rare but very interesting pathology. During the formation of the fetus, a genetic failure occurs, and a puppy is born with the external genital organs of the female, and the internal ones are male. Or vice versa – with the uterus and testes. Under such conditions, the body does not give a command to start estrus, because male sex hormones disrupt the work of women. If, in principle, the animal is male, then there should be no estrus.
Diagnostics: Almost always, this diagnosis is made by chance, when the owners bring the patient for castration or clinical examination, since outwardly the pet is healthy and has no complaints.
Treatment: Removal of reproductive organs, otherwise the risk of developing tumor processes is high.
Excess weight
Excess weight is a violation of all metabolic processes in the body and uncontrolled hormone surges. Estrus is a complex and delicate hormonal process that does not tolerate such gross interventions. There is no absolutely ideal weight for a dog, it is individual for each pet, and it is necessary to evaluate the constitution. When viewed from above on the animal in a standing position, the waist should be visible, and the ribs should be easily palpable. Otherwise, you need to lose weight.
Additional symptoms: Increased fatigue and strong appetite.
Diagnostics: Visually, it is quite easy to determine the presence of excess weight.
Treatment: Active walks, dog fitness classes and reduced calorie intake.
Prevention: Compliance with nutritional norms and an active lifestyle.

Drug administration
Many drugs affect the onset of estrus. Hormonal agents directly act on ovarian function (oxitrol, sinestrol) and stop it. Indirect agents include antibiotics and corticosteroids. They, together with the disease for which they were prescribed, can push back the onset of estrus.
Diagnostics: Before giving the drug to a dog, it is enough to familiarize yourself with the side effects indicated in the instructions for it.
Treatment: As soon as you stop the drug, the cycle will be restored.
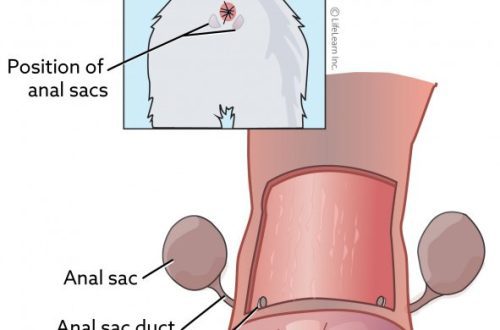
Inflammatory processes: endometritis, vaginitis, pyometra
A very large and dangerous group of diseases. Any inflammatory process in the uterus or vulva can contribute to delayed estrus in a dog. With its development, as a rule, discharge from the loop is still present, but they are cloudy and smell of pus.
Additional symptoms: Fever, lethargy, a lot of licking under the tail, he drinks a lot and eats little.
Diagnostics: Doctor’s examination, blood tests and smears from the vagina, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Treatment: Antibacterial drugs, vaginal douching, in severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Prevention: Castration.
Hidden estrus is another special condition that does not require treatment and does not affect reproductive function. All stages of follicular maturation and estrus in dogs are asymptomatic. There is no discharge, the loop does not swell, the female behaves normally, but becomes extremely attractive to males. Hidden estrus does not equal infertility, and the animal can also become pregnant. It is just much more difficult to recognize the period favorable for fertilization.
It is known for sure that this is not a hereditary feature, but reliable reasons for the development of latent estrus have not yet been identified.
What to do if the dog is not in heat?
If the dog does not have a heat, first of all, you should find out if this is a norm or a pathology.
When an animal older than 2 years has not yet shown signs of estrus, it is necessary to consult a veterinarian and conduct an examination – ultrasound of the abdominal cavity for abnormalities.
If the female used to be in heat, but now she doesn’t come in time, then it is required to analyze the conditions of her maintenance. Just like in humans, many factors affect the sexual cycle – stress, an unbalanced diet, overweight or underweight, active physical activity. In a situation where the conditions of detention are normal, but there is no heat, visit a specialist.
Unfortunately, we can definitely say that the owner will not be able to figure out the complex issue of the sexual cycle on his own and will need the help of a specialist. A veterinary reproductive specialist is the best assistant in restoring the hormonal background of an animal and controlling pregnancy.
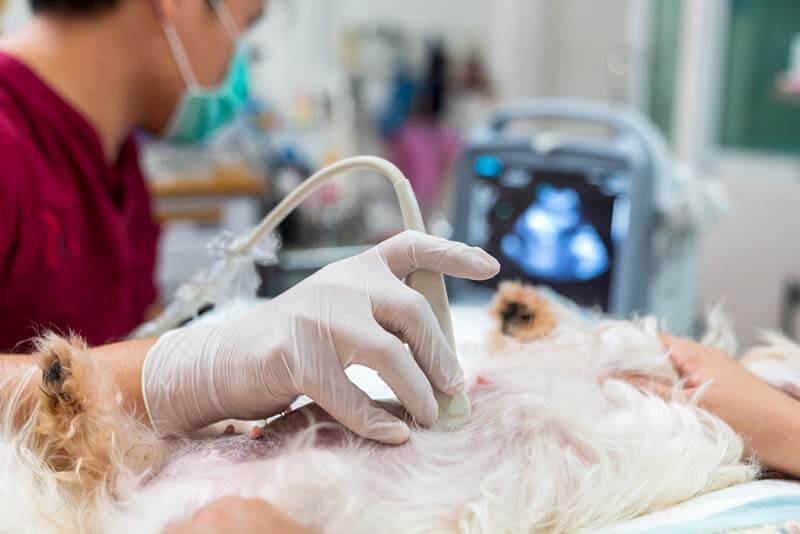
Which of the reasons are dangerous?
Most diseases of the reproductive system are quite dangerous and require medical supervision. Some of them can lead to fatal consequences and require urgent treatment.
Extremely dangerous causes include cancer and purulent inflammation in the uterine cavity.
With the development of inflammatory processes in the uterus, the entire body suffers. This disease is called pyometra (purulent uterus). Pus accumulates, which can lead to perforation – the uterus will burst, and it will leak into the abdominal cavity. Then comes death from sepsis, which occurs as a complication of any prolonged purulent inflammation.
Sepsis is very dangerous and leads to the failure of all internal organs and death of the animal.
The treatment for pyometra is usually removal of the uterus.
Chronic inflammation or hormonal disruptions lead to the formation of tumors in the uterus, ovaries and mammary glands. Cancer tumors are growing rapidly. When treated in the early stages, pets achieve remission (weakening of the disease) and live long.
It is possible to identify diseases only with the help of visual diagnostics – ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, CT, MRI.
When a dog does not have estrus, but the stomach increases in volume, there are unpleasant discharges from the vulva, she drinks a lot, problems with urination appear, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Can a dog get pregnant if there is no estrus?
No, it cannot, because in this case the egg did not leave the follicle.
However, if the animal has a hidden estrus, there are no symptoms, but the egg is still released, pregnancy is quite likely.

Summary
The age of the first estrus depends on the size and breed of the individual, individual conditions of detention.
Estrus is divided into 4 phases – proestrus, estrus, metoestrus and anaestrus. Pregnancy occurs only in estrus, a period that lasts only a couple of days.
If the dog does not have estrus, she has prolonged stress, malnutrition, very low body weight or, on the contrary, obesity, she is older than 7 years, then this may be a conditional norm. It is necessary to correct the general condition of the body, and not the reproductive system.
The presence of purulent discharge from the loop, general malaise, an increase in the volume of the abdomen and increased thirst indicate the development of extremely dangerous diseases and require urgent treatment to the clinic.
All diseases of the reproductive system are quite dangerous conditions. Only a veterinarian can determine the cause of the violations.
Answers to frequently asked questions