Bloating in Dogs: Causes and Treatment

Contents
Acute and chronic bloating in dogs
An increase in the volume of the abdomen occurs over different time intervals. When it lasts for several weeks or even months, then the owners do not even notice it. And only if the stomach becomes significantly enlarged, they begin to sound the alarm. But other situations are also possible, when bloating in a dog occurs literally in a matter of hours. In most cases, the general well-being of the animal deteriorates sharply, the situation requires immediate contact with the clinic.
Causes of Bloating in Dogs
Flatulence
Flatulence – increased gas formation in the stomach and intestines of a dog. Often occurs with improper feeding, for example, when eating foods such as white cabbage, legumes, flour products. Flatulence leads to excessive swallowing of air during meals. Pets often eat food at lightning speed, swallowing a very large amount of air. The development of pathogenic bacteria in the intestine can also lead to flatulence. In the course of their life processes, fermentation and decay occur with the release of gas.

Helminthiasis
The presence of a large number of helminths (parasites) in the intestines often leads to the fact that the dog’s stomach is bloated. This is especially noticeable in very young puppies. When there are very few helminths, there is usually no increase in the volume of the abdomen. But if the animal is not processed for a long time, then the worms can very seriously multiply and greatly inflate the intestines.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the increase in the abdomen occurs evenly over two months. There are cases when the owners do not know about the pregnancy of their dog and go to the clinic with complaints of bloating. It is not always possible to feel the fruits with your hands, but with the help of additional studies, it is not difficult to confirm pregnancy.

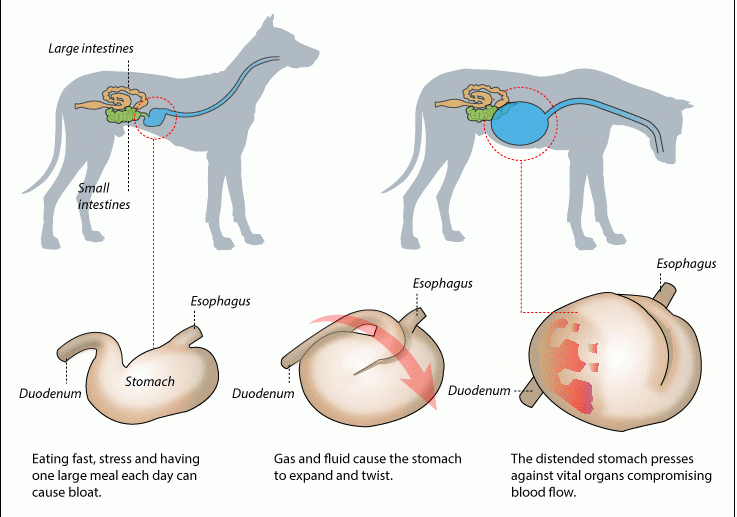
Volvulus of the stomach
This disease is typical for dogs of large breeds and large mestizos. It occurs due to the displacement of the stomach and twisting it around its axis. It is characterized by a sharp increase in the volume of the abdomen and depression of general well-being. Often occurs after active games on a full stomach.
Without emergency surgery, the pet may die from stomach torsion.
The animal becomes restless, looking for a comfortable position, as this condition is quite painful. Sometimes there is vomiting or profuse salivation. Percussion of the abdomen (tapping to produce sound) produces a tympanic (drum-like) sound. The mucous membranes may suddenly become cyanotic or pale. The body temperature drops, the dog gradually weakens, cannot stand up. In the absence of emergency assistance within six hours, most pets die.
Inflammation of the uterus
Inflammation of the uterus leads to bloating in the dog due to the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in its cavity, which is purulent, bloody or watery. The belly can grow both within a few hours and within a few days. A purulent lesion of the uterus will be manifested by a serious depression of the condition, vomiting, refusal to eat, increased thirst. If left untreated, the animal will most likely die. If the contents of the uterus are not purulent, most often there is no deterioration in general well-being.
Neoplasms in the abdominal cavity
The growth of a large neoplasm of some internal organ leads to a gradual increase in the volume of the abdominal cavity. For example, such a benign formation as a lipoma (tumor of adipose tissue) can grow quite quickly. The abdomen will enlarge rather slowly over the course of several months, and will likely be firm to the touch, but not acutely painful. But it is impossible to exclude the possibility of developing malignant tumors – lymphoma, carcinoma and others.

Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to collect a detailed anamnesis (medical history). First, the doctor will clarify what is included in the diet of the animal, when helminths were treated, and whether it was castrated. Then it will be necessary to tell how quickly the symptoms developed, for what time interval the dog’s stomach swelled up, what other complaints the pet has (refusal to eat, vomiting, increased thirst).
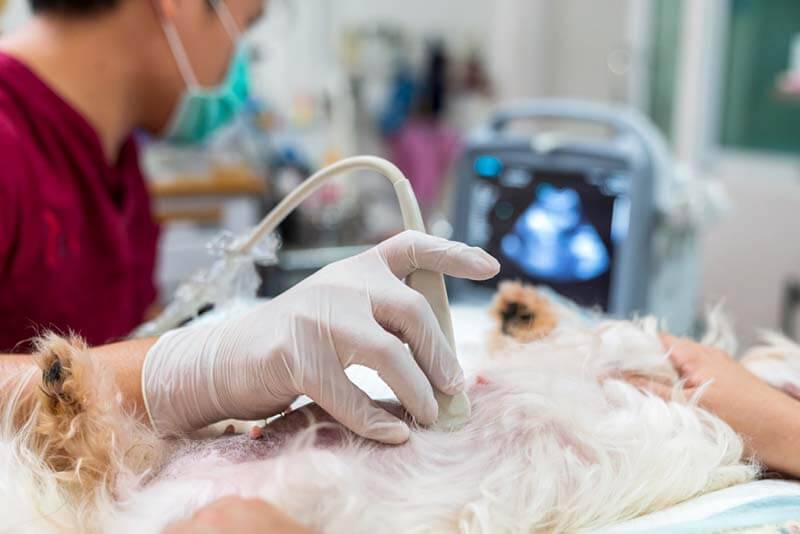
First of all, an ultrasound will be performed on the animal. With it, you can see increased gas formation in the intestines, the presence of viable fetuses, fluid in the uterus, large tumors, even helminths are often visible.
The diagnosis of helminthiasis is confirmed by fecal analysis or trial treatment with anthelmintic drugs.
If gastric volvulus is suspected, x-ray diagnostics is most often used. Determine the type of tumor using histological examination. Through clinical and biochemical blood tests, inflammatory and infectious processes can be detected, and the performance of internal organs can be assessed. Sometimes it is recommended to take a fecal analysis for PCR – a study to search for pathogenic microflora that can cause bloating in a dog.
Treatment for Bloating in Dogs
In the presence of flatulence, carminative drugs are prescribed to the animal to remove excess gases.
If the reason is improper feeding, then the most suitable diet is selected for the pet, all gas-producing foods are excluded.
To reduce the speed of eating food, a pet may be offered feeding from a special interactive bowl in the form of a maze.
If the cause is the development of pathogenic flora, antibacterial drugs are prescribed to eliminate it, depending on the detected causative agent of the problem.
Worms are treated with broad-spectrum anthelmintic drugs.
Gastric volvulus requires emergency surgery, during which the stomach is given an anatomically correct shape, and its wall is sutured to the peritoneum to prevent this from happening again.
Inflammation of the uterus is most often treated surgically. The inflamed uterus and ovaries are removed, antibiotics and painkillers are prescribed. When the condition of the animal is stable, therapeutic treatment is used instead of surgery, but this method is less preferable due to the high risks of recurrence of the disease in the next estrus.
Tumors in the abdominal cavity will be treated according to their type, which is revealed by the results of histology. Oncologists prescribe surgical removal if possible, as well as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.

When do you need immediate veterinary help?
Usually it is impossible to independently determine what happened to the pet. Any case of distended abdomen in a dog will require an examination by a doctor to determine the cause. But there are situations when you need to seek help urgently. Most often, patients are large animals with a sharply enlarged abdomen due to gastric volvulus. Sometimes there is a sharp weakness of the limbs, depression of the state, vomiting. The operation must be carried out in the next few hours, otherwise the pet will most likely die.
What can I do by myself
If the general condition is stable, there is no lethargy, refusal to eat, vomiting, then you can carry out preventive treatment yourself. First of all, it is necessary to treat helminths with tablets or suspension. If you know that the dog eats very quickly and swallows air, changing the bowl to an interactive one will help. It is permissible to use carminative drugs such as Espumizan, Bobotik. In the absence of improvement, it is recommended to contact the clinic for research.
Predisposition of some breeds
Large and giant breeds, such as Great Dane, Setter, Boxer, St. Bernard and others, are prone to the appearance of gastric volvulus. There is no breed predisposition to other diseases.

Prevention
Prevention of flatulence consists in high-quality balanced feeding, preventing excessively fast eating of food. Preventive treatments for helminths are carried out for dogs at least 4 times a year. It is possible to prevent the development of inflammation of the uterus with the help of planned castration. Unfortunately, it is difficult to prevent the development of tumors of the abdominal cavity.
There are the following ways to prevent gastric volvulus:
Feed your dog at least twice a day
Avoid active physical activity immediately after feeding
Eliminate gas-producing foods from the diet
Avoid stressful situations immediately after feeding
Perform prophylactic gastropexy – surgical suturing of the stomach to the abdominal wall in order to prevent its displacement.
Puppy bloated belly
Quite often, owners come to the appointment with the concern that after eating the puppy becomes bloated. This situation does not require treatment if the stomach is rounded only after eating, and the rest of the time it is in a normal state. If the stomach is constantly round, we can talk about flatulence due to errors in feeding or helminthiasis. Other conditions are almost non-existent in puppies.

Summary
There are quite a few reasons for bloating – from flatulence to tumor formation.
Treatment will depend on the cause of the bloating and may include medication or emergency surgery.
Large dogs are at risk for gastric volvulus. A sharp bloating with a deterioration in general well-being is an emergency reason for contacting the clinic
It is possible to prevent this condition with the help of timely treatments for helminths, normalization of the diet, exclusion of activity after feeding.
Answers to frequently asked questions