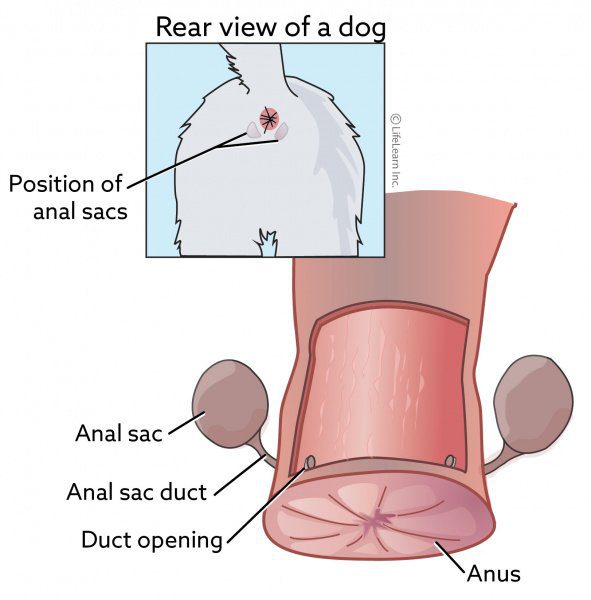
Paraanal glands in dogs

Contents
About the anal glands
Paraanal sacs (or sinuses) are located in the thickness of the soft tissues, to the right and left of the anus. They secrete a special secret into the lumen of the rectum, lubricating it and feces as they exit the intestine. Therefore, when meeting a dog, the first thing they pay attention to is sniffing the opponent’s anus or feces – the secret of these glands is a kind of identification code for each caudate.
Thus, sines perform the following tasks:
marking territory
scare away enemies
promote intraspecific recognition
attract other individuals.

Causes of problems
Sometimes the lumen of these sacs becomes clogged, they become inflamed, the process can even reach the development of purulent inflammation. Regular prophylactic cleaning of the paraanal glands is required only for dogs whose anatomy predisposes to the constant clogging of these ducts, but normally, they are cleared on their own during a bowel movement.
There are a number of predisposing factors why these diseases can occur:
Low physical activity and lack of long games.
Rare walks, the frequent need to endure before going to the toilet, the lack of prolonged games and physical activity can contribute to clogging of the ducts of the paraanal glands. More often these changes are typical for indoor dogs and older animals.
Genetic predisposition.
Hereditary displacement or narrowing of the lumen of the glands is more common for small and dwarf breeds of dogs – Chihuahua, Toy Terrier, Yorkshire Terrier, Pomeranian, French Bulldog and others.
Wrong diet.
Fatty, fried foods, bones, excess protein, cereals are contraindicated for dogs. Inflammation of the paraanal glands is the least of what can provoke a violation of the pet’s diet.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Violations in the frequency and regularity of bowel movements, poor digestibility of food – all this also contributes to the disease of the paraanal glands.
Lack of hygiene or infection.
Injuries, bites.
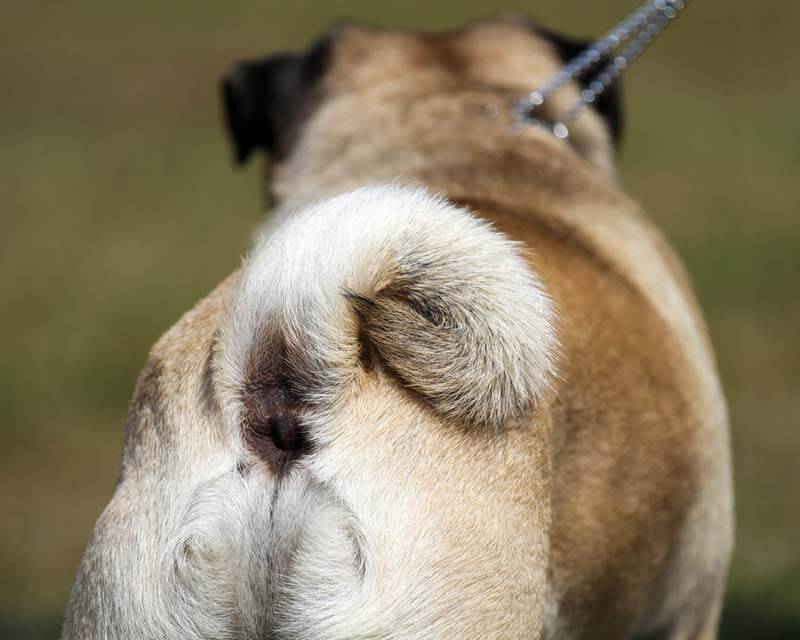
Symptoms
Usually, these sinuses clear up on their own during a walk. Inflammation in each animal can manifest itself in its own way, but there are several characteristic changes:
The dog rides on the floor on the priest, actively scratches the anus on the surface. Owners usually perceive these body movements as a sign of the presence of helminths (parasites).
The anus looks edematous, red, brown due to the inflammatory process and friction on the surface.
The pet shows pain during bowel movements, sometimes frequent and small.
Bald patches may appear near the hips, the root of the tail, or the near-anal region – the dog actively licks the skin in these places in an attempt to reach the painful place.
In a neglected form, a purulent abscess develops near the paraanal sac. After maturation, it opens outward. The area of the inflamed gland is hot, red, painful. The dog may be restless or lethargic if the general temperature rises.
Diagnostics
This disease is determined after a thorough collection of the medical history and examination of the animal by a therapist. With a local inflammatory process, a simple visual inspection is enough. In the case of a neglected condition, general diagnostic measures may be required to identify the consequences or the primary disease that provoked these changes:
General blood analysis;
Blood chemistry;
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and reproductive system;
Endoscopic examination of the rectum.
The owner himself cannot always identify the disease if he has not previously encountered it.
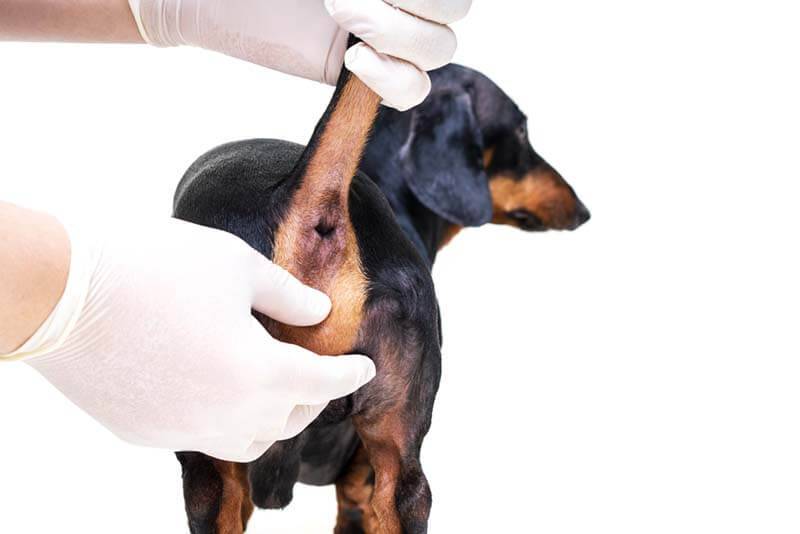
Treatment
Treatment of paraanal glands in a dog varies depending on the degree and severity of the disease.
With simple violations of the patency of the ducts, the doctor performs a simple cleaning of the glands by manually (manually) squeezing them into the lumen of the rectum. Followed by regular treatments and cleanings. It is also necessary to correct the main causes that contributed to the violation of their emptying.
Complex, mature abscesses require the following procedures:
Primary surgical treatment. The wound is examined and cleaned under mild sedation (drug sleep). Anesthesia minimizes stress and injury to the animal. The wound opening is cleaned, expanded to the size required for regular procedures. Soft drainage may be required.
Processing. Held regularly. Washing of the wound opening and cavity is carried out with antiseptic solutions (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Betadine) or saline sodium chloride solution. They are introduced into the cavity with a syringe. The skin around the wound is also thoroughly cleaned to prevent dermatitis.
Painkillers. The animal is prescribed systemic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablet form (Petkam, Trokoksil, Onsior), suspensory (Meloxidil) or injectable (Onsior, Meloksivet) form.
Restriction of access to the wound. The dog is put on a plastic protective collar as a prevention of constant licking and contamination of the wound.
Additionally, therapy is prescribed to treat the primary disease that provoked the inflammatory process.
In the case of a frequently recurring inflammatory process of the paraanal glands, the veterinarian may recommend a surgical operation to remove them. It is technically simple and prevents the occurrence of recurrent diseases.

When is an anal gland cleaning needed in dogs?
Not every dog needs prophylactic cleaning of the glands; normally, they are cleared on their own with regular bowel movements.
This procedure is required:
with general signs of impaired patency of the ducts without an obvious inflammatory process of the soft tissues around the gland;
with constant clogging – the timing of the procedure is strictly individual, they can be clarified with the attending veterinarian.
Normally, the secretion of the gland is soft, liquid, from light gray to brownish in color, easily squeezed out. In case of pain, anxiety of the animal at the time of cleaning, it is recommended to immediately contact a veterinarian.
How to clean the anal glands in dogs
Before proceeding with the manipulation, it is necessary to prepare all the necessary equipment:
lubricant (fatty cream, oil, petroleum jelly);
clean gloves of a comfortable size;
material for draining liquid (for example, rags, napkins, toilet paper, gauze, cotton wool).
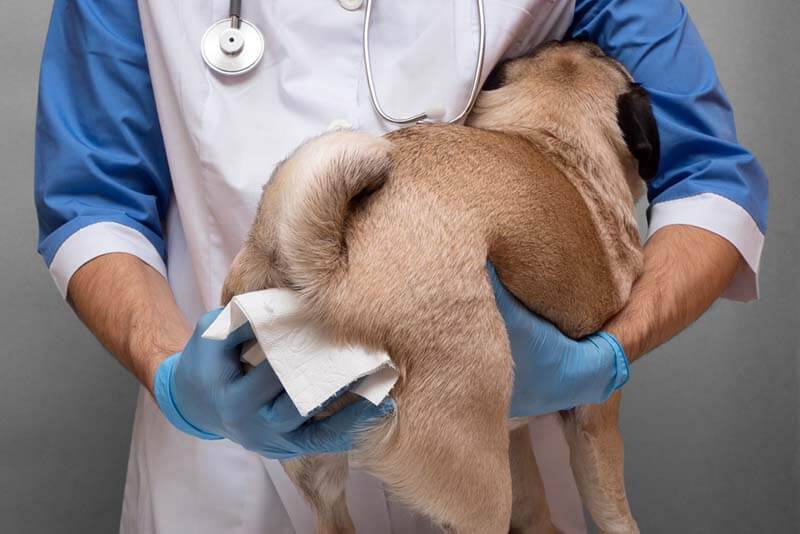
There are two cleaning options – for small and for large breeds.
For small dogs:
It is necessary to place the pet in a basin or on a washable surface.
One person fixes the animal in a standing position and raises its tail.
The second puts on gloves and gropes for the glands in the thickness of the anus.
With the same hand, he takes a rag and applies it to the anus, simultaneously squeezing the glands with his thumb and forefinger. You need to press both at once, keeping your fingers on the sides of the anus. During the manipulation, the sinuses are squeezed out, pulling back. Thus, the liquid that has accumulated in the sacs is removed.
The remnants of the secret are removed from the anus and skin with wet wipes or soapy water.
For large dogs:
The animal is fixed in a standing position by one person.
With the second, one hand in a glove fixes the tail, and uses the other to clean the glands. The index finger is inserted into the lumen of the rectum, pressure is applied to each gland separately with the help of the index finger inside and the thumb outside.
After removing the secret, the skin is treated with napkins or soapy water in order to remove residual dirt and odor.
Cleaning the paraanal glands is a necessary but painful procedure. Its comfortable carrying out is possible only in case of good fixation of the animal and the rapid implementation of all manipulations.
Prevention
Prevention includes the following steps. Good exercise – long walks, physical activity, regular bowel movements. Properly calculated diet – commercial feed or natural nutrition selected by a nutritionist, taking into account the daily needs of the animal. Regular examination of the paraanal glands and their cleaning if necessary.
Possible complications
The neglected inflammation of the paraanal glands can be further complicated by a purulent abscess of the surrounding soft tissues.
Frequent recurring disturbances in the activity of the paraanal glands may require surgical intervention – removing them from the dog once and for all. This operation is technically simple, the animal does not experience any unpleasant consequences after it.
Home
Paraanal glands – sacs, located on both sides of the anus. They carry the main marker function – they emit an individual smell characteristic of a dog.
The main causes of violation of the patency of the ducts of the glands and their inflammation: violations of exercise, lack of regular walks, poorly selected diet of the animal, obesity, hereditary predisposition and others.
Characteristic symptoms that a dog shows in case of inflammation of the paraanal glands: riding on the priest, nervous licking of the perianal region, painful defecation, redness of the anus.
The diagnosis is often made by a doctor during the course of familiarization with the history of the disease and examination of the animal. An inexperienced owner can not always recognize this disease.
Treatment of paraanal glands in dogs is prescribed based on the degree of development of the inflammation process: it varies between simple cleaning and surgical debridement.
Possible complications include purulent inflammatory processes and frequent relapses (return of symptoms) in the absence of work with the primary causes that provoked this condition.
Answers to frequently asked questions







