The structure of the skeleton and body of hamsters, temperature and distinctive features from the mouse

All pet owners need to study in advance the characteristics of those they want to tame: be it a dog, cat or hamster. For the latter, many lower the requirements, which is wrong: the structure of the hamster’s body is just as complex, it needs a special approach. The skeleton of a hamster is fragile, so it is advisable to study its features.
Contents
Anatomy of a Syrian hamster
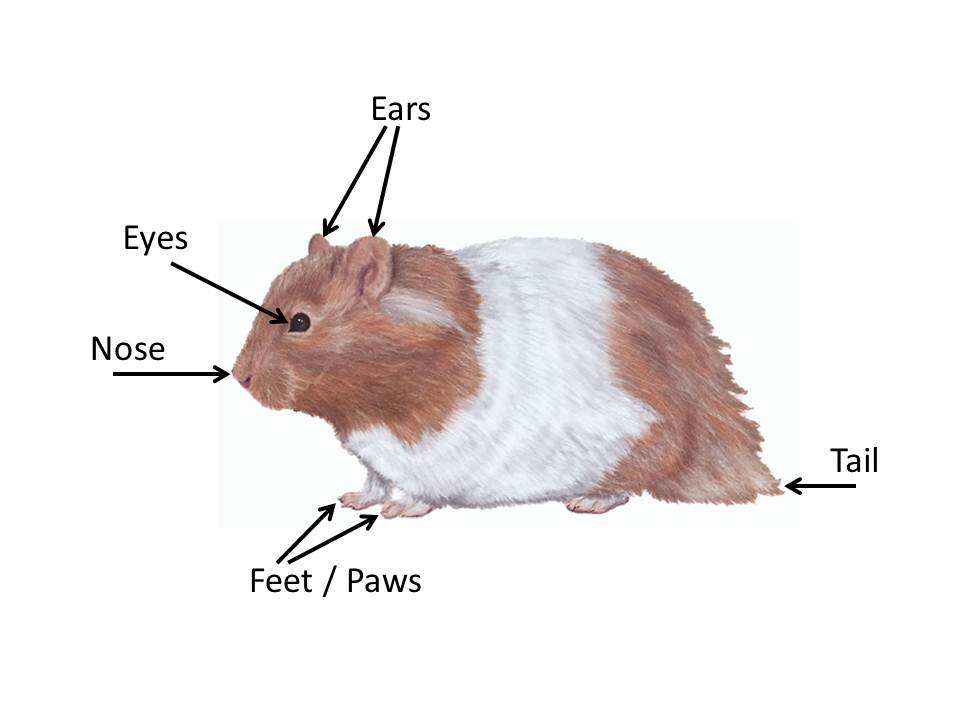
The main difference between the hamster is the presence of cheek pouches: they are used to temporarily store food and transfer it to secluded places. They fit up to 18 grams of food. If you fill them completely, the head of the animal increases up to two times.
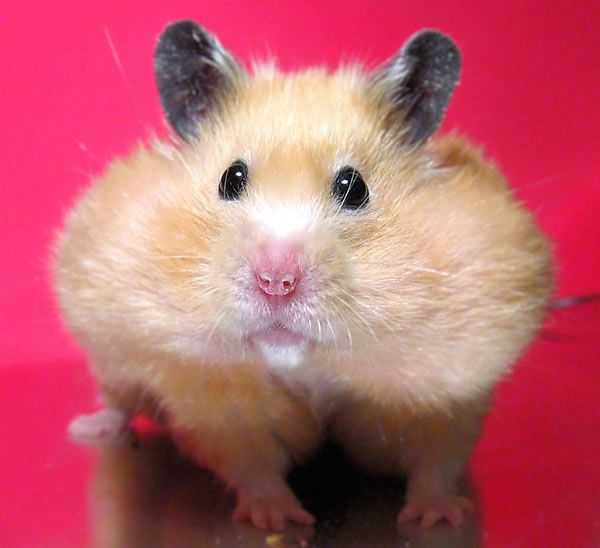

The structure of the jaw of a hamster is not complicated at first glance, but in addition to two pairs of self-sharpening incisors, there are 6 more pairs of molars designed for chewing food. The incisors are in constant growth, so it is necessary to buy a variety of hard toys for your pet or provide them with wooden sticks.
The skeleton of the Syrian hamster is built on the same principle as that of other mammals, but its bones are highly fragile.
So, if cats tend to “spring” from the surface, then a hamster, when jumping from a height, will most likely break its limbs, and can also damage the insides.
The structure of the internal organs of the hamster is also monotonous, but there is a peculiarity: a two-chamber stomach. It has two departments:
- the front one is for soaking food;
- glandular is responsible for the process of digestion.
The sex of the animal is determined by the distance from the anus to the genitals: in males it is about 1-1,5 cm, in females – 3 mm.
Anatomy of the Dzungarian hamster
This is one of the most popular pets among rodents. The anatomy of a Dzungarian hamster is essentially the same as the Syrian one, but it also has its own peculiarities: the presence of hair on the feet, which is called leggedness. Also, the species can be distinguished from the rest by a gray stripe on the back, running from head to tail. The fur coat is usually painted in beige tones or smoky shades.
The skeleton of the Dzungarian hamster differs from the Syrian one only in length: the latter is much larger – up to 20 cm, when the Dzungarian grows no more than 10 cm. What is the same for both is the ability to fertilize as early as 16 hours after birth.
They also have the same location of the auricles – on the temporal part of the skull. In addition to the main purpose – hearing – they are needed for coordination in space and maintaining balance.
How many fingers does a hamster have
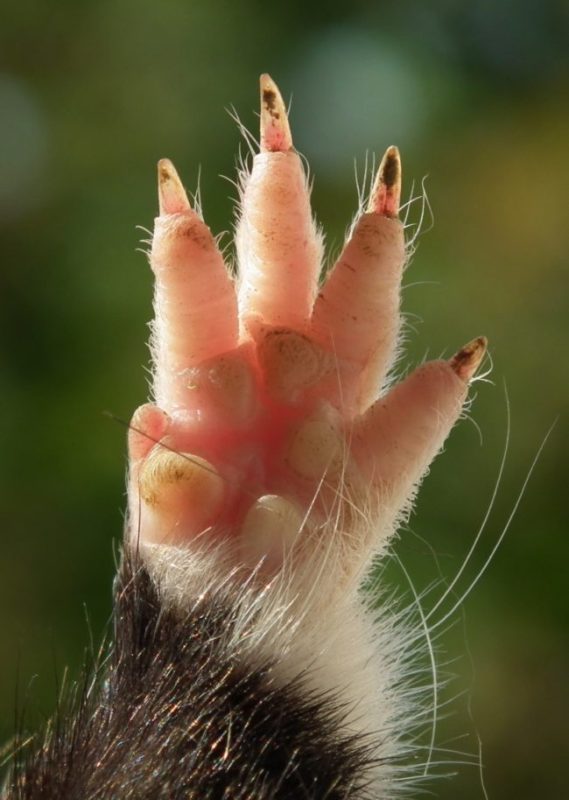

Despite the small size, the front legs of the animal are quite strongly developed; in nature, in the wild, they dig the ground with them. There are four fingers on these paws, there is also a fifth, but it is almost not developed (atrophied). There are five fingers on the hind legs, but the limbs themselves are weak, with which he removes the dug ground, throwing it back.
What is the body temperature of a hamster?
For this pet, the optimal temperature is in the range of 37,5 – 38,5 degrees. Method of measurement – rectal. To do this, the thermometer is inserted into the anus and stays there for 5 minutes. The temperature of the hamster can be either low or high. The first option is worse, as it indicates a running infectious process. In this case, you need to pour warm water into the heating pad, wrap it in a cloth and put the animal on it, hold it for up to 10 minutes, then wrap it in a heated towel, and then contact the veterinarian.
At elevated temperatures, it is necessary to place the pet in a cool place, near a balcony or refrigerator, but also do not delay going to a specialist – this is most likely some kind of infection.
Does a hamster have a tail
Like most mammals, hamsters also have a tail, but usually it is very short and not always noticeable, the average length is 7 mm (in some species it can reach 10 cm). Its main function is to cover the anus from infections.
It is important for the owners to monitor his condition – a disease called “wet tail” is common among hamsters. This is the main syndrome, the cause is diarrhea caused by poor quality food, dirty water, or a poorly cleaned cage. This disease is serious, as 90% of pets will die if not contacted by a veterinarian as soon as it is noticed.
What is the difference between a mouse and a hamster
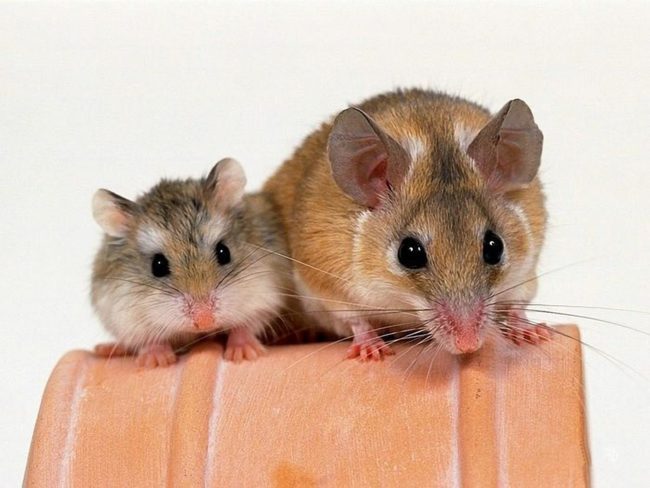

Although both species belong to rodents, they are still very different in appearance:
- tail: in a mouse it is long, almost like the body itself, in a hamster, as they said, it is considered invisible;
- muzzle: the muzzle of the mouse is elongated and rather narrow, the skull of the hamster is rather wide and almost flattened;
- body: in a hamster it is shorter, most have thick hair, so a rounded shape is obtained, while in a mouse the body is more elongated and thin;
- wool: the mouse is gray or white in color, its relative is multi-colored: white, gray, black, sandy, red, usually a mixture (spotted).
So, a hamster, although small, has its own characteristics that you need to know before buying.
Hamster anatomy and features of the body and skeleton
3.2 (63.53%) 17 votes





