cystitis in dogs

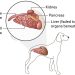
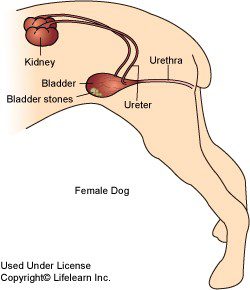
If the symptoms of the dog revealed cystitis, then urgent treatment is required. Cystitis is observed more often in bitches, which is due to the peculiarities of the anatomy of the female urinary system. The disease is affected by estrus, pregnancy, childbirth, since hormonal changes contribute to a decrease in immunity, which affects the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. Cystitis can also develop as a result of an unprofessional surgical intervention: non-compliance with the rules of sterility causes inflammation in dogs. Inflammatory processes in the bladder are the leading among other diseases of the genitourinary system in dogs. The most common cause contributing to the development of cystitis is hypothermia. In second place is the pet’s weak immunity. It is not difficult to treat cystitis in dogs if changes are noticed in time. But advanced forms of the disease are very dangerous for the health of dogs. So how does cystitis manifest in dogs? And what are the causes of cystitis in dogs?

Contents
Symptoms of cystitis in dogs
Cystitis has two main forms of flow — acute and chronic, they differ symptomatically. The owner must present the main signs of cystitis in dogs in order to determine in time by the behavior of the pet that something is wrong.
In the acute form of cystitis, the following are more often observed:
- increased urination, a decrease in the portion of the pet’s urine;
- change in color of urine up to brown. Inflammation of the walls of the bladder causes a change in the composition of urine, there is the presence of pus, epithelium of the bladder, particles of necrotic tissue;
- the cloudy consistency caused by the appearance of impurities changes the smell of urine;
- in the process or at the end of urination, whining from pain is observed;
- sudden aggression is possible when trying to stroke or feel the stomach. Also indicative are the pet’s attempts to avoid examination of the abdominal cavity;
- the pet urinates in the apartment, unable to tolerate walking;
- the pet is constantly thirsty, drinks a lot and often;
- there may be a slight increase in temperature;
- there may be a decrease in appetite;
- unwillingness to play, run and move actively.
If you do not pay attention to the change in the behavior of the dog and start the disease, against the background of the existing inflammation, acute pyelonephritis develops, which is likely to become chronic. Such a development is possible with an insufficiently pronounced clinical picture that does not cause concern to the owner.

The chronic form of cystitis consists of relapses and remissions against the background of a sluggish general course of the disease.
This form is characterized by:
- general malaise of the pet. In behavior, apathy may alternate with irritability;
- puddles in a house or apartment due to urinary incontinence;
- there is a drip of urine;
- females sit down more than 2-3 times per walking;
- symptoms of cystitis in a male dog: when urinating, dogs may stop raising their paw, and begin to urinate while sitting down, because the pain experienced causes discomfort;
- discharge in the form of yellowish-purulent and bloody spots is noticeable on the bed;
- possible febrile state;
- when palpated, tension is felt in the abdomen.
A sick pet does not always have all the symptoms at the same time. At the initial stage, one can observe only increased urge to go to the toilet and slight apathy.
Types of cystitis
Cystitis in a dog can occur in an acute form — it is assessed by veterinarians as primary. If cystitis appeared on the background of another disease, then it is considered secondary.

According to the way the infection enters the bladder, veterinarians divide cystitis into descending and ascending. In the first case, the infection enters the genitourinary system with blood flow or from the kidneys, more often this is a consequence of inflammatory processes or pyelonephritis. Ascending cystitis develops when the infection actually ascends to the bladder. And the source of infection is the dog’s genitals or anus. Types of cystitis differ in the nature of the inflammatory process.
catarrhal cystitis
The catarrhal appearance is characterized by the course of the inflammatory process within the mucous membrane. Clinical analysis of urine shows the presence of protein, the urine itself has a sediment or turbidity.
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Hemorrhagic cystitis in dogs is characterized by marked excretion of blood in the urine.
Dystrophic cystitis
The dystrophic appearance indicates the presence of a chronic disease. Epithelial cells are present in the urine.
Idiopathic cystitis
Idiopathic cystitis in dogs occurs for an unknown cause. But there are factors that predispose to the development of the disease. Cystitis in a male is observed less frequently than in a female due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the ureter. Pathology occurs quickly, is acute, and only at an early stage does the treatment of the pet go without complications.
Purulent cystitis
A purulent appearance is observed in the absence of therapy in advanced cases. Urine has an unpleasant odor, purulent exudate is excreted in the urine.

Dystrophic cystitis
The dystrophic type is diagnosed when epithelial cells are detected in the clinical analysis of urine with a visually normal appearance and color of urine.
Diagnosis of cystitis in dogs
How to identify cystitis in a dog — a common question of owners, the answer to which is given by diagnostics. To make a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a certain number of tests and procedures.
Urinalysis shows changes in the structure of urine, reveals the presence of salt crystals, protein, mucus, epithelium, pus, blood.
Clinical and biochemical blood tests reveal problems in the kidneys, show the presence of a pathogen.
Bacteriological examination is necessary to obtain a response to sensitivity to antibiotics.
Endoscopic diagnostic method — bladder cystoscopy — will show deviations in the state of the organ.
Ultrasound and X-rays give a detailed picture of the state of the internal organs, show the state of the mucous membranes of the affected organ, the presence or absence of neoplasms, salt deposits.
A smear from the urethral canal allows you to identify infectious agents.
Radiography is performed in the pelvic organs, showing the structure and function of the pelvic organs in a pet.
Upon completion of the necessary examinations, the veterinarian can choose the appropriate treatment regimen. But the appointment of symptomatic therapy is possible even at the first appointment, before obtaining laboratory results. Only a veterinarian can diagnose the cause of cystitis, prescribe the appropriate treatment for the disease, and correctly calculate the dosage of drugs. If the dog whines when urinating and its condition is depressed, you should take a closer look at other manifestations of diseases associated with the kidneys.
Treatment of cystitis in dogs
Treatment of cystitis in dogs is always under the supervision of a veterinarian. All changes in therapy must be agreed with the doctor, based on the interim results of studies and changes in the general condition of the pet.
In general therapy, drugs are prescribed for the treatment of cystitis in dogs: broad-spectrum antibiotics, and if necessary, the veterinarian will add an agent that affects the causative agent of the infection.
Antispasmodics help relieve pain and relax the muscles of the bladder, which makes it easier to pass urine and improves the condition of the pet. uroseptics — drugs that relieve inflammation of the bladder, — contribute to the removal of edema and improve blood circulation in the area of inflammation. Since urine flows better, pathogenic bacteria are washed out of the bladder cavity, which significantly improves the condition of the dog.

The course of therapy can be supplemented with hemostatic drugs.
If cystitis has developed against the background of an allergic reaction, antihistamines are used.
In a serious condition of the animal against the background of the rapid progression of the disease, infusion therapy is indicated. Diuretic and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. After a course of antibiotics, probiotics must be prescribed to the pet to normalize the intestinal microflora.
A sick pet needs to create comfortable conditions for keeping, to minimize the stress from treatment.
Antibiotics for cystitis in dogs, like all treatment, continue the course without stopping. Even with the disappearance of visible symptoms of the disease, the prescribed medications should not be abandoned in order to avoid the return of the infection. Control diagnostics at the end of the course shows the general condition of the pet and specifically the bladder. The owner of the dog should prepare for the fact that the treatment process will drag on for several months.

Medications
Drugs for the treatment of cystitis in dogs should only be prescribed by a veterinarian. If a bacterial infection is confirmed in a dog, the veterinarian will prescribe a course of antibiotics. They are designed to fight the infection that caused inflammation of the bladder and canals. The course ends with the therapy of dysbacteriosis with the use of probiotics and enterosorbents.
Antispasmodics help relieve spasms, remove the intensity of spasms in a pet.
With blood loss, hemostatic drugs are used.
Good results in therapy show diuretic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs on a natural basis.
In severe conditions and the indication of droppers, the solutions necessary for catheterization are used.
Various drugs are used to combat the underlying cause of cystitis.
The dosage of each drug is calculated by the doctor based on the data on the disease, condition, weight, age of the pet. The owner must strictly follow the recommendations of the veterinarian on the order and time of taking the prescribed drugs and injections.

Diet for cystitis
Dog food for cystitis — an important component of the medical complex. Due to the difficulty of accurately determining the rate of proteins and fats needed for a pet at home, it is recommended to cancel feeding with natural products and temporarily transfer the dog to a special medical food. Major pet food manufacturers have long included dry and canned medicated foods designed for dogs with certain disorders in their product line.
It is important that the dog has constant access to fresh water during the treatment of cystitis. This will speed up the elimination of toxins from the body and bring recovery closer.

cystitis in puppies
Cystitis in puppies has a different origin than in adult dogs. The source of the disease is most often not an infection or a decrease in immunity. Cystitis begins in a puppy under the condition of improper feeding, namely the lack of drinking water. Water deficiency affects the stasis of urine by irritating the urethra. Because puppies’ urine is concentrated, it quickly crystallizes, settling on the walls of the bladder and causing inflammation. Irritated mucosa affects the narrowing of the urethra, which favors the growth of pathogenic bacteria. It is extremely important for the owner to notice the symptoms of cystitis in a puppy in time in order to prevent the development of a serious process.
The manifestations of cystitis in a puppy and an adult dog are similar. it — frequent urination, small amount of urine, in acute cases mixed with blood and mucus. The puppy whines when urinating, which indicates a painful process. There may be irritation, swelling, or rashes in the pet’s genital area, which causes him concern: he often licks this area. If the puppy has symptoms of cystitis, then treatment is required.
Ignoring the owner of such symptoms often leads to a chronic form of the disease. It is fraught with complications of diseases of the genital organs, as well as infertility and inability to bear healthy offspring. Due to the peculiarities of the physiology, cystitis is more common in female puppies.

Possible complications
The disease is dangerous with complications, including the formation of ulcers, necrosis, paracystitis, inflammation of the renal pelvis and nephritis. Ignoring or improperly treating the acute form of cystitis leads to a chronic course of the dog’s disease. Pathology entails a number of complications: pyelonephritis, which can lead to the death of a pet, urinary incontinence, kidney and heart failure, high blood pressure.
Prevention of cystitis
Prevention consists of simple rules, following which any owner helps the pet to maintain health and immunity:
- Get vaccinated annually, regularly fill out the dog’s passport: dates of deworming and protection against blood-sucking parasites.
- Walk your pet at least twice a day. Eliminate urinary retention by walking your pet for a long time if it is a male.
- Make sure your dog has XNUMX/XNUMX access to clean water.
- Do not feed with low-quality ready-made feeds and low-quality natural food.
- Keep your dog in a warm, dry environment. Exclude drafts and dampness, being on a tiled or concrete floor without heat-insulating bedding.
- Purchase and wear warm overalls so that the short-haired pet does not freeze on a walk.
- Long walks in cold weather are not recommended. Avoid swimming in unknown water bodies and swimming in cold weather when walking.
- During walks on the street, avoid contact of the bitch in heat with males. During estrus, males, licking the loop of the female, can bring the infection. Avoid accidental mating of dogs.
- Cystitis of infectious etiology is sexually transmitted, so it is important to carefully choose a partner for mating.
- It is advisable to visit a veterinary clinic once a year, undergo a preventive examination and, if possible, donate blood and urine for tests.
Cystitis in dogs in general has a favorable prognosis with a timely visit to the doctor, therefore, when observing similar symptoms and even a single case of urinary incontinence, you should not delay the visit to the veterinarian.
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
1 2020 June
Updated: September 12, 2020