
Why does the hamster’s hair fall out and the skin peels off: does it shed or get sick?

Every owner of a hamster, whose pet has lived for more than a year, at least once wondered why the hamster’s hair falls out. This is not always a sign of pathology – hair loss can be a sign of molting – a natural process for animals.
To understand whether to contact the veterinarian, the pet is carefully examined and observed for behavior. In the absence of itching and scratching on the skin, there is no need to rush to the clinic. A veterinarian, having ruled out the most common causes of skin problems in rodents, can only guess why a hamster sheds. It is useful for the owner to know for himself about the conditions that provoke hair loss.
Increased hair loss is not always accompanied by baldness. Signs of molting are shreds of fur in a cage, hairs on the palm, after the animal has sat on its hands, or it has been stroked.
Contents
Shedding in hamsters
Shedding is a complete or partial change of coat. It can be age and seasonal. In the first case, in young animals, the soft “childish” fur coat is replaced by denser and coarser adult hair. In hamsters, it most often goes unnoticed, at the age of about 4 months.
Seasonal molting is associated with the seasons. Usually, animals have an autumn and spring molt. For those who sleep in winter, molting takes place in summer. There is no single answer to the question – do hamsters shed. Yes, the fur is updated, but in healthy animals this happens unnoticed by the owners. The molting process largely depends on genetics and conditions of detention. The Syrian hamster must renew its hair without bald spots. Areas of baldness are difficult to notice if the animal is densely covered with hair. And Dzungarian during molting become spotty.
If a hamster has hair falling out on its back, but it does not itch, is active and eats well, it is possible that it is shedding.
There is a visual shedding test: blow on the coat and inspect the hair. Dzungarians have 3 coat colors: black tips, a light middle part and a gray base. If the animal grows new fur, up to 6 new, intermediate colors will appear.
Bare patches can appear on any part of the body, but are more common on the belly and hind legs.
Some Djungarian hamsters change color for the winter, turning white or gray in January. In February, in such animals, the reverse change of wool begins. Such a molt is laid down by genetics, depends on the length of daylight hours and air temperature.
Video: how a hamster molts
Causes of pathological hair loss
Avitaminosis
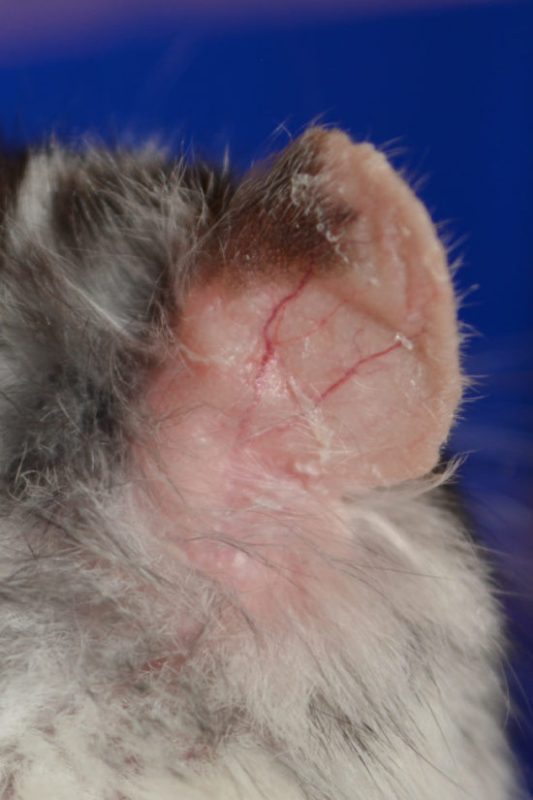
If a hamster eats only dry food, cereals for a long time, the animal may have beriberi. It is not known what lack of substances causes baldness, so the treatment is reduced to a variety of diet. With beriberi, the hamster’s skin is flaky and the coat is peeling off, but there are no signs of inflammation. The body of the animals is covered with thick dense fur, so the first thing the owner notices is that the ears are peeling.
You should give the animal greens, vegetables and fruits, in addition to dry food, and occasionally offer a piece of boiled egg or meat. There are liquid vitamins for rodents that are given with food or drinking water, such as 8 in 1 Hamster & GerbilVitaSol.
Stress
In a stressful situation, hamsters use their scent glands heavily and may begin to shed their hair. Moving, intrusive attention, systematic interruption of daytime sleep, loud TV sounds – the owners of the rodent do not even think about how much discomfort these factors can bring to the pet.
If a dzhungarik’s hair falls out, as a first aid, you need to review the diet, and then eliminate irritants. A hamster that is running wild, or just recently in the house, does not need to be picked up for a while.
reproductive functions
Lactating females lose belly hair. The fur grows back after weaning the young. Also, females can shed heavily during pregnancy.
For hamsters that are kept alone, other problems are relevant. With polycystic ovaries and endometritis (inflammation of the uterus), there may be hormonal alopecia. Symmetrical bald spots are formed on the sides, itching is absent.
Gastrointestinal disorder
If a hamster has diarrhea, regardless of the cause of the disorder, the animal’s fur will not be as thick and shiny as before for a while. Nutrients are not absorbed, the body weakens. Possible poisoning with poor-quality food, nitrates from succulent feed. With intoxication, one of the symptoms is hair loss.
Problems with teeth
In case of violation of the grinding of constantly growing teeth, with a fracture of the incisors, inflammation of the cheek pouches, the leading symptoms will be: the inability to eat normally and constant salivation. The hair on the neck is always wet, and soon begins to fall out.
Old age
Almost all pathologies of the internal organs in one way or another affect the condition of the coat. It is impossible to diagnose kidney or liver failure in a tiny rodent: it is difficult to obtain enough blood for analysis. Tumor processes are possible, but the Djungarian hamster is too small for ultrasound diagnostics. One can only guess what organs and systems are junk in an elderly animal, but after 1,5-2 years, continuous molting in hamsters is a common thing.
Conclusion
If a pet’s coat has peeled off in the spring, this does not always mean that he needs treatment. Diagnosis requires a consultation with a veterinarian. A ratologist or an experienced hamster breeder will tell you what to do if, during a molt, the hair falls out faster than a new one grows. Often use the drug “Tsamaks” for decorative rodents (90% zeolite, 10% sulfur) or ordinary fodder sulfur (0,01 g), which accelerates hair growth and improves skin condition. It is useful to introduce flax or sesame seeds, rich in fatty acids, into the diet.
Video: what to do if a hamster goes bald behind the ears
Hair loss: natural and pathological molting in hamsters
2.2 (44%) 20 votes





