What can you get from a domestic cat?
Infections common to animals and humans are called zooanthroponoses or anthropozoonoses. One of the most famous and most dangerous diseases is rabies. It is transmitted by contact through bites and injuries to the skin and mucous membranes. The disease, unfortunately, is fatal. Possible prophylaxis is only an annual vaccination of a clinically healthy animal.
It is not so difficult to identify this disease in a pet. Infected cats may have a long incubation period. The first symptoms will be aggressiveness, impaired coordination of movements, spasms of the pharyngeal muscles (the animal cannot swallow and refuses food and water). Later, paralysis of the muscles of the limbs, respiratory muscles, photophobia develops.
If a person has been bitten by a cat with suspicion of rabies, it is urgent to contact the nearest medical facility for a course of vaccination.
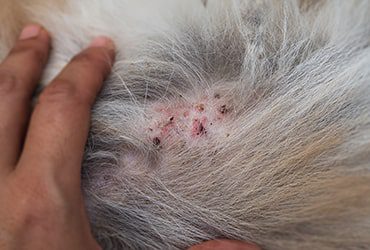
Another equally well-known, but, fortunately, less dangerous common disease of domestic cats and humans — it is dermatomycosis (or lichen). In most cases, the disease is caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton, Microsporum. Spores can persist in the environment for up to one and a half years. An animal becomes infected directly through contact or care items.
In 90% of cases, people get this disease from cats.
The first signs of the disease will be alopecia (that is, baldness), redness, peeling of the skin, miliary dermatitis (redness, similar to flea bites), itching is most often absent. For a proper diagnosis, you need to see a doctor. Usually an inspection is done with an ultraviolet lamp, but not all strains are luminous, so further studies may be required. For example, trichoscopy (examination of hairs under a microscope), cytology (examination of the cellular structure of scrapings of affected skin for the presence of spores) is used. For a more accurate diagnosis, wool is taken from the site of the lesion for sowing. For treatment, antimycotic drugs, local therapy with special antifungal lotions are prescribed.
There is a vaccine against lichen, but it is not effective for cats.
Another common disease for humans and cats — these are helminthiases (opisthorchiasis, dipilidiosis, toxocariasis, toxascariasis, etc.). Helminths can parasitize in all organs, but most often live in the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms can be different: vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, the presence of helminths in the stool, etc. The sources of infection are very different: food (meat and fish), street shoes, and more.
The simplest, but important step in order not to get infected is the prophylactic treatment of the animal from helminths.
It is recommended to do this once every 1 months, since the average development cycle of helminths is 3 months. If the animal is already infected with parasites, then a double treatment with an interval of 3 days is recommended. Before doing this, it is better to consult with a specialist.
Toxoplasmosis is also a common disease for humans and cats. Toxoplasma — These are protozoa related to coccidia. They parasitize in the intestines of the final host – cats. Both mammals, including humans, and birds can be infected. The infection is often asymptomatic. The animal becomes infected by eating raw meat infected with toxoplasma (rodents and birds). Toxoplasma cysts can be brought on shoes with street dirt. Toxoplasmosis is most dangerous for pregnant women.
For diagnosis, blood is taken for ELISA. Treatment is prescribed only by a veterinarian after a clinical examination. On the one hand, ways to prevent toxoplasmosis are simple, on the other hand, they are complex: do not let the cat eat rodents and birds, do not feed thermally processed meat, do not drink water from dubious sources, and avoid contact with stray cats.
Another parasitic disease common to humans and cats is giardiasis. Infection occurs through contaminated sources, eating feces, through household items, eating contaminated products (meat, vegetables, fruits). Symptoms vary — offensive diarrhoea, sometimes foamy stools, sometimes vomiting, etc.
The process of Giardia transmission from animals to humans (and vice versa) is not yet fully understood. Therefore, it would be more appropriate to consider infected dogs and cats as contagious for the transmission of giardiasis to humans.
Dangerous for humans and chlamydia. This disease is caused by intracellular bacteria. The route of infection is contact. PCR diagnostics of flushing from the mucous membrane of the eyes of a cat will help to establish the diagnosis. Prevention is pretty simple. — timely vaccination.
Photo: