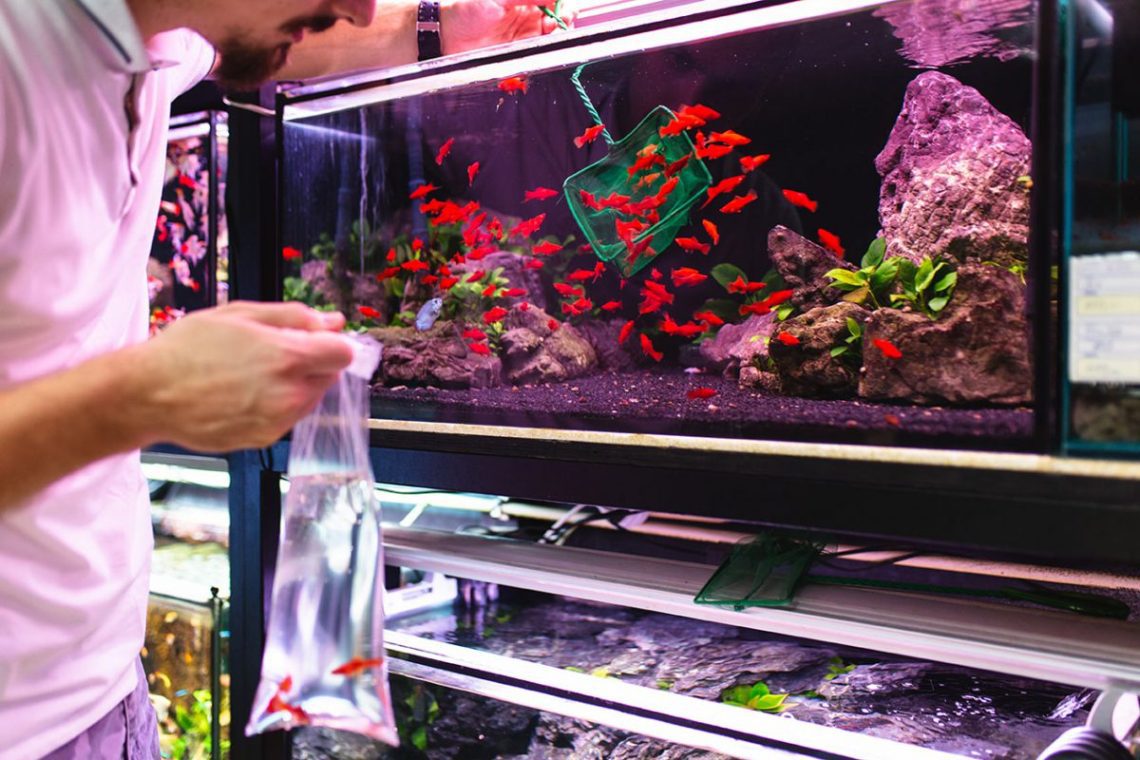
Transportation and launch of fish in the aquarium
Moving is always stressful, including for fish, this is probably the most dangerous time for them. The transport from the place of purchase to the home aquarium and the launching process itself are fraught with many potential dangers that can lead to fatal consequences for the fish. This article lists a few key aspects that beginner aquarists should pay attention to.
Contents
Proper Packing Methods
An important condition for the successful transportation of fish is the correct packaging, which is able to maintain acceptable conditions for the life of the fish for a considerable time, protect it from spilling water, excessive cooling or heating. The most common type of packaging is plastic bags. When using them, keep in mind that:
It is necessary to use two bags, one nested inside the other in case one of them leaks or the fish pierces it with its spikes (if any).
The corners of the bags should be tied (with rubber bands or tied in a knot) so that they take a rounded shape and do not trap the fish. If this is not done, fish (especially small ones) can get stuck in a corner and suffocate there or be crushed. Some stores use special bags with rounded corners designed specifically for carrying fish.
The package must be large enough; its width must be at least twice the length of the fish. The height of the bags should be at least three times greater than the width, so that there is a sufficiently large airspace.
Small adult fish of non-territorial or non-aggressive species, as well as juveniles of most species, can be packed several individuals in one bag (as long as the bag is large enough). Adult and near-adult territorial and aggressive fish, as well as fish over 6 cm in length, must be packed separately.
Solid containers
Convenient for transportation are plastic containers, containers with lids (intended for foodstuffs) or in plastic jars. In pet stores, fish are usually packaged in bags, but if you wish, you may well bring your own container.
Solid containers compared to bags have a number of advantages:
The chance of a fish piercing it is minimal.
They do not have corners in which you can pinch the fish.
During the trip, you can remove the cover and let in fresh air.
Water for packing fish
Water must be poured into a bag or container for transportation from the same aquarium, and this must be done before the fish are caught, while the water has not yet been muddied. A large amount of suspended matter in the water of the container can cause irritation and blockage of the gills in fish.
If fish are transported from one home aquarium to another, the day before the fish are packed, part of the water in the aquarium must be changed to minimize the content of nitrogen compounds (nitrites and nitrates), since there is no equipment in the container to neutralize them. There are no problems with the concentration of nitrogen compounds when buying at a pet store,
There should be enough water in the bag or container to cover the fish completely – for most fish species, it is enough that the depth of the water is three times the height of the fish’s body.
Oxygen
During transportation, in addition to the water temperature, it is necessary to monitor the oxygen content, since often the fish does not die at all from hypothermia or overheating, but
Dissolved oxygen inhaled by fish is absorbed by water from the atmosphere; however, in a hermetically sealed container or bag, the amount of air is limited and the entire supply of oxygen can be used up before the fish are delivered to their destination.
Recommendations:
The volume of air space in the fish bag must be at least twice the volume of water.
If you have a long trip, ask for the bags to be filled with oxygen, many pet stores offer this service for free.
Use a bag or container with a lid as deep as possible so that you can renew your air supply at regular intervals by opening the lid or opening the bag.
Purchase special tablets that are added to a bag of water and release oxygen gas as they dissolve. Sold in pet stores and / or in thematic
Transportation of fish
Fish should be transported in thermal bags or other heat-insulated containers, this prevents sunlight and overheating of the water, and protects from cooling in cold weather. If fish bags or plastic containers are not packed tightly so that they do not roll or slip, the free space should be filled with soft materials (rags, crumpled paper
Launching fish into the aquarium
It is advisable to place newly acquired fish in a quarantine aquarium for a while and only then in the main one in order to avoid entering
Step number 1. Aligning the temperature of the chemical composition of water

Water parameters even within the same city can vary greatly, so check with the store specialists for the water parameters in their aquariums – water hardness and pH level. Prepare in advance your own water of approximately similar parameters and fill the quarantine aquarium with it. To avoid temperature shock, the fish, directly in a container or bag with water poured from its former aquarium, is placed in a quarantine aquarium for a short time so that the water temperatures even out. Before leveling, use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the water in both tanks – it may not be necessary to equalize at all.
Time to equalize temperatures – at least 15 minutes.
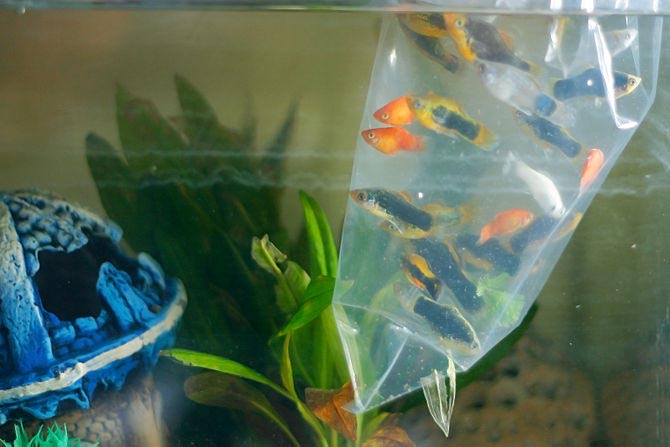
Step number 2. Open the bag with fish

Now take the package and open it. Since the bags are packed very tightly, it is recommended to cut off the top part so as not to shake the fish bag in an attempt to open it.
Step number 3. Catch the fish
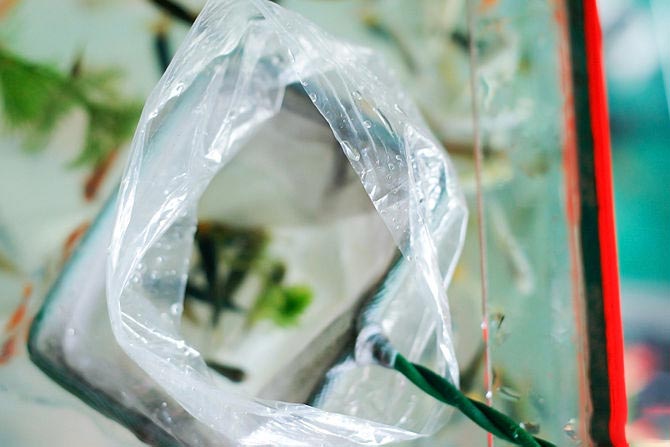

Fish should be caught with a net right in
Step #4: Dispose of the carrier bag
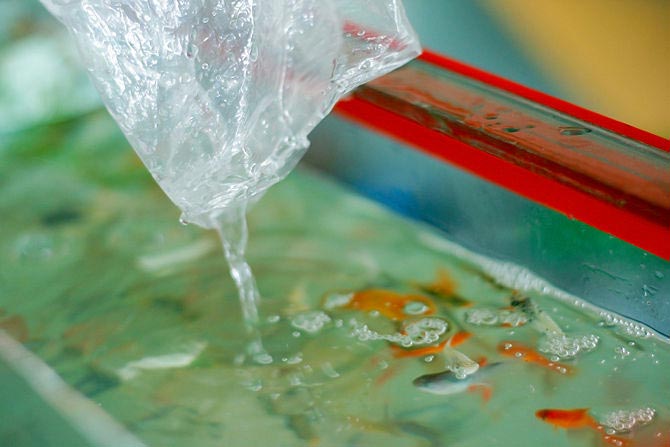

The remaining water bag should be poured into the sink or toilet, and the bag itself should be thrown into the trash. Do not pour water from the bag into the aquarium, as it may contain various pathogenic bacteria and microbes that old inhabitants of the aquarium have no immunity to.
During quarantine, the chemical composition of the water in the quarantine tank can be gradually brought closer to the composition of the water in the main tank by repeatedly mixing in a small amount of water taken from the main tank.
Chemical composition equalization time — 48–72 hours.