Ringworm Dogs
Lichen in dogs is caused by several types of dermatophyte fungi – Microsporum and Trichophyton. Hence the terms microsporia and trichophytosis appeared, describing lichen in animals. Much less often, lichen in dogs is caused by other types of pathogenic dermatophytes. There are about forty species of dermatophyte fungi. For small pets, four species are the most important: Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, which attack the hair, and Microsporum persicolor, which causes lesions in the keratinized layers of the skin. Depending on the habitat and the nature of the transmission of infection, dermatophyte fungi are divided into zoophilic and geophilic.
For zoophilic fungi, the habitat is animals, while for geophilic fungi, the habitat is the environment and soil. Dermatophyte fungi also have characteristic ways of introduction into the animal body. Thus, infection with fungi Microsporum canis most often occurs when animals come into contact with each other or through contact with fungal-infected wool and skin scales. The fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes likes to settle on rodents, and Microsporum gypseum is most often localized in the soil. The leader in the number of cases of dermatophytosis among dogs are fungi of the genus Microsporum.
Dermatophytes use keratin, which is part of the upper layers of the skin, hair and claws, for nutrition and their vital activity.
Contents
Infection methods

Ways of infection deprive dogs are quite diverse. These are the external environment, and animal care items, ammunition, exhibition cages, boxes for transportation, as well as direct contact with an infected animal. Sources of infection with dermatophytosis can be flakes of skin and wool of animals affected by lichen in the external environment and dust.
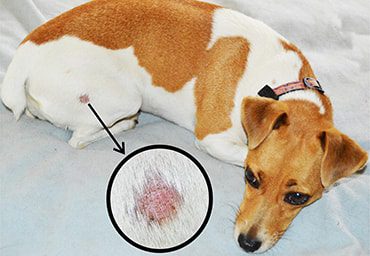
Photo ringworm in dogs
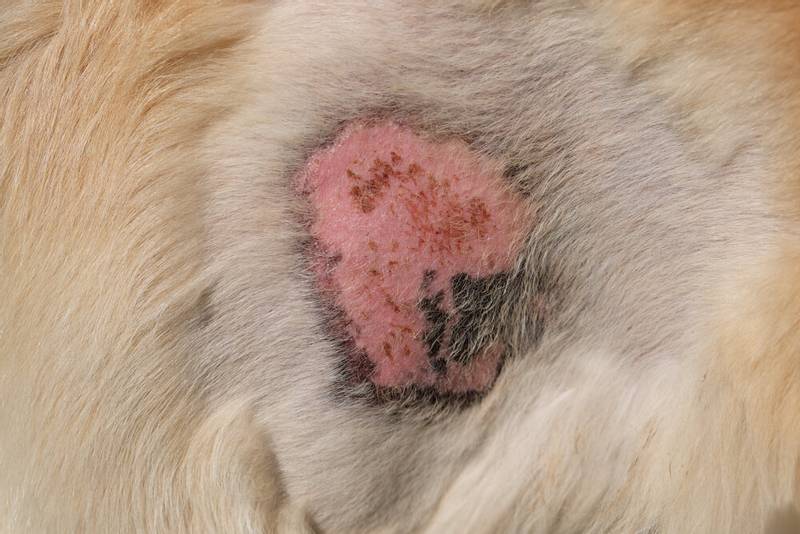
What does ringworm look like in dogs?
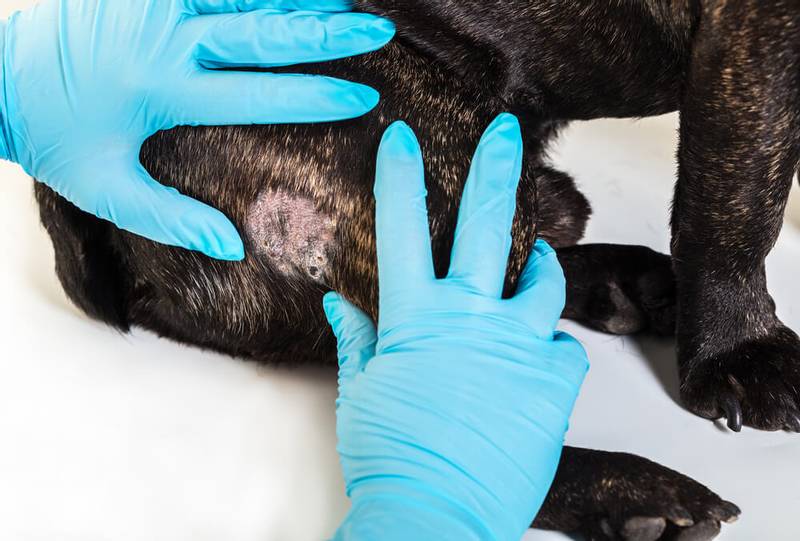
Photo ringworm in dogs
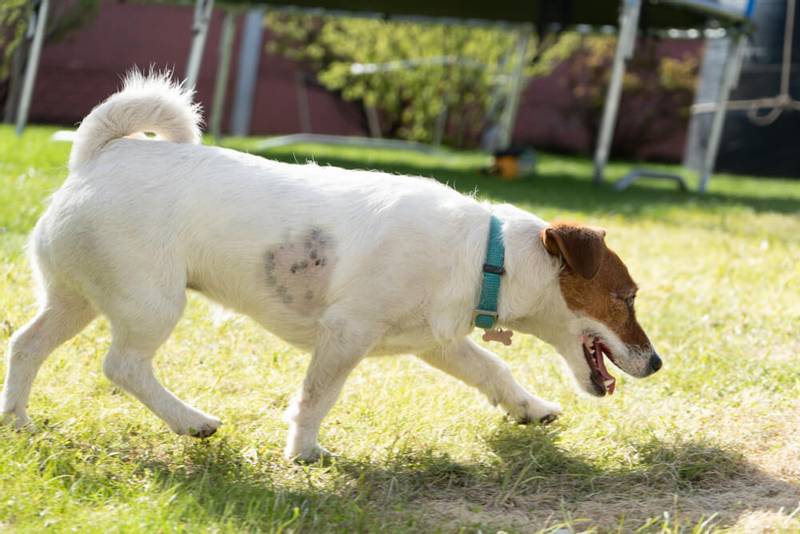

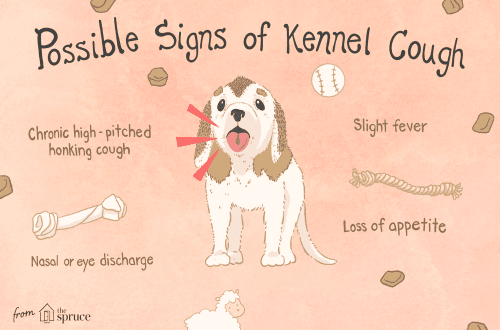
Signs and symptoms of ringworm in dogs
We tend to think of ringworm in dogs as round, scaly, hairless patches on the dog’s skin. Indeed, microsporia most often damages the upper sections of the dog’s skin – the hairs of the coat and the keratinized layers of the epidermis, much less often the lichen affects the claws. But lichen in dogs does not always manifest itself in this way, and the symptoms can be varied. What are the signs of lichen in dogs?
Clinically, lichen can proceed in a very diverse way, and it depends on what stage the disease is at, how long the dog has been sick, and on which areas or derivatives of the skin the pathogen is localized.
initial stage
At the initial stage of the disease, as a rule, lichen in dogs is most often manifested by localized skin lesions. Most often, lesions are noted on the head, auricles and paws, that is, in places subject to the closest contact with the external environment. Most often, lichen is manifested by peeling of hairless lesions on the skin and hair loss in large areas of the body. Sometimes with an uncomplicated or latent course in dogs, there is no increased hair loss, large hairless areas do not appear on the skin of the animal. A small amount of hair or individual hairs is affected, and the animal can be a carrier of the infection, while not having a pronounced clinical picture. In this case, the main method of making a diagnosis can only be laboratory tests for the detection of lichen pathogens.
Running stage
At an advanced stage of the disease, with a long course, dermatophyte fungi often infect the claws of animals. They become thinner, become dull, bumpy, begin to exfoliate and break. As a rule, one or more claws of the animal are affected, and in most cases these lesions are asymmetrical – only on one paw or on different limbs. Most often, fungi of the genus Trichophyton become the culprit in the defeat of the claws.
When affected by spores of depriving hair follicles, folliculitis will most often be clinically observed, which also develops with demodicosis and pyoderma in dogs.
When spores of dermatophyte fungi enter the deep layers of the skin in dogs, a rounded dense formation, a kerion, can develop at the sites of their introduction. Most often, kerion can be found in dogs on the limbs and muzzle.
With the development of a generalized form of lichen, lesions similar in course to dry or oily seborrhea can be observed, in which the coat becomes oily, sticky, or, conversely, dry and brittle. Dogs are less likely to develop generalized lichen than cats.
According to statistics, lichen infection among dogs of long-haired breeds is more common than among short-haired ones. There is also a breed predisposition to infection with dermatophytosis in terriers of medium and small sizes. But dogs of all breeds and ages can get sick with lichen.
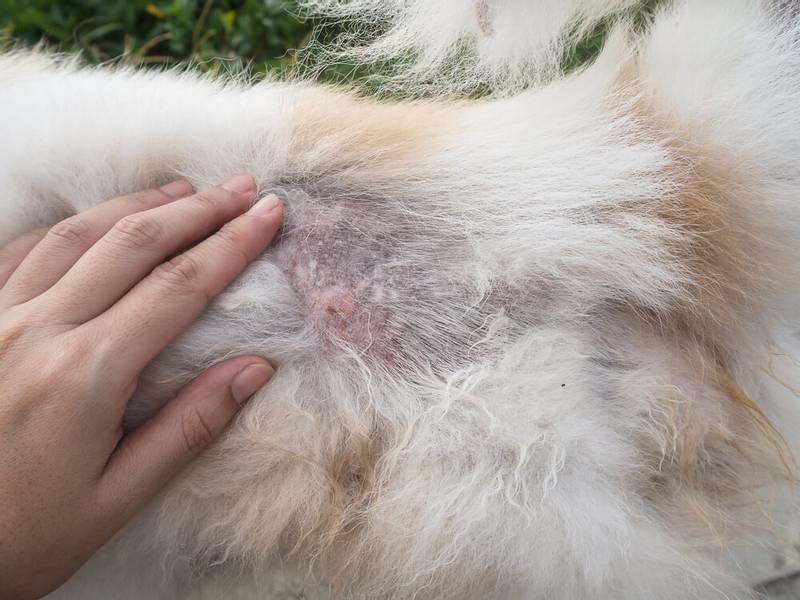
Diagnostics
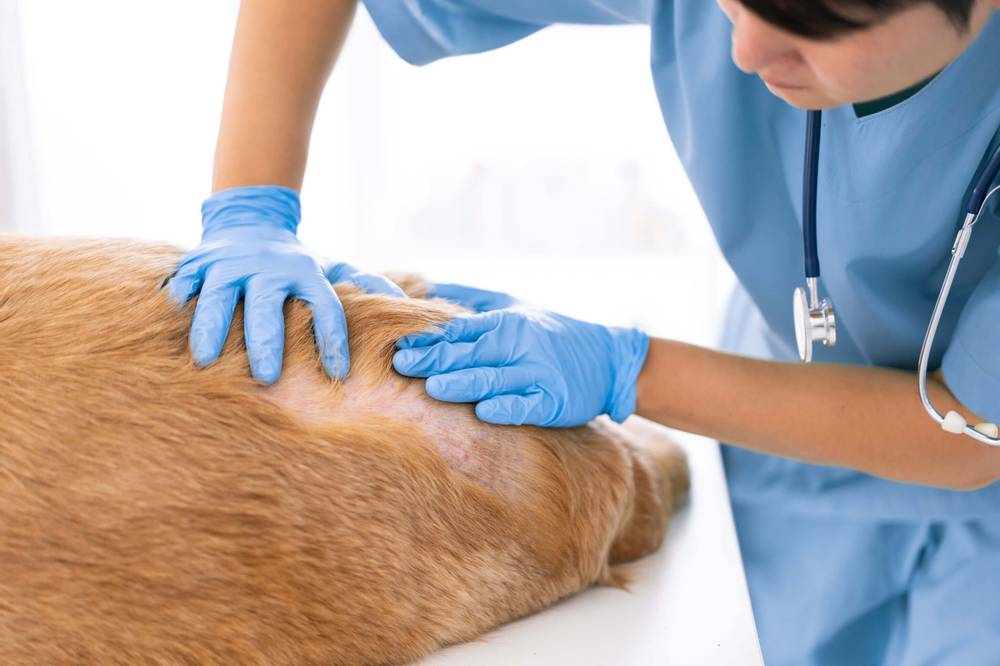
For the diagnosis of lichen, an integrated approach is used: the clinical signs of infection are analyzed and a number of diagnostic studies are carried out. The diagnostic methods of dermatophytosis include the following: hair microscopy, luminescent diagnostics, sowing on special nutrient media. In rare, difficult-to-diagnose cases, a skin biopsy is used to make a diagnosis. The method of express PCR diagnostics is also used to detect lichen pathogens. The latest methods for diagnosing dermatophytosis, such as the ELISA method and the immunohistochemistry method, have a high diagnostic value and are beginning to be introduced into practice in modern veterinary medicine.
For microscopy (examination under a microscope), scales of the affected skin and hairs of wool with a modified structure are selected. Detection of hair affected by fungal hyphae allows a positive diagnosis of lichen.
Sowing on special nutrient media (or the fungal culture method) is one of the most accurate ways to detect dermatophytosis. This method allows not only to detect the presence of pathogenic fungi, but also makes it possible to grow its culture on a nutrient medium and allows you to determine the type of pathogen. On average, the growth of colonies of dermatophyte fungi lasts from seven to thirty days. Despite the high accuracy, this method can give false negative and false positive results and requires control studies. With a complicated course of the disease, when a bacterial infection is attached to a fungal infection, weeping lesions appear on the skin. In this case, in addition to the main diagnostic methods, a cytological method is used to detect fungal spores in the exudate.
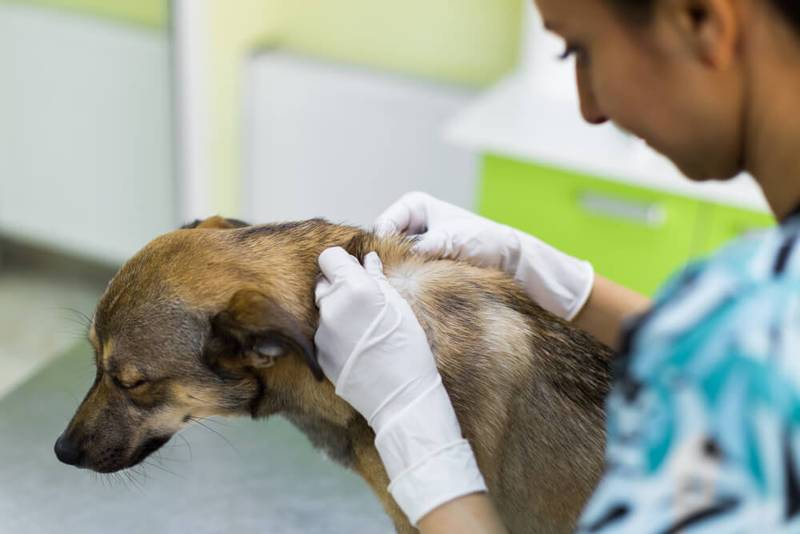
The method of luminescent diagnostics using a Wood’s lamp is an exclusively auxiliary test in making a diagnosis of lichen. As an independent diagnostic method, it is not used, since it gives both false positive and false negative results in a fairly high percentage of cases. The accuracy of luminescent diagnostics is influenced by many factors: the type of pathogen, the quality of the Wood’s lamp itself, how warm it was before the study (the lamp must be warmed up before the study for 10-15 minutes), the presence of contaminants on the skin and coat of the animal. For the Woods lamp test, a completely dark room must be used. With the help of luminescent diagnostics, it is possible to detect traces of vital activity only of fungi of the genus Microsporum canis, which contains the pigment pteridine in its hyphae. Under ultraviolet rays, the hairs affected by the fungus Microsporum canis glow with an emerald-apple light. The characteristic glow of the hairs helps the doctor to take more accurate samples for microscopy and donation of material for inoculation on special nutrient media. With a negative result of fluorescent diagnostics, infection cannot be ruled out.
Treatment for ringworm in dogs
How to get rid of lichen in a dog? For the treatment of ringworm in dogs, an integrated approach is used: this is the therapy of the animal itself, and measures to reduce the number of lichen spores in the environment, in the room where the animal lives. In the treatment of trichophytosis in dogs, both systemic treatment with antimycotic drugs and local treatment in the form of bathing animals using medicated shampoos, solutions, and local treatment of small skin lesions are used. For better penetration of local medicines into the affected areas of the skin, it is recommended to shear animals with long hair before starting local treatment. Grooming dogs with long or very thick hair speeds up the healing process, prevents contamination of the environment with infected hairs.
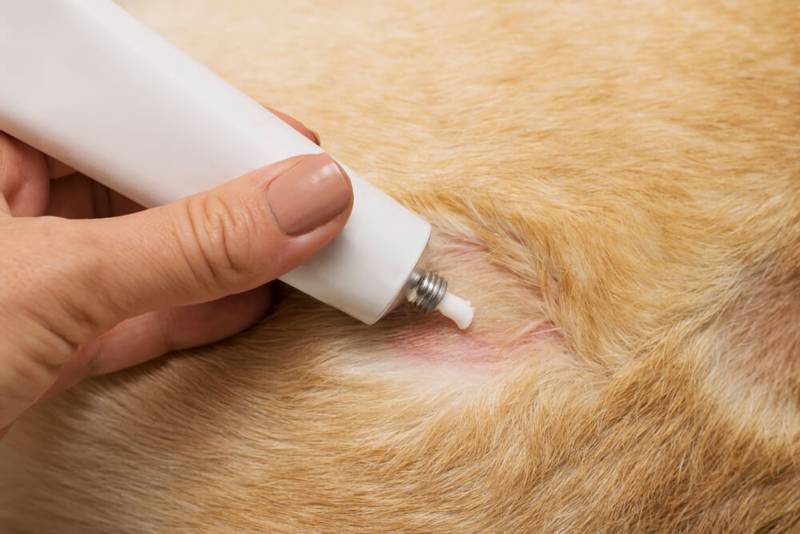
The use of vaccines for the prevention and treatment of trichophytosis in dogs and cats has shown very low effectiveness, and modern veterinary dermatologists, as a rule, do not use them. Antifungal vaccines have been developed for the treatment and prevention of dermatophytosis in productive animals: cattle, sheep, goats and pigs. But for dogs and cats, according to modern research, the use of lichen vaccines is controversial and found to be ineffective.
It is important to remember that it takes a long time to treat ringworm in a dog. And even after the disappearance of lesions on the skin, an additional control examination is required to ensure the final victory over the infection. Otherwise, in case of untimely cancellation of the course of treatment, a relapse of the disease is possible.
To control the results of treatment, the method of sowing on special nutrient media is used with an interval of 14 days until two negative results are obtained. The physician decides to discontinue treatment after receiving a control negative culture result.
It is important to treat all animals that come into contact with an infected pet. To prevent infection of healthy animals, it is necessary to regularly apply treatment with local agents (shampoos and solutions). Lichen spores are quite stable in the environment. Thus, spores of the fungus Microsporum canis can survive in the environment for up to 18 months. Therefore, careful processing of the place of residence of animals is a necessary measure for the fastest recovery. Regular cleaning of areas where animals are kept is one of the important methods of preventing lichen among pets and people.
Common household disinfectants are used to clean the premises. Regular wet cleaning, even with clean water, significantly reduces the number of spores in the environment. Vacuuming is an excellent method of cleaning rooms where a dermatophyte-infected dog is kept. It is important to dispose of used vacuum cleaner bags to prevent contamination of the external environment. Hot steam is used to disinfect carpets and upholstered furniture. A garment steamer does the job perfectly. It is also necessary to disinfect care items, beds, collars, muzzles and leashes.

To disinfect bed linen and items that can be washed in a washing machine, use washing at a temperature of 30 to 60 degrees. For complete disinfection, it is enough to carry out two complete washing cycles in a row.
Prevention
Prevention of dermatophytosis is the observance of hygiene rules. It is not recommended to use someone else’s care items, ammunition, sunbeds, leashes, muzzles, boxes for transportation and exhibition cages. These rules must be observed when visiting exhibitions, receiving guests, and possible contacts with potential carriers of the infection should also be excluded.

Danger to humans
Dermatophytosis refers to zoonoses – diseases common to animals and humans. Most often we deprive children, people with oncological diseases, undergoing chemotherapy courses, the elderly and people with immunodeficiency conditions are at risk of becoming infected.
Clinically, dermatophytoses in humans can have a varied course and are more often localized in open areas of the body and places that are most often in contact with animal hair: on the face, limbs, and abdomen. Typically, people have round or oval, scaly lesions that may be accompanied by itching.

To prevent infection of people who come into contact with an infected pet, it is important to treat the dog with gloves and minimize contact with the pet’s hair during the entire treatment period. Cases of dermatophytosis in adults and children after contact with the causative agent of lichen without the participation of your pet are not excluded – for example, on the street, at a party, at exhibitions. After communicating with other animals and people, a person can become infected with dermatophytosis and himself become a source of danger for his pet. In this case, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of the pet, even if it does not show signs of the disease, in order to prevent re-infection of people already from the dog.
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
October 16 2020
Updated: 21 May 2022