Blood in dog stool

Contents
Blood in the stool of a dog: the main thing
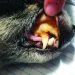
If we see red blood in a dog’s stool, it is most likely from the intestines or from the anus. Blood from the stomach almost always gives a dark (black) color to the stool.
Visible blood in a dog’s stool can be due to:
Infections: canine parvovirus enteritis, canine coronavirus enteritis, leptospirosis, canine distemper, rotavirus, food poisoning (salmonellosis, clostridium, campylobacteriosis, listeriosis, yersineosis, botulism).
Poisoning (of particular danger are poisoning with drugs that are used for deratization), drugs.
A gross violation of the diet – eating sharp bones, unusual food, gluttony. Injury to the intestines when swallowing a foreign object, trauma to the anus.
Neoplasm (tumor) of the intestine.
Injuries or neoplasms (adenomas, rarely adenocarcinomas, mastocytomas) in the anus.
IBD (a group of idiopathic inflammatory bowel diseases).
Manifestations
Bloody diarrhea in dogs
Such a symptom is certainly life-threatening and indicates the need to seek veterinary help as soon as possible, regardless of what caused it.
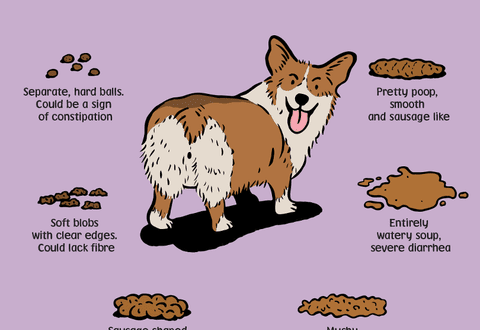
Normal blood in stool
If the dog is pooping blood when feeling well, with normal frequency of defecation, density and volume of feces, then, as a rule, this indicates a chronic problem or its exacerbation.

Causes of blood in the stool in dogs
Parvovirus enteritis
The most common infection that occurs with diarrhea with blood is parvovirus enteritis. Usually, parvovirus enteritis is manifested not only by the fact that the dog goes to the toilet with blood, but also by severe vomiting, refusal to feed, lethargy, and temperature.
Other infections
Canine distemper can cause a dog not only to have blood in the stool, but also other symptoms: conjunctivitis, pneumonia, fever.
Other infections (canine coronavirus enteritis, leptospirosis, rotavirus, foodborne illness – salmonellosis, clostridium, campylobacteriosis, listeriosis, yersineosis, botulism), of course, can also occur in a dog with loose stools with blood, but more often the symptoms will be less bright, especially in the first sick days.
food poisoning
Food poisoning can be caused by eating excessively bacterially contaminated foods, it manifests itself in acute vomiting and diarrhea, often with blood. The main toxic infections are salmonellosis, campylobacteriosis, clostridium, less often listeriosis, yersineosis, botulism.
Poisoning
Diarrhea with blood can be caused by poisoning – for example, household chemicals, rodent control drugs.
Some drugs, if the dosage regimen or individual sensitivity is not followed, can provoke bloody diarrhea (for example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids).
Parasitosis
Parasitosis (helminthiasis, infection of the dog with protozoa) can also cause bloody diarrhea in the dog or cause small streaks of blood in the stool of normal consistency.
Associated symptom
A small amount of scarlet blood in the feces with diarrhea in a dog is probably a secondary symptom (trauma of the vessels of the rectum, anus, with painful urge to defecate), here, first of all, you need to stop diarrhea, establishing its cause in a timely manner.
Neoplasms and injuries of the intestine and perianal region
The cause of the appearance of blood from the anus without diarrhea in a dog may be an injury or neoplasm (tumor) in the anus, a violation of the diet (for example, feeding bones), ingestion of non-food items by the dog, diarrhea or constipation of any etiology, poisoning, infection, parasitosis (helminthic invasions).
Injury in the anus can be obtained by accident or be the result of self-injury – for example, with itching in the perianal region (blockage of parallel glands, post-gum dermatitis).
Neoplasms in the intestine can be represented by adenomas, adenocarcinomas, leiomyosarcoma, less often other tumors. As a rule, at the stage when the tumor begins to bleed, we are already talking about its decay, and the prognosis is from cautious to unfavorable. In the anus, benign tumors of the hepatoid glands are usually found, but they can cause many problems, since the area is “dirty”, they often ulcerate.
VZK
A group of idiopathic inflammatory bowel diseases that includes lymphoplasmacytic enteritis or gastroenteritis, eosinophilic colitis or gastroenterocolitis, and rarely granulomatous enteritis and enterocolitis.
The diagnosis is made by exclusion and confirmed histologically.

Diagnostics
When an owner notices blood from his dog’s anus, he should definitely seek veterinary help.
At the appointment, the doctor will first of all conduct a survey of the owner and a detailed examination of the animal.
The doctor will assess the general condition, the degree of dehydration (turgor, moisture of the external mucous membranes), the degree of blood loss. Be sure to take thermometry, auscultation, palpation and percussion of the abdominal organs (the doctor will listen, feel, tap on the patient’s stomach). Perhaps, on the spot they will conduct a test to determine the bleeding time and the rate of blood clotting (this may require the dog to “scratch”), rectal examination.
Depending on the severity of the case, after examination, additional diagnostic measures may be required to make a diagnosis:
A general clinical blood test will be required to accurately determine the degree of blood loss, the presence of inflammation, and decide on the appointment of antibiotics.
A biochemical blood test can help find out how the internal organs cope with the problem.
Tests for infections (blood samples can be taken to detect antibodies to infections, or rectal swabs can be taken to detect antigen – the cells of the causative agent of the disease themselves).
Microscopy of a native rectal swab can be performed to detect helminth and protozoan eggs.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity makes it possible to see the shape, size, structure of internal organs, assess the patency and peristalsis of the intestine, detect neoplasms, foreign objects.
X-ray examination allows visualizing the topography, volume and structure of internal organs, detecting radiopaque foreign bodies. Drinking a radiopaque substance to the animal (eg, barium sulfate) is sometimes also indicated, it stains the food pipe, and it becomes possible to visualize a problem that was previously hidden. Also, this method allows you to evaluate the speed of passage of the food coma and detect complete or partial obstruction, intussusception of the intestine.

Treatment
Treatment, of course, depends on the cause of the appearance of blood in the dog’s stool, the severity of the patient’s condition, comorbidities, age, and many other factors.
After assessing the condition of the animal at the moment and performing diagnostic procedures, the doctor either starts treatment immediately, or chooses outpatient treatment, or, if the patient’s condition allows, postpones the appointment of therapy until the results of the tests.
If the dog’s condition is severe, significant blood loss, anemia, dehydration is detected, then the doctor conducts intensive therapy. This may be oxygenation, infusion therapy, transfusion of blood or its components, surgery. If test results for bleeding time and clotting rate are poor, or if there are multiple bleeding lesions, rodenticide (rodenticide) poisoning is suspected. In such a situation, the use of an antidote is required – vitamin K1 (konakion, kadzhekt). It is important to remember that in case of poisoning with an unknown rodenticide, therapy must be continued for 4-6 weeks, because this is how long modern poisons against rodents can be active in the body of an animal.
If the appearance of blood in the dog’s feces is caused by an infection, then the doctor, having prescribed symptomatic treatment and correction of the condition immediately, prescribes etiotropic therapy based on the results of the tests.
If a traumatic foreign body is found in the intestine or a volumetric neoplasm, then with a high degree of probability surgical treatment is required – immediately or after stabilization of the condition.
If the reason for the detection of blood in the feces is parasitosis or infection with protozoa, then specialized treatment is prescribed.
Diet correction is necessary if a violation of feeding has caused a problem.

puppy blood in stool
Blood in the stool in a puppy can appear for the same reasons as in an adult dog. But in the first place there will be parvovirus enteritis and other infections, helminthic invasions, but neoplasms, if they occur in puppies, are extremely rare.
If you notice that a puppy is pooping with blood, especially if it is accompanied by diarrhea, then you should contact the clinic immediately, because puppies are very difficult to tolerate dehydration and the risk of pet death is huge.

Prevention
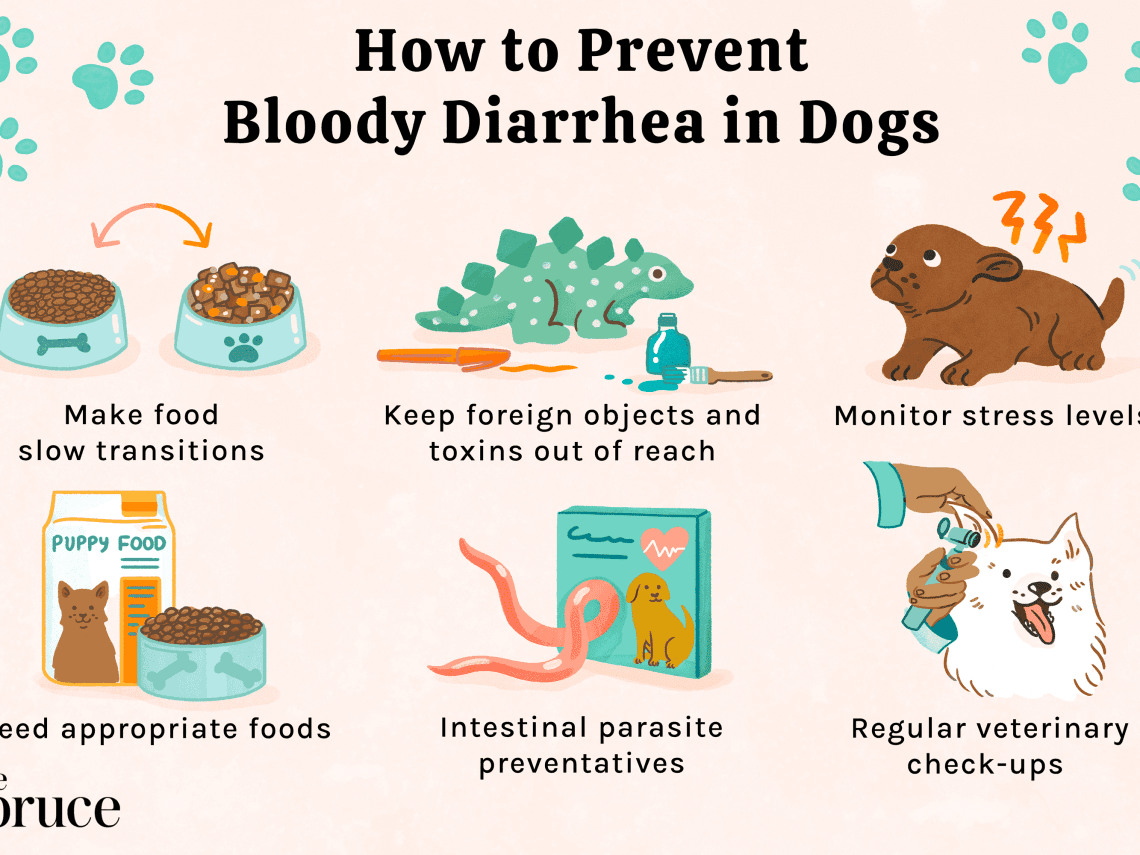
In order to minimize the risk of blood in the dog’s stool, you must adhere to the following rules:
Strictly observe quarantine measures for puppies not vaccinated by age.
Timely carry out scheduled vaccinations of puppies, revaccination of adult animals.
Choose a balanced diet that is right for your dog, and make it from fresh, quality products.
Do not allow the selection of food and non-food items on the street.
Older animals regularly conduct medical examinations.
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
March 10 2021
Updated: 15 March 2021