Renal failure in dogs

Contents
Symptoms of the disease
The functions of the kidneys in the body are diverse – they include not only the excretory role, but also participation in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids, regulation of acid-base balance, osmotic pressure, water balance, blood pressure, etc. Accordingly, with the development of the disease in The body is disturbed by a huge number of processes, and the symptoms of kidney problems in dogs can be very diverse. For example, these can be symptoms of a gastrointestinal disease, diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, gum disease, in some cases, you can even suspect the presence of a foreign body in the stomach or intestines.
The main symptoms of kidney failure in dogs include:
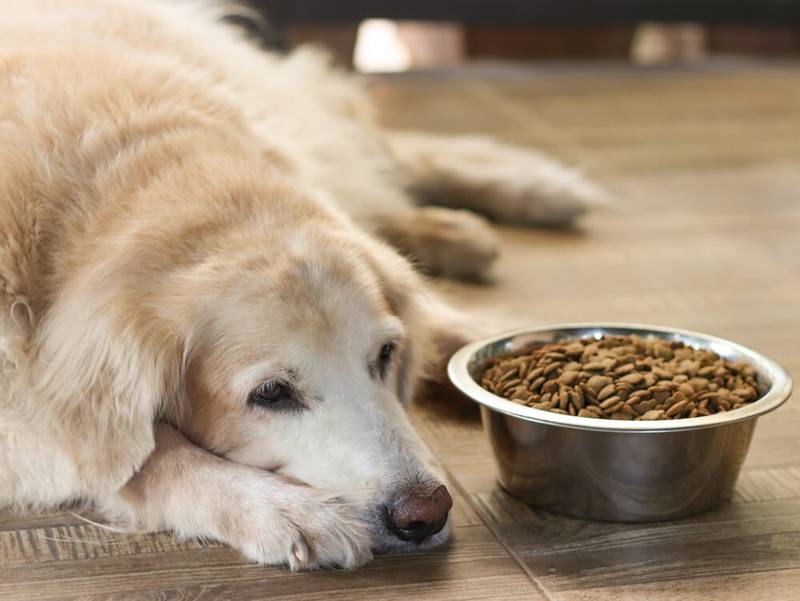
refusal to eat or loss of appetite;
vomiting;
lethargy, depression;
unpleasant smell from the mouth;
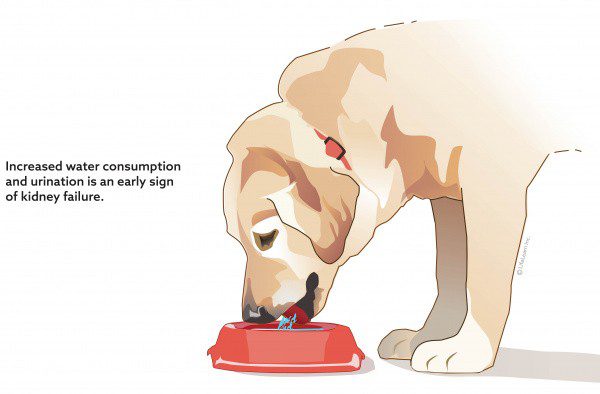
increased thirst;
frequent urination;
weight loss.

As we can see, the symptoms of the disease are characteristic of a wide range of pathologies, so the diagnosis should be confirmed by tests. In the clinic, you must perform the following diagnostics:
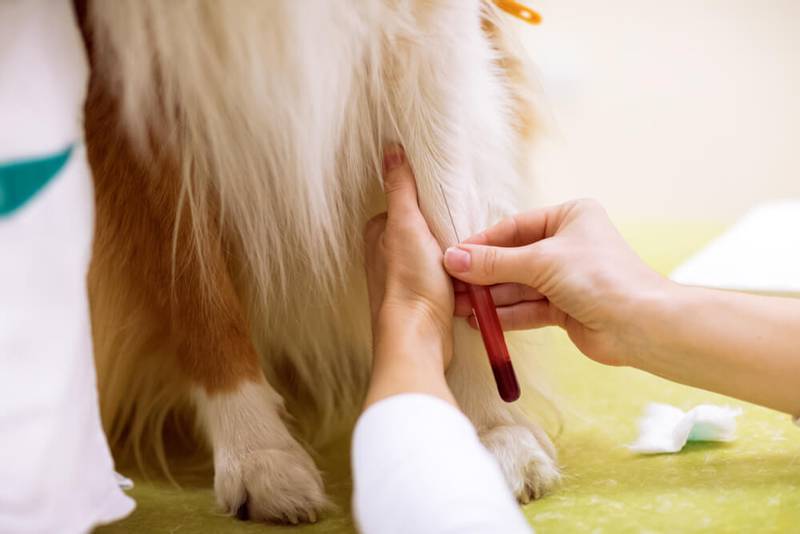
take a general and biochemical blood test;
do a general urine test;
perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
measure blood pressure (tonometry);
to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms, it is desirable to conduct an x-ray of the abdominal cavity.
Based on the results of the examination, the following specific signs of kidney failure in dogs can be identified:
increase in urea, creatinine, phosphorus in biochemistry;
anemia according to the general blood test;
proteinuria, hematuria, decreased urine density;
increase in blood pressure on tonometry.
Given the significant reserve capacity of the kidneys, at least 60-70% of the kidney tissue must die for the development of symptoms of the disease, and until then the dog may not have any signs of the presence of the disease. In the early stages of kidney disease, the proportion of dead nephrons can reach up to 75%! The poor prognosis of the disease is associated with this feature – by the time the pet has symptoms of the disease and it is possible to make a diagnosis, as a rule, nothing can be done to help. Another factor in the poor outcome is the fact that often the owners do not even realize that the dog has kidney problems, write off all the symptoms for old age and do not go to the veterinary clinic.
Acute renal failure (ARF)
Acute renal failure in dogs is a syndrome that develops as a result of acute impairment of kidney function and is accompanied by azotemia (i.e., an increase in urea and creatinine in blood tests), disorders of fluid and electrolyte balance and acid-base balance.

The reasons for the development of OPN include:
violation of the circulatory system as a result of shock, blood loss, cardiac pathology, renal vascular thrombosis and other serious conditions;
the use of nephrotoxic drugs, such as certain antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressive and chemotherapy drugs, or poisoning with nephrotoxic substances, such as ethylene glycol;
the presence of severe systemic pathologies, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases (for example, leptospirosis), etc.
Diagnosis is complex based on:
A characteristic history (taking medicinal or other nephrotoxic substances, surgery, trauma, etc.);
Specific symptoms (sudden refusal to eat, apathy, vomiting, diarrhea, bad breath, convulsions, incoordination in space and a decrease in the amount of urine formation up to the complete absence of urination);
By laboratory diagnostics:
a blood test can detect an increase in hematocrit, an increase in the number of leukocytes with lymphopenia;
according to blood biochemistry, a progressive increase in the content of urea, creatinine, phosphorus, potassium and glucose is noted;
urinalysis determines a decrease in urine density, proteinuria, glucosuria;
the results of X-ray and ultrasound in the acute development of the process, as a rule, are unchanged.
How long a dog has left to live if her kidneys fail depends on the degree of their damage, the speed of contacting the clinic and the correctness of the prescribed treatment.
Chronic renal failure (CRF) in dogs
Chronic renal failure is a pathological condition of the body characterized by irreversible damage to the kidneys, a violation of the excretion of nitrogen metabolism products from the body and a disorder of many types of homeostasis (that is, the relative constancy of the internal environment of the body).
This disease can be considered as the final stage of the progression of a wide variety of kidney diseases: congenital malformations, glomerulonephritis, amyloidosis, pyelonephritis, nephrolithiasis, polycystic disease and many others. Most of these diagnoses can only be made by biopsy (taking a piece of an organ for histology), therefore, in most cases, they speak of chronic bilateral nephropathy as a conclusion.
As mentioned above, damage to more than 75% of the mass of the kidney tissue leads to disruption of the kidneys: the concentration function decreases (which leads to a decrease in the density of urine), there is a delay in the excretion of nitrogen metabolism products (this is the final stage of protein metabolism in the body), and at a late stage CRF in dogs develops uremia – poisoning of the body with decay products. Also, the kidneys produce the hormone erythropoietin, which is responsible for the synthesis of red blood cells – therefore, when the kidneys fail, the synthesis of the hormone decreases and anemia gradually develops.
As in the case of acute pathology, the diagnosis of chronic renal failure is made on the basis of anamnesis and characteristic examination results: hypoplastic anemia, increased creatinine and blood urea nitrogen, hyperphosphatemia, acidosis, hyperkalemia are detected. Decreased density of urine (in dogs below 1,025 hl), moderate proteinuria is also possible (protein in the urine increases).
On the radiograph in case of renal failure in dogs, an uneven structure of the kidneys and a decrease in their size can be detected, according to ultrasound – a heterogeneous structure, sclerosis of the parenchyma, complete loss of layers (impaired cortico-medullary differentiation), a decrease in the size of the organ.
Based on the value of the concentration of creatinine in the blood serum, 4 stages of CRF in dogs are distinguished:
nonazotemic stage – this can include any violation of the kidneys without a clearly identified cause associated with the presence of nephropathy. Initial changes in the kidneys by ultrasound can be detected, in the urine – an increase in the amount of protein and a decrease in density. According to blood biochemistry, a persistent increase in creatinine content is noted (but within the normal range).
Mild renal azotemia – Serum creatinine values are 125-180 µmol. The lower threshold of creatinine values uXNUMXbuXNUMXbmay be a variant of the norm, but at this stage, any disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system are already observed in pets. Symptoms of kidney failure in dogs may be mild or absent.
Moderate renal azotemia – Serum creatinine values are 181-440 µmol. At this stage, as a rule, various clinical signs of the disease are already present.
Severe renal azotemia – creatinine values over 441 µmol. At this stage, severe systemic manifestations of the disease and pronounced signs of intoxication are observed.
Treatment of kidney failure in dogs
So, if a dog has kidney failure, can it be cured? Treatment tactics and the chances of eliminating kidney failure in dogs differ dramatically depending on its type.
Treatment of acute renal failure is carried out exclusively in a hospital under the constant supervision of a doctor. Specific (pathogenetic) therapy is prescribed, aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. Symptomatic intravenous therapy is regularly carried out to normalize the water-electrolyte balance and acid-base balance, and to remove toxins. Blood tests, the general condition of the patient, the amount of urine separated are monitored daily – for this, catheterization of the bladder and the installation of a urinal are mandatory.
When maintaining appetite, special feeds are prescribed for kidney failure in dogs, with vomiting and lack of appetite – the main nutrients must be supplied intravenously or through special tubes (nasoesophageal probe, etc.).
In case of severe intoxication, the absence or almost complete cessation of urine production and the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment in the first 1-3 days of hospitalization, dialysis is recommended (this is the process of artificial removal of waste products and excess fluid from the body).
With the development of acute renal failure of any etiology, the pet owner must understand that the prognosis of the disease is cautious up to unfavorable, various complications are possible in the course of treatment. You also need to be prepared for expensive long-term hospitalization – when trying to treat a pet in serious condition at home, you can lose time, and then the chances of recovery are significantly reduced. But with proper and timely treatment, the dog has every chance for a full recovery and recovery.
Treatment of chronic renal failure in dogs can only be symptomatic. In this case, it is important to realize the fact that CRF is a progressive, irreversible disease with a fatal outcome: if the pet was given the 4 (terminal) stage, then most likely he will not live for more than a month.
While maintaining appetite in a pet with CRF, the main thing is to follow a special diet (the principles of which we will discuss below) and evaluate blood tests over time.
In the presence of vomiting and refusal to feed, antiemetic drugs (such as maropitant, metoclopramide), as well as gastroprotective drugs (sucralfate) and H2 receptor antagonists (ranitidine) are used.
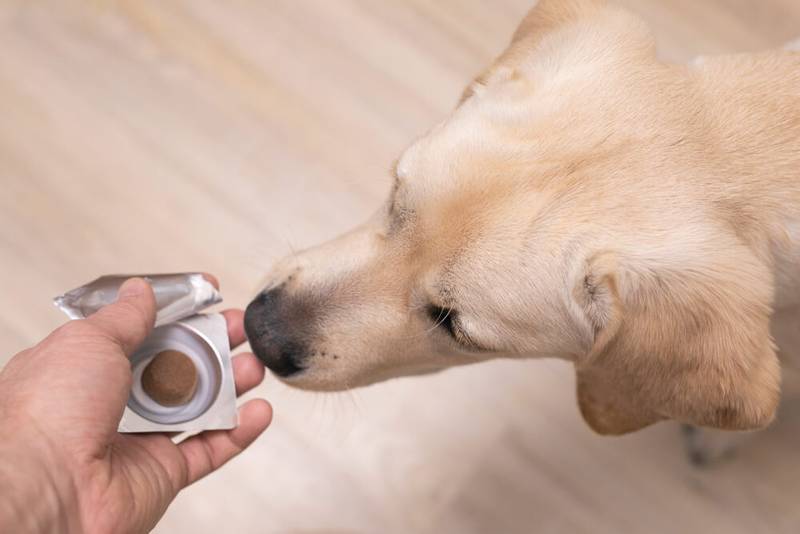

With an increase in the amount of phosphorus in blood biochemistry, drugs that bind phosphorus in the intestine, the so-called phosphate binders (for example, ipakitine), are prescribed.
With persistent refusal to eat, uncontrolled vomiting, and other signs of uremic intoxication, inpatient treatment with intravenous therapy and monitoring of blood tests is required to stabilize the pet.
Also, with the development of CRF in pets, an increase in blood pressure is often observed, for the control of which angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are prescribed with the obligatory control of proteinuria and azotemia (since these drugs can worsen the severity of CRF).
When the pet’s condition stabilizes, the course of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment are periodically assessed. With a moderate course of the disease, it is advisable to examine the dog once every 1 months.

How long dogs with CRF live depends on the degree and nature of the progression of the disease. The long-term prognosis is unfavorable, the disease passes into the terminal stage in a few months or years.
Diet
Let’s talk about nutrition in kidney failure. Diet is one of the most important methods of maintaining the body and slowing down the development of symptoms in chronic kidney disease, and in acute kidney failure is one of the most important components of treatment. Moreover, the answer to the question of how long a dog with kidney failure will live depends on a properly composed diet.
The goals of dietary therapy for renal failure in dogs include:
providing the body with full energy;
relief of symptoms of kidney disease and uremic intoxication;
the maximum possible reduction of violations of water, electrolyte, vitamin, mineral and acid-base balance;
slowing the progression of renal failure.
Next, we will dwell on the main features of the diet for renal failure.
To reduce the risk of protein breakdown in the body, which leads to weight loss and aggravates intoxication, it is necessary to provide the pet with a sufficient amount of easily digestible energy. It should be remembered that non-protein energy components include carbohydrates and fats. When formulating diets for dogs with kidney disease, more fats are usually added, which increase the energy content of the food, improve its palatability and palatability.
Because high protein diets exacerbate the severity of nephropathy, high quality proteins should be used in moderation when developing diets. It has been proven that a decrease in the amount of protein by limiting the intake of non-essential amino acids can reduce the accumulation of nitrogen metabolism products and, as a result, alleviate the clinical manifestations of the disease.
No less important is the reduction in the amount of phosphorus in diets, which (proven) increases the survival rate of dogs, prevents the decrease in the amount of calcium in the body (due to the development of secondary hyperparathyroidism) and, as a result, slows down the development of osteodystrophy and calcification of soft tissues.
It is also important to limit sodium (which is part of table salt) in diets to reduce hypertension (which is a consequence of diseased kidneys).
It should be borne in mind that water-soluble vitamins are excreted in the urine, therefore, with polyuria against the background of kidney disease, their deficiency is possible. This loss of vitamins can contribute to anorexia, so feeds should be supplemented with water-soluble vitamins.
The addition of an increased amount of dietary fiber is indicated for kidney diseases, as they are accompanied by a slowdown in intestinal motility, and dietary fiber can improve the condition and motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
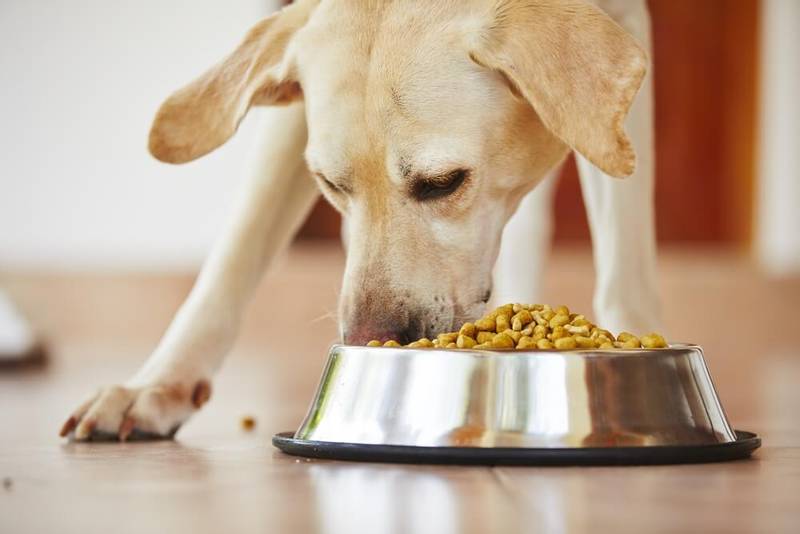

Thus, if the dog is properly fed in the presence of renal failure, diet therapy is the main effective means of relieving the clinical symptoms of uremia in animals. And a veterinary nutritionist can choose the right food for kidney failure: moreover, it can be either a ready-made industrial food (such as Royal Canin Renal, Hill’s K / d, Purina NF), or an individually formulated home diet (usually based on beef, potatoes and vegetable oil).
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
October 8 2020
Updated: February 13, 2021