Pregnancy and childbirth in a cat
In cats, puberty occurs at 7 to 9 months. However, mating should not be carried out at this age: the cat’s body is not ready for such overloads, and kittens can be born weakened.
Contents
Preparing a cat for mating
You can take a cat for mating after she turns 1 year old. It is necessary to prepare for mating. Even before the onset of the heat, vaccinate and deworm, and also make sure that the cat is completely healthy. This is important to do in advance: during pregnancy, vaccinations, many antihelminthic drugs, flea remedies and most drugs are contraindicated. The veterinarian checks the physical condition of the animal. This allows you to timely detect violations that may interfere with mating or normal pregnancy and childbirth. After 2 – 3 weeks after mating, the cat is brought for a second examination. The veterinarian checks if she is pregnant and gives advice on care.
Diagnosis of pregnancy in a cat
Diagnosis of pregnancy is carried out in the following ways:
- Palpation (palpation) of the abdomen. This requires experience and extreme caution. If you palpate carelessly, you can damage the amniotic membrane or the fetuses themselves. This is fraught with miscarriage.
- Ultrasonic echography. This is a fairly safe method, thanks to which you can observe the course of pregnancy throughout its entire length. On the 20th day, you can hear the heartbeat of future kittens. So they are viable.
- Radiography. This method is not entirely safe, as it is associated with x-rays. A radiograph already on the 43rd day can show the fetal skeleton. This method is informative to distinguish true pregnancy from false and pyometra. But in the first half of pregnancy, it is better to refrain from it.
The course of pregnancy in a cat
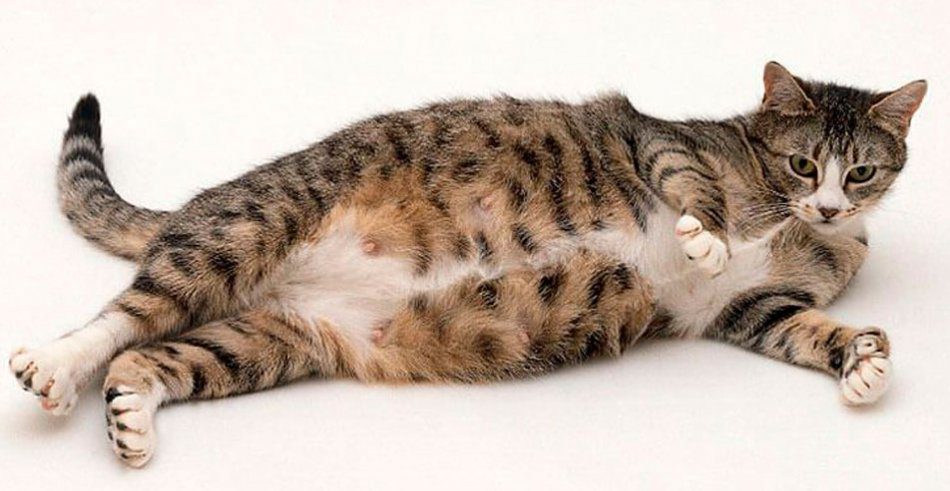
The average duration of pregnancy in cats is 9 weeks (+- 4 days). The exact period will depend on the breed of the cat, the number of kittens, the individual characteristics of the expectant mother and the conditions of detention. If kittens were born before the 60th day, they are considered premature and often do not survive. A cat’s pregnancy is divided into trimesters.
| Period | Signs of pregnancy |
| 1 – 3 weeks | There are no obvious signs of pregnancy. By the 21st day, the nipples swell and turn pink. You can conduct the first study (ultrasound), it will also give an idea of the number of kittens. |
| 4 – 6 weeks | There may be nausea and vomiting in the morning – this is caused by hormonal changes. The cat may refuse to eat, look depressed and oppressed. Do not be afraid – after a few days this condition disappears. The stomach gradually increases, and from the second month it grows rapidly. |
| 7 – 9 weeks | You can feel the fruit stirring. In the last 2 weeks, the stomach becomes pear-shaped, nipples sag, colostrum appears. The cat moves less, eats worse, begins to search for a suitable nest. |
1 week before the expected birth, the cat should be shown to the veterinarian again. He will explain how a normal birth proceeds and what to do to care for newborns. Ask where you can go if you need emergency help.
Pathology of pregnancy in a cat
Visits to the vet are not a luxury. Only a veterinarian can understand that something is wrong and help your pet. Pregnancy can be complicated by the following pathologies: 1. Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy. It can be primary (embryos immediately develop outside the uterus) or secondary (1 or more fetuses enter the abdominal cavity due to rupture of the wall of the uterine body or horn). Primary ectopic pregnancy is interrupted at an early stage: the embryos resolve. failure of uterine scars as a result of caesarean section. Fruits may die or continue to develop. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy in a cat:
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy in a cat:
- “sharp” belly
- external or internal bleeding
- abnormal discharge from the genital loop
- if the pregnancy is full-term – unproductive attempts and contractions
- intoxication
- shock.
All this can end in the death of the cat. Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy in cats is difficult. Radiography, ultrasound or laparoscopic examination are used. Late diagnosis makes the prognosis unfavorable. A premature ectopic pregnancy is interrupted by an induced abortion. At term, a caesarean section is used. 2. Abortion. The pregnancy is terminated before the fetuses are mature and capable of life outside the mother’s womb. In cats, the fruits are considered mature from the 56th day. Abortions are artificial and spontaneous. induced abortion – this is a forced termination of pregnancy at the request of the owner or for medical reasons. An operation is performed or medications are used.Spontaneous abortion can occur at any stage of pregnancy. Result: resorption of embryos (hidden abortion), death of fetuses and their subsequent mummification, maceration, putrefactive decomposition, expulsion of dead or living, but non-viable and immature fetuses from the uterus. Abortions are complete and incomplete.Complete abortion – this is the resorption of all embryos, the expulsion of all immature and / or dead fetuses from the birth canal.Incomplete abortion – this is the resorption of some of the embryos and the bearing of the rest, or the death and / or expulsion of part of the fetus from the uterus, while others are born on time, as well as the retention of all or part of the dead fetuses in the uterus. It is impossible to stop an abortion that has begun. All that can be done is to observe the cat and, if necessary, administer antibiotics. If dead fetuses remain in the uterus, drugs are prescribed that stimulate uterine contractions. If the drugs do not help or their administration is dangerous, the fetuses are removed from the uterus with the help of an operation. 3. Post-term pregnancy. In cats, pregnancy is considered post-term if delivery does not occur even on the 71st day. As a rule, the fruits in this case are dead, there are discharges from the genital slit. If the cat is helped in a timely manner, the prognosis is usually favorable. Most often, surgery is used (caesarean section, extirpation of the pregnant uterus), since it is more reliable and safer than drug treatment. 4. Twisting of the uterus. As a rule, it is caused by a fall, sudden movement or jump of a pregnant cat in the second half of pregnancy. Symptoms: anxiety, discomfort. In severe cases, septic shock and death of the cat are possible. But with timely assistance, the prognosis is favorable. Treatment usually involves surgery: a caesarean section or removal of the uterus.
Preparing a cat for childbirth
Prepare a spacious box. It should close at the top. An entrance should be located at the level of the cat’s chest. At the bottom, put paper (many layers) or disposable baby sheets. You can use a cat house, but its bottom also needs to be prepared accordingly. “Rodzal” should be quiet and warm. Keep other pets and children away. Prepare food, water and a trash can. You will also need:
- veterinarian’s phone number
- surgical gloves
- clean scissors
- box for kittens
- warmer
- pipette
- gel lubricant or vaseline
- antiseptic
- thread.
Cat birth
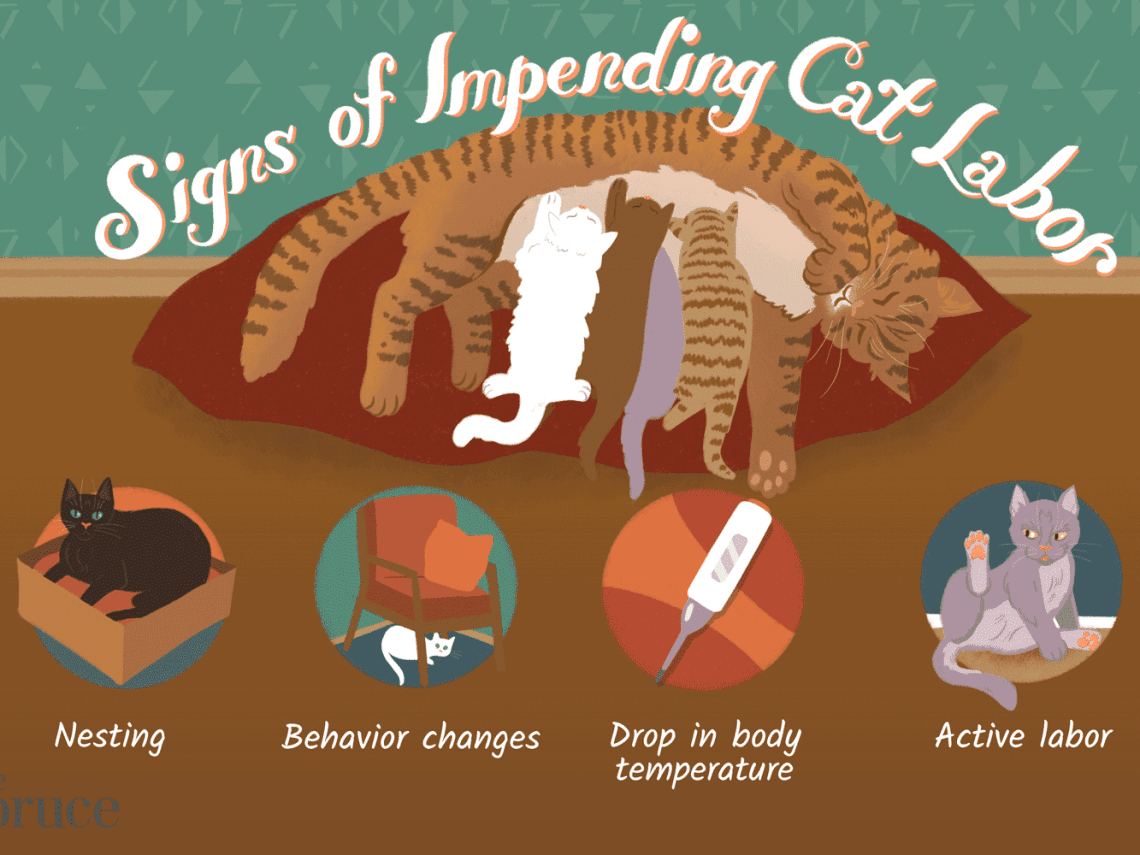
As a rule, childbirth passes quickly enough. Keep an eye on your cat so you don’t miss the start. Signs of an impending labor:
- The cat is worried, licks the genitals and belly, rushes about.
- The breathing of the animal becomes heavier and more frequent.
- The body temperature (rectal) of the future mother drops below 37 degrees. This is normal, don’t worry.
- The genitals swell, discharge may appear (light brown or pink).
- The rush of colostrum causes the mammary glands to swell.
Stage of birth of a cat | Evidence |
First | Contractions, attempts that “push” the fetus through the birth canal. |
The second | The birth of kittens. First, fluid flows out of the amniotic sac, then part of the fetus appears. As a rule, the kitten lies with its head towards the exit, but it can move forward with its hind legs – this is not a pathology. Sometimes a kitten is born in a bubble. Normal delivery: the kitten appears, the mother releases it from the bubble, licks it, gnaws the umbilical cord, the newborn breathes and screams for a while, then starts to suck. |