Parasites in guinea pigs: withers, ticks, fleas and lice – symptoms, treatment and prevention

Funny guinea pigs are considered very clean pets that require minimal care and simple, affordable food to keep. The owners of fluffy rodents should be aware that parasites in guinea pigs are found even in the absence of animal walking in the external environment and regular high-quality cleaning of the animals’ cages.
The main symptom of damage to a pet by external parasites is severe itching, from which the guinea pig often itches, gnaws its hair, numerous scratches and bleeding wounds are found on the skin. In this situation, it is recommended to urgently deliver the pet to a specialist to clarify the type of parasites and prescribe timely treatment.
If your pet itches and his hair falls out, this does not always indicate the presence of parasites, perhaps he has an allergy or a protracted molt, read about it in our materials: “What to do if the guinea pig’s hair falls out and the skin is flaky” and “What to do if the guinea pig the pig sheds.”
Contents
Where do guinea pig parasites come from?
Small pets become infected with ectoparasites through contact with infected relatives or dogs and cats, through poor-quality filler or hay. Sometimes parasitic insects in search of food get into city apartments from the basements of the house and the sewer. The owner can infect a beloved animal with external parasites brought on clothes from the external environment.
Parasitic insects of guinea pigs, other than lice, are not transmitted to humans, they do not have the ability to bite people or reproduce on the human body. Lice when attacking a person cause pediculosis.
Parasitism of insects in pets causes allergic reactions in many owners to the waste products of parasites.
Symptoms of an ectoparasite infection in a guinea pig
Parasitization on the body of guinea pigs of different types of ectoparasites is accompanied by similar symptoms:
- the pet is very worried, often scratches the skin to the point of blood and gnaws out the hair due to the unbearable itching from insect bites;
- there is also hair loss on the limbs and head, there is a decrease in appetite and body weight;
- in advanced cases, large hairless areas and purulent wounds form on the skin.
With such symptoms, it is recommended to urgently seek help from specialists. Improper treatment of a guinea pig at home can provoke the development of anemia, malnutrition, blood poisoning, intoxication and death.
Common parasites in guinea pigs
In guinea pigs, the following types of parasitic insects are most often found.
pliers
Hypodermic mites in guinea pigs cause:
- severe itching;
- soreness;
- the formation of strong scratching on the body, accompanied by edema and purulent inflammation.
In domestic rodents, three types of subcutaneous mites parasitize, causing:
- trisaccharose;
- sarcoptosis;
- demodicosis;
- guinea pigs are also affected by fur and ear mites.
Treatment of a guinea pig with parasitism of subcutaneous, ear and fur mites should be carried out by a veterinarian. Self-use of insecticides can cause intoxication and death of a beloved animal.
Trixacarose
The causative agent of the disease is the microscopic spider mite Trixacarus caviae, which parasitizes and multiplies in the subcutaneous layers.
This type of parasitic insect is found only in guinea pigs, so infection can occur through contact with sick relatives.
In healthy pets with strong immunity, the tick may be inactive, multiply and parasitize on the body without showing a clinical picture of the disease.
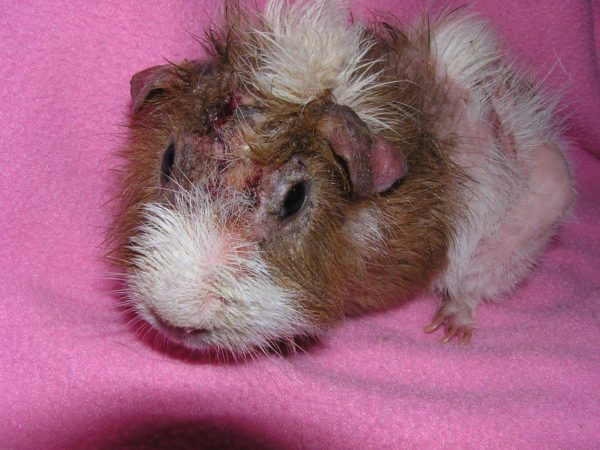
Young, elderly, malnourished, sick, pregnant guinea pigs and animals kept in uncomfortable conditions or exposed to frequent stressful situations are most severely ill. When sick, a pet experiences:
- severe itching and soreness of the affected areas;
- strongly itches and gnaws itself;
- hair loss is observed;
- extensive foci of baldness;
- open wounds, ulcers and scratches on the skin;
- lethargy, refusal of food and water;
- convulsions, abortions.
In advanced cases, if left untreated, the guinea pig may die from dehydration. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in a veterinary clinic, microscopic examination of a skin scraping is used to detect and establish the type of tick.
Treatment of a guinea pig affected by a scabies mite is carried out by a specialist; most often, injections of Otodectin, Ivermectin or Advocate, Stronghold drops are prescribed to the sick animal. The filler from the pet’s home must be removed. The cell is first disinfected with alkaline solutions, then treated with insecticidal preparations.
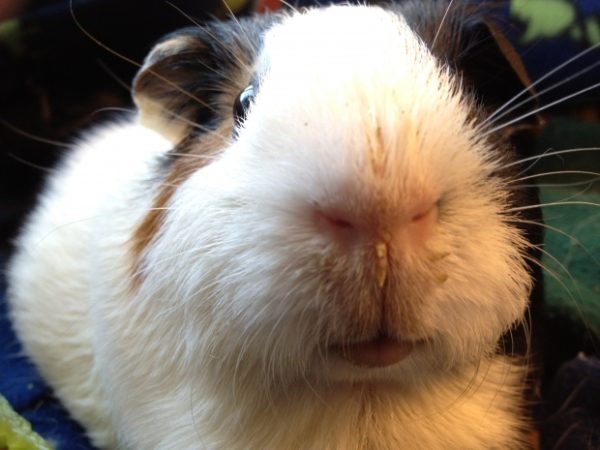
Sarcoptic mange
The disease is caused by microscopic mites of the Sarcoptidae family, which gnaw through passages in the subcutaneous layers. Guinea pigs become infected through contact with sick animals, through hay or litter. It is possible to understand that subcutaneous mites parasitize in a small animal by the characteristic triangular growths on the skin with gray crusts. The disease manifests itself:
- itching;
- the formation of alopecia on the muzzle and limbs.
The diagnosis is confirmed by the detection of pathogens in a skin scraping during microscopic examination in a veterinary clinic. For treatment, the treatment of the guinea pig with acaricidal sprays based on selamictin is prescribed, the animal’s cell is subjected to thorough disinfection.

Demodecosis
The causative agent of the disease are microscopic worm-like mites of the genus Demodex, which feed on the blood of an animal. Parasitic insects live in the subcutaneous layers of a domestic rodent. Infection of guinea pigs occurs through contact with sick individuals, young animals often get sick from their mother. Demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of numerous papules and pustules on the skin of the head and extremities in the places of a tick bite. In the future, the formation of ulcers and alopecia in the affected area. Often, the pathology is accompanied by swelling of the limbs, which is manifested by a slight lameness. The diagnosis is established after microscopic examination of skin scrapings. It is necessary to treat a guinea pig for demodicosis under the supervision of a specialist with ivermectin-based toxic drugs, its overdose is deadly for a guinea pig.
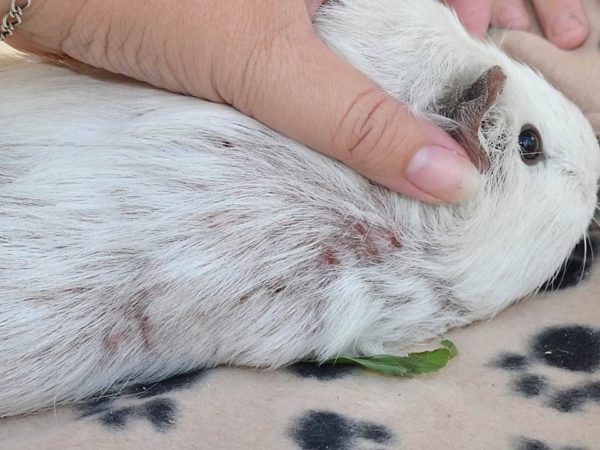
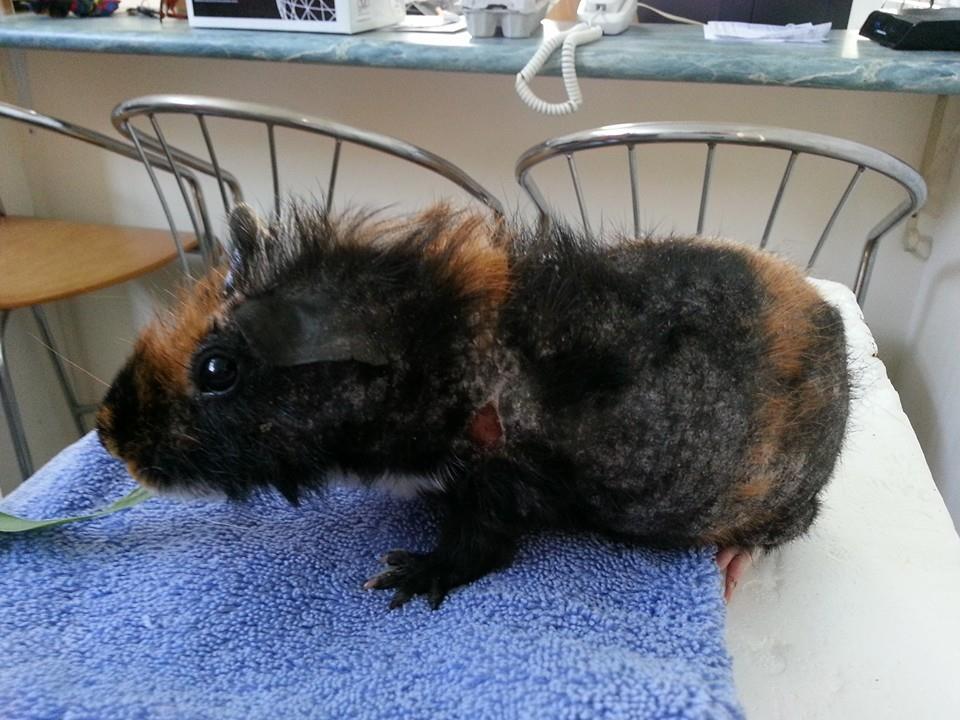
fur mite
Fur mites Chirodiscoides caviae parasitize the skin and coat of guinea pigs.
It is impossible to detect a microscopic pathogen with the naked eye.
Pets become infected through direct contact with sick animals. Invasion of parasitic insects manifests itself:
- itching;
- hair loss;
- the formation of ulcers and erosions on the skin;
- refusal of the animal from food and water.
To clarify the diagnosis, a microscopic examination of the pet’s hair is used, the treatment is based on the use of Otodectin or Ivermectin preparations.

Ear mite
In guinea pigs, the rabbit ear mite Psoroptes cuniculi can parasitize in the auricle. Infection of pets occurs through contact with sick animals.
Ticks can be seen with the naked eye, and infected individuals show red-brown wax accumulations in the ears and dark insects with an oval body.
When parasitizing an ear mite, the following is observed:
- redness of the skin of the auricle with the formation of a yellow-red growth;
- otitis and torticollis, the guinea pig often scratches the ear and shakes its head.
Treatment is based on the use of Ivermectin preparations and antibiotics.
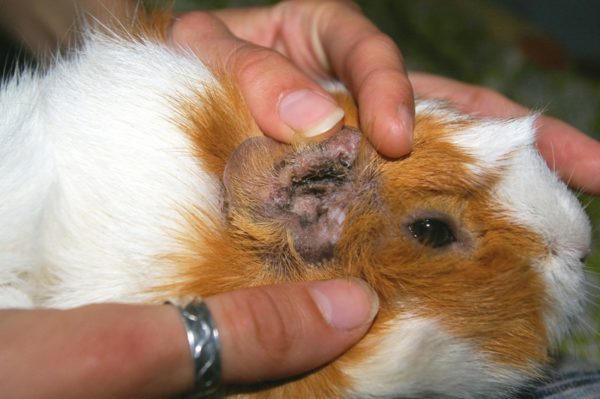
Ixodid tick
If a guinea pig is bitten by an ixodid tick while walking in the external environment, it is necessary to contact a veterinary clinic to extract and examine the insect and prescribe symptomatic treatment.
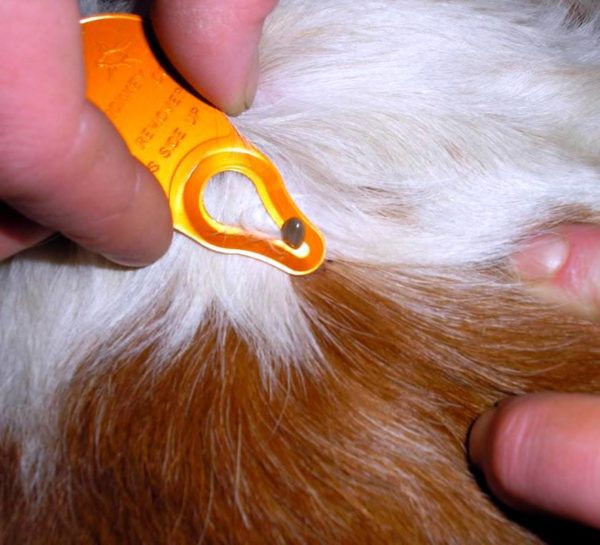
Fleas
Guinea pigs sometimes get fleas. Most often, the cat flea Ctrenocephalides felis lives on the body of fluffy rodents – a blood-sucking insect 3-5 mm in size, which can parasitize cats, rats, guinea pigs and humans. Fleas in guinea pigs appear when a small animal comes into contact with infected pets, most often dogs and cats. Insect parasitism causes:
- itching, restlessness and anemia;
- the pet constantly itches and bites the fur;
- scratches and wounds appear on the skin.
When combing a guinea pig with a fine comb between the teeth, red-brown insects with a flattened body or their dark excrement are found, which, when wet, turn the water pink. Treatment of guinea pigs for fleas is based on the use of preparations for cats containing pyrethrin.
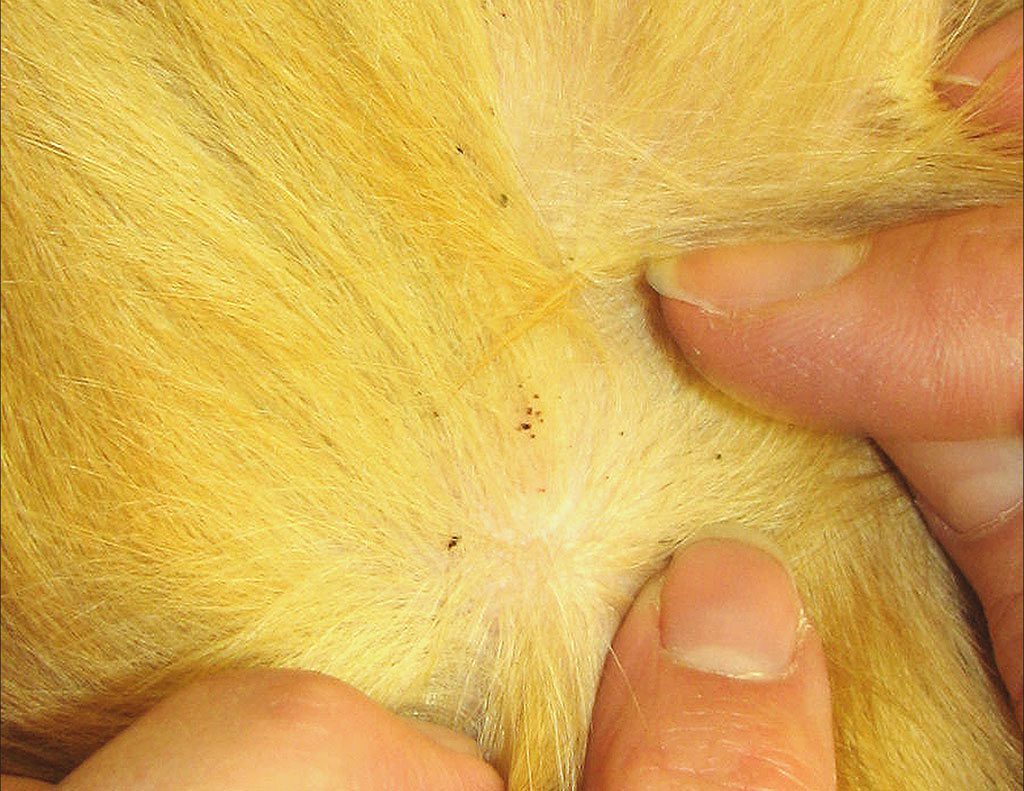
Vlas-eaters
Withers in guinea pigs cause trichodecosis.
Ectoparasites are not dangerous to humans, but their parasitism on the body of a small animal causes severe itching and exhaustion, which can be fatal.
The source of infection with parasites is food, hay, filler or contact with sick relatives. Fluffy insects are affected by the lice Chirodiscoides caviae, causing trichodecosis. Parasites live on the skin of the animal, clinging to the base of the hair of the guinea pig with their limbs, and feed on the scales of the epidermis and the blood of the guinea pig. Insects can be seen with the naked eye when the fur is pulled apart. Vlasoyed look like rapidly moving light worms about 1-3 mm in size. Reproduction of parasites occurs on the body of a guinea pig, the female insect lays about a hundred nit eggs, firmly sticking them in the pet’s fur.
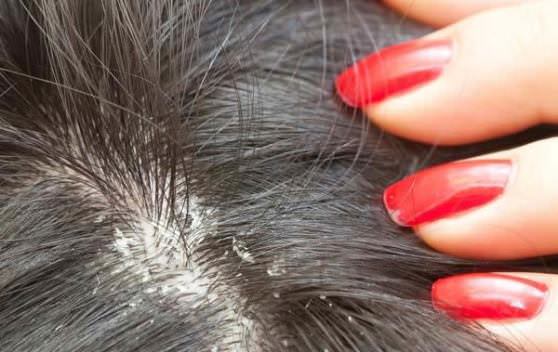
The owner can detect light dandruff on the pet’s coat, which cannot be removed or shaken off the fur of a hairy pig. With trichodectosis, the animal:
- itches intensely;
- gnaws fur and skin;
- refuses food and feed;
- on the skin there are extensive numerous alopecia with wounds and ulcers.
The diagnosis is confirmed in a veterinary clinic by microscopic examination of the parasite.
Treatment of guinea pigs affected by withers should be carried out by a veterinarian. With trichodectosis, the animal is prescribed treatment with sprays for cats based on permethrin: Celandine, Bolfo, Acaromectin.
To reduce the toxic effect of therapeutic agents, it is preferable to use not sprays, but drops: Lawyer, Stronghold, Neostomazan.
Video: how to deal with guinea pigs with lice
Lice
Lice in guinea pigs provoke itching and anxiety of the pet. Parasites feed on the blood of a small animal, adult insects look like yellowish oblong fast-running dots 1-3 mm in size, parasite nits resemble light dandruff on a rodent’s coat.
Ectoparasites are transmitted to humans, causing pediculosis, a disease characterized by itching, fever, and anemia.
The louse has a cutting mouth apparatus; before sucking, the insect injects toxins that prevent blood clotting. One parasite is able to dig into the skin of a guinea pig up to 10 times during the day, which is accompanied by severe itching and anxiety of the pet.
The small animal constantly itches, twitches, bites and scratches itself, hair loss, scratching and abrasions on the skin, refusal to feed, lethargy and apathy are observed.
Lice parasitism is dangerous for the development of anemia, blood poisoning and death.
Treatment of a guinea pig for lice is carried out by a veterinarian after a microscopic examination of the parasite, sprays based on permethrin or injections of Ivermectin, Otodectin are prescribed to the pet.
Prevention of infection of guinea pigs with ectoparasites
To prevent infection of guinea pigs with ectoparasites, simple preventive measures must be observed:
- feed guinea pigs with a balanced diet using vitamin preparations to strengthen the immunity of animals;
- treat guinea pigs that walk in the external environment with insecticidal sprays, use special flea shampoos when bathing;
- purchase filler, feed and hay only in specialized stores;
- wash your hands and change street clothes before interacting with your beloved pet.
Insect parasitism, if left untreated, can cause progressive exhaustion or death of a pet. If itching and anxiety appear in a guinea pig, it is recommended to start treatment immediately under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Withers, fleas, ticks and other parasites in guinea pigs
3.4 (68.75%) 32 votes





