Pancreatitis in dogs: symptoms, why it develops and how to treat
Contents
- How does pancreatitis develop in dogs?
- Types of pancreatitis in dogs
- Causes of inflammation of the pancreas
- How does pancreatitis manifest in dogs?
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment for pancreatitis in dogs
- Complications of pancreatitis in dogs
- First aid for an attack of pancreatitis
- Pancreatitis in puppyhood
- Prevention of pancreatitis in dogs
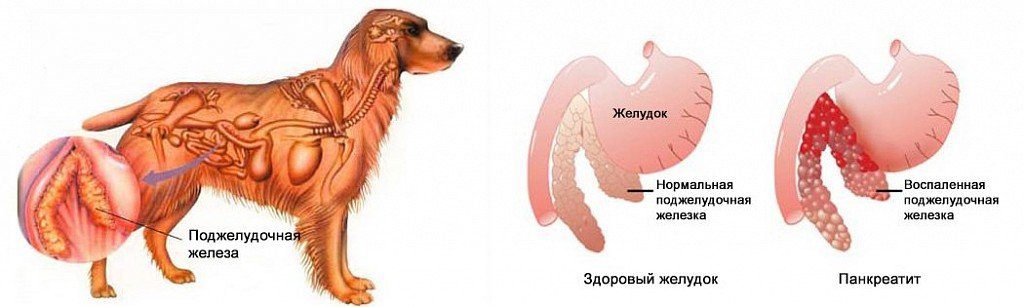
How does pancreatitis develop in dogs?
Under the influence of provoking factors, an inflammatory process occurs in the pancreas. The secretion of enzymes that ensure digestion in the intestine stops. Food is not digested and the supply of nutrients to the body stops.
Since the enzyme systems in the body continue their work, under the action of enzymes, the tissues of the pancreas itself are digested. This leads not only to its destruction, but also to the release of toxic decomposition products into the blood, poisoning of the body, and the development of numerous complications from the organs of other systems.
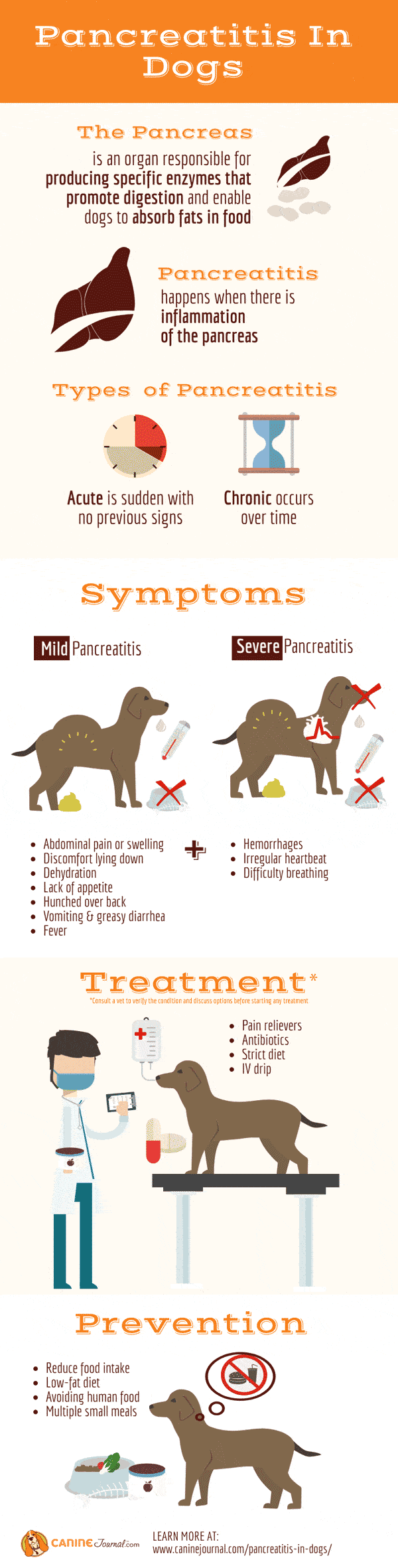
Types of pancreatitis in dogs
There are two types of pancreatitis in dogs.
- Primary. It occurs under the influence of provoking factors as an independent disease (for example, with malnutrition).
- Secondary. It is a consequence of existing pathologies, for example, hepatitis, helminthiases, neoplasms. This type of pathology is considered irreversible, therefore, it will be necessary to maintain the state of the dog’s pancreas at the desired level throughout its life.
According to the course of the disease, two forms are distinguished:
- acute pancreatitis – manifested by pronounced symptoms, characterized by intense decay of organ tissues, the development of necrosis (necrotizing pancreatitis), abscesses, sepsis, peritonitis;
- chronic – proceeds with subtle signs, gradually destroying the pancreas.
With timely access to a specialist, the likelihood of a pet recovering is quite high, especially in the acute course of the disease. The chronic form due to a mild clinical picture in most cases ends in death. Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis worsen and become noticeable when the animal has less than 20% of healthy tissue in the organ.
pancreatitis in dogs
Causes of inflammation of the pancreas
Among the many causes of pancreatitis in dogs, the most common can be noted.
- Too much fat in the diet
- Elevated blood lipids
- Lack of physical activity in the dog
- Infections in the body
- Liver Disease
- Pathology of the gallbladder
- Frequent use of a number of drugs (paracetamol, tetracycline and others)
- Obesity
- High blood calcium
- Sudden changes in diet
- Organ injury
- Low blood pressure for a long time
- Diseases of the small intestine
- Duodenal reflux
Pancreatitis can develop in any dog, but the following breeds are genetically predisposed to it: Miniature Schnauzers, German Shepherds, Poodles, Collies, Yorkshire Terriers, Cocker Spaniels, Boxers, Cavalier King Charles Spaniels.
How does pancreatitis manifest in dogs?
Symptoms of acute and chronic pancreatitis in dogs are different. The acute form, as a rule, begins with signs resembling an intestinal disorder, which gradually worsen. Chronic pathology manifests itself when the gland is severely destroyed.
Acute pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis
- Severe itching of the skin
- Refusal to eat
- Vomiting (sometimes even after drinking water)
- Abdominal pain
- Restless behavior, apathy
- Dehydration, dry mucous membranes
- Diarrhea
- Slight temperature increase
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath
- Heart rate increase
- Yellow tinge of mucous membranes
- Reducing the amount of food eaten, refusal to eat
- Enuresis
- Weight loss
- paw trembling
- Apathy, lack of interest in walking, playing
- Increased tone of the abdominal wall
- Gas formation
- Wool tarnishing
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostic measures, first of all, are aimed at eliminating a condition requiring urgent surgery. To do this, the veterinarian will prescribe the following procedures:
- laboratory blood test for enzymes, nitrogenous compounds, lipids, and so on;
- X-ray examination of the body;
- ultrasonography;
- ultrasonography;
- duodenography;
- gland biopsy.
If necessary, it is possible to conduct a laparoscopic examination of the organ.
Treatment for pancreatitis in dogs
The direction of treatment for pancreatitis in dogs is based on diagnostic data. At the moment, there is no drug in domestic veterinary medicine that could save the animal from suffering, so the therapy is symptomatic. In this case, the nutrition of the dog is of great importance – only with an appropriate diet, medications can have a therapeutic effect.
Medication Therapy
The prescription of drugs is determined by the symptoms.
Symptom
How to fix
Preparations
Pain syndrome
The use of antispasmodic and analgesic agents, often in the form of injections, is indicated.
No-Spa, Butorphanol
Vomiting
The animal is given antiemetics.
Cerukal, Ondansetron
Dehydration
Restoration of water-salt balance
Dextran 70
Increased production of hydrochloric acid
It is necessary to reduce the acidity of the secret
Omeprazole
Joining the infection
Prescribe a course of antibiotic therapy
At the discretion of the doctor
Operative therapy
In the presence of irreversible destruction in the tissues of the pancreas, surgery is indicated. During surgery, the doctor can clean the excretory ducts of the organ, excise cysts or ulcers.
Diet
Compliance with the diet during the treatment of pancreatitis in dogs is the key to improvement and recovery. A number of products are subject to exclusion from the pet’s diet:
- egg yolk,
- kefir, sour cream,
- sausages,
- Fried fish,
- raw vegetables,
- rye flour bread,
- cabbage,
- corn grits,
- rich broths,
- beans,
- fried and fatty meat.
When feeding an animal, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- give small portions;
- exclude smoked meats, fried and fatty foods, salt;
- food should be slightly warm;
- feed frequently, up to 6 times a day;
- avoid large and hard pieces in a bowl, bring food to a state of porridge;
- Make sure your pet always has clean water.
You can feed your four-legged friend with lean meat, buckwheat, millet porridge, adding chopped boiled vegetables and fat-free cottage cheese. If the pet is accustomed to industrial mixtures, then for pancreatitis you need to select a special food, for example, Royal Canin Gastro Intestinal Low Fat.
Complications of pancreatitis in dogs
In the absence of timely treatment, the inflammatory process in the pancreas in dogs can lead to serious consequences:
- necrosis of organ tissues, necrosis;
- intoxication of the body;
- blood poisoning;
- blockage of the bile ducts;
- peritonitis;
- diabetes mellitus and other consequences, up to the death of the animal.
First aid for an attack of pancreatitis
During an attack of pancreatitis, the owner, unfortunately, can do little to help the pet. First of all, you need to call a veterinarian or take the animal to the clinic. If a quick examination by a specialist is not possible, it is recommended to take the following actions:
- put an injection of No-shpy, carefully calculating the dosage of the drug;
- remove food, provide the dog with complete hunger;
- pour clean water into a bowl, preferably filtered, without chlorine;
- leave your pet in complete peace and quiet.
In no case should you give your pet “tested” medicines, use folk methods, try to feed. All subsequent actions are determined only after the diagnosis and identification of the cause of the pathological condition.
Pancreatitis in puppyhood
Puppies can also get pancreatitis, this is facilitated by various negative factors, most often infections. Predisposed to inflammatory processes in the pancreas are babies who are intensively fattened. Excess weight leads to a weakened immune system, malfunctions of internal organs, including the pancreas, and disorders in the digestive system. Puppies should be fed according to their age. Due to the imperfection of the enzyme system of the gastrointestinal tract, “adult” food does not suit them.
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis in puppyhood are the same as in adult dogs. If vomiting, diarrhea and other signs appear, the dog should be taken to the clinic as soon as possible for examination and first aid. The puppy’s body is not able to independently resist the disease, so the baby can die in a short period of time.
Preventing the development of chronic pancreatitis in a puppy is the primary task of the veterinarian and owner. During the rehabilitation period, the owner must strictly follow the specialist’s instructions: give the animal medicine in a timely manner, feed it in accordance with the diet, administer preventive vaccines, and so on.
Prevention of pancreatitis in dogs
The most important preventive rule is to provide your dog with a healthy and adequate diet. You can not give the animal food “from the table” or feed low-quality food. It is necessary to monitor the pet during the walk – released from the leash, he can pick up food leftovers from the ground. In addition, the dog should not be allowed to take food from strangers, in most cases it is something tasty, but forbidden.
The owner needs to add raw meat and vitamins to the four-legged friend’s food daily. If the animal is on industrial feeding, it is recommended to carefully study the composition of the feed in order to exclude the presence of harmful substances and an abundance of fat. It is forbidden to feed the dog fatty foods, sweets, salty, smoked and fried foods.
If it is known that the pet’s parents have suffered liver or pancreatic diseases, it is worth undergoing preventive diagnostics to identify the dog’s predisposition to pancreatitis. With positive results, periodic intake of a number of medications is recommended to maintain the activity and healthy state of the gland.
Prevention of pancreatitis in dogs will be the following measures:
- timely vaccination (will prevent the development of infection in the body);
- regular examination by a veterinarian;
- complete exclusion of self-administration of drugs.
Do not hope that the removal of symptoms will lead to a cure. Pancreatitis cannot be cured quickly and permanently: even if an acute attack is eliminated and a full course of treatment is completed, the slightest error in nutrition can provoke deterioration. Diet and attention from the owner will be required for a long period of time, and in the case of a chronic course of the disease – until the end of the dog’s life.