Dog poisoning: symptoms and treatment

Contents
What can poison a dog?
Conventionally, all toxic substances are divided into food and non-food. You can easily find some of these products in your apartment, while others can be eaten by a dog on the street.
Food poisoning
Animal metabolism is different from human metabolism. Some foods that are perfectly safe for humans are harmful to dogs. Therefore, try to keep your pet away from the following foods and substances to save his life.
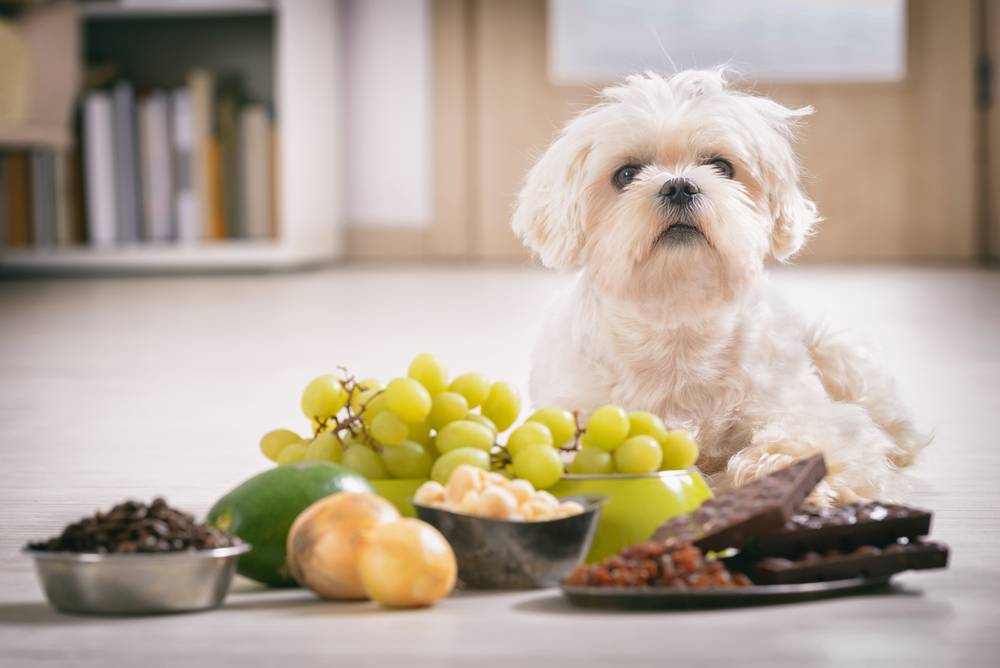
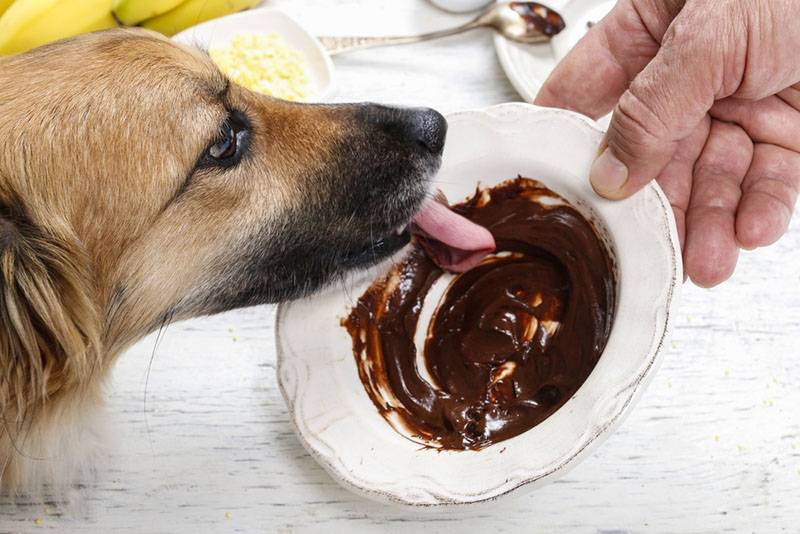
Chocolate
In products containing chocolate, there is a substance theobromine, which affects the cardiovascular, nervous, and respiratory systems.

Alcohol
Symptoms of alcohol poisoning in animals are similar to those in humans and include digestive disorders and breathing problems. In severe cases, death may occur.
Nuts
Nuts, including almonds, pecans, macadamia and walnuts, are high in oils and fats. This high concentration has the potential to cause pancreatitis or gastrointestinal (GI) upset.
Grapes and raisins
They contain a toxin that negatively affects the dog’s kidneys. Even a small amount of the product can cause kidney failure.
Xylitol
Such a sweetener is found in many foods: chewing gum, sugar-free candies, toothpaste, etc. Xylitol causes a rapid release of insulin, which leads to a drop in blood sugar levels. In animals, this manifests itself in the form of weakness, convulsions, liver failure.
Onion and garlic
Products contain substances that cause anemia, that is, a syndrome accompanied by the destruction of red blood cells directly in the bloodstream. In addition, a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract is possible.

Salt
It contains a lot of sodium ions, which in excess leads to increased thirst, electrolyte imbalance (balance of anions and cations) and a serious condition in a pet.
Non-food poisoning
This is a very large group of toxins found everywhere.
These include medical and veterinary drugs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
For example, such as Diclofenac, Ibuprofen and Naproxen. They cause serious toxic damage. Their use in dogs is contraindicated.
As for veterinary NSAIDs, if the dosage regimen is incorrect, they can also lead to poisoning.
Isoniazid
This is an anti-tuberculosis drug that dog hunters often add to baits. The mechanism of action of Isoniazid is that it disrupts the activity of the nervous system, affecting the transmission of nerve impulses.
pyrethrins and pyrethroids
Included in some veterinary preparations for fleas and ticks. They are neurotoxins, that is, they affect the brain. It is recommended to purchase funds without them.
Separately, it is worth mentioning breeds with the ABCB1 (MDR1) genetic mutation, which include collies, shelties, Australian shepherds (Aussies), whippets, and many others. They have a high sensitivity to certain drugs of various groups, manifested by neurological symptoms – convulsions.
Poisonous plants
The list of dangerous plants is quite extensive. Often eating them leads to damage to the gastrointestinal tract, but other organ systems can also be affected. The most toxic among them: azaleas, tulips, daffodils, sago palms, all spurges, aroids (diffenbachia, spathiphyllum, monstera, caladium), ficuses, aloe, etc.

Chemicals and household products
These include:
Rodenticides (rat poison). The mechanism of action of drugs is associated with impaired blood clotting, which leads to massive internal bleeding.
Heavy metals. Lead, found in paint, linoleum, batteries, causes neurological and gastrointestinal disorders. Zinc found in coins leads to severe anemia.
Fertilizers. They contain a variety of substances (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, herbicides, insecticides and fungicides) that cause damage to the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Household cleaners. Bleaches, detergents and disinfectants, if swallowed, often lead to damage to the gastrointestinal tract, and if inhaled, to burn the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
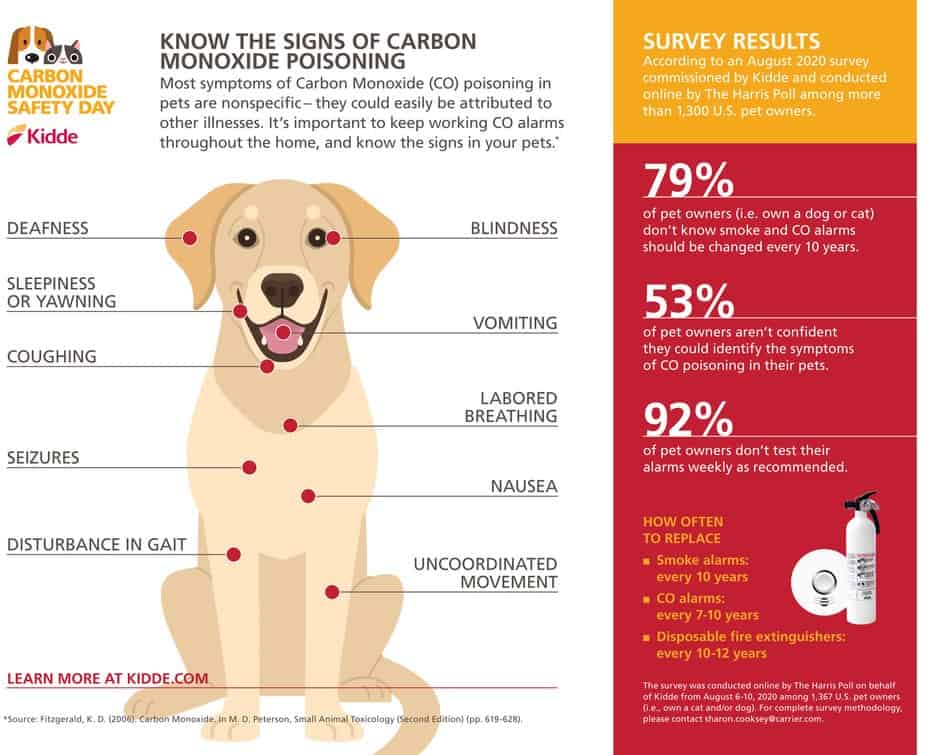
Signs and symptoms of food poisoning in dogs
Symptoms of poisoning a dog with poison will directly depend on the way it enters the body, as well as on the amount of the substance itself. Depending on the mechanism of action of the chemical compound, gastrointestinal, neurological, cardiac or respiratory disorders may be observed.
The following are the main signs of poisoning in dogs. But, it is worth noting that they are nonspecific, that is, they also appear in other pathologies:
Vomiting
Salivation
Diarrhea
Depression or vice versa restless behavior
Impaired coordination
Painful stomach
Decreased appetite.
Sometimes signs of poisoning progress to rapid breathing, fainting, convulsions, bleeding, etc. In the worst case, the death of the pet occurs.

First aid for a dog with poisoning
In this block, we will write down what to do if the dog is poisoned. It is important to act quickly, but rationally:
Stop the effect of the poison. Make a note of what was eaten and save any product information labels. This will help veterinarians make the right decision about treatment.
If the poison gets on the wool, wash it thoroughly and dry it.
Do not use home remedies as some medications for humans and other animals can be poisonous to dogs.
Do not try to make your pet vomit at home, as this will only make the situation worse in some cases.
It is better not to wash the dog’s stomach on its own at home, because sedation (drug sleep) is required for the quality of the procedure.
You should not offer water, as such unintentional actions will lead to faster penetration of the poison into the body.
Contact your veterinarian if poisoning is suspected. The sooner you seek help, the more likely your pet will be saved.
What to give a dog in case of poisoning
In case of poisoning, the dog can be given activated charcoal, which is sometimes used in veterinary medicine to absorb toxins. But it should never be given to animals that have ingested caustic materials or chemicals, or for heavy metal poisoning.
It is better to immediately contact a veterinary clinic and not try to provide first medical aid to your pet on your own.
Treatment of poisoning in dogs
The choice of treatment tactics will directly depend on the poison. For some of them, there are antidotes (antidotes): for example, in case of poisoning with rodenticides – vitamin K1.
When swallowing lead, copper objects, they are removed from the gastrointestinal tract. In case of chocolate poisoning, NSAIDs are used to induce vomiting or gastric lavage (it will depend on the time the poison enters the body), sorbents. However, there are situations in which induction of vomiting, gastric lavage is unacceptable. So, when swallowing alkalis, acids, heavy metals, due to the risk of aspiration (inhalation) or chemical burns of mucous membranes, inducing vomiting is contraindicated.
Despite the various types of toxins, in most cases, symptomatic therapy is used to maintain the vital functions of the body: intravenous infusions to stabilize the water and electrolyte balance and reduce intoxication, drugs that relieve symptoms – painkillers, antiemetics, anticonvulsants, gastroprotectors (antiulcer), etc. .
Symptoms for immediate hospitalization
When a dog has been poisoned, the alarming symptoms are: convulsions, lack of response to external stimuli, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing up blood, fainting, rapid breathing, or its complete stop.
Animal care after poisoning
Recovery will largely depend on what substance the dog was poisoned with and how quickly veterinary care was provided.
After stabilization of the pet’s condition, they will be discharged from the clinic home. He needs to be provided with peace, access to fresh water and the necessary nutrition. It is necessary to monitor the general condition and, if it worsens, immediately contact the veterinary clinic.
Diet
What can you feed a dog with poisoning, the veterinarian decides. In some cases, a special diet is prescribed to maintain a stable condition. So, for example, in case of damage to the kidneys or the gastrointestinal tract, medicated feed is used.
If the pet is not accustomed to ready-made veterinary foods, then it is necessary to draw up the correct natural diet with a veterinary nutritionist.
Prevention of poisoning
Prevention is always better than cure. These recommendations will help reduce the risk of poisoning in your pet.
Store all medications, chemicals, and cleaning products in resealable containers out of the reach of your dog.
Always follow the instructions for the medications you are using. Stick to the dosage and course chosen by your doctor.
Keep all used fertilizers, poisons (rodenticides) in places where your pets will not be able to find them. When using them, be sure to inform your neighbors so they can protect their pets from poisoning, and ask them to do the same for you.
When buying plants for your home, choose ones that are safe for dogs. If there are toxic ones among them, make sure that access to them is limited.
Home
Do not try to treat yourself! This is likely to aggravate the condition, and precious time will be lost.
It is not necessary to induce vomiting and / or force the animal to drink water. So you will only make it worse.
The chance of successful treatment is higher if the patient arrives at the veterinary clinic in a timely manner.
Symptoms of poisoning are nonspecific and can be confused with other diseases.
First aid includes stopping the effects of the poison on the body and immediately contacting a veterinary clinic.
Do not feed your dog from the table with foods that are harmful to him.
Keep all medicines, various chemicals out of reach. Dangerous plants should be out of the pet’s reach.
Answers to frequently asked questions about poisoning