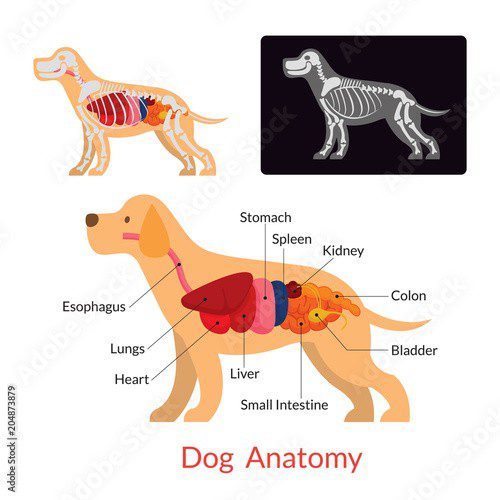
dog anatomy

There are over 400 dog breeds in the world today. And, despite external differences, from the point of view of biology, they have exactly the same structure. Even the French Bulldog and the Tibetan Mastiff, no matter how surprising it may sound.
Skeleton
The basis of any vertebrate organism (and the dog is no exception) is the skeleton. It helps animals move around and protects their internal organs from damage.
Skull. The skull of a dog is made up of twenty-seven bones. Moreover, the younger the animal, the more elastic they are: in older individuals, the connective tissue hardens, and the bones become brittle and brittle.
Scientists distinguish three types of skulls in dogs:
With the help of a movable joint, the lower jaw is attached to the skull. Adults have 42 molars. Puppies have fewer milk teeth – only 28, but all of them should appear by the age of two months. At three months, the process of changing teeth gradually begins, which ends by the year.
Dolichocephalic – elongated. It occurs in animals with an elongated muzzle – for example, in the Russian borzoi;
Mechophalic is normal. Three-quarters of the breeds have just this type of skull: huskies, sheep dogs, etc.;
Brachycephalic – shortened. Pekingese, bulldogs and others have this type of skull.
Bite. One of the most important external characteristics is the dog’s bite. This is not only aesthetics, but also her health, because the wrong position of the teeth can cause the development of numerous diseases.
Types of bite:
For most breeds, the most correct bite is considered to be a scissor bite, in which the lower incisors touch the inner surface of the upper ones;
A tick-like bite is considered a deviation from the norm, when the incisors rest against each other;
A more serious deviation is undershot, that is, the lower incisors do not touch the upper ones at all. Its danger lies in the fact that the molars quickly wear down;
The most serious pathology for many breeds is a bulldog bite, in which the lower jaw is moved forward. But for brachycephalic dogs, such a bite is the norm.
Torso. The basis of any skeleton is the spine. Like a human, it consists of interlocking vertebral discs to which ribs and other bones are attached.
The exterior of the dog is evaluated by the harmony of its addition, not only the skeleton is important here, but also the muscles. Most often, dog owners are faced with three types of deficiencies in the musculoskeletal system: defects in bones, joints and muscular apparatus. The reasons for their appearance can be both genetic and acquired as a result of diseases and improper care.
The cervical spine connects the trunk and the skull – these are seven vertebrae. Moreover, the first two vertebrae, the most mobile, like in all vertebrates, are called atlas and epistrophy;
The thoracic region consists of thirteen vertebrae – this is the basis for attaching thirteen pairs of ribs. In the region of the first ribs, the scapula, humerus, radius and ulna, as well as the hand, are attached to the body;
The loin is made up of seven vertebrae;
The sacrum or sacrum is three fused vertebrae. In many ways, it is the sacrum that determines the position of the dog’s tail. It is connected by a fixed joint to the pelvic bone. The pelvic limb consists of the pelvis, thigh, lower leg and foot;
The tail of a dog also consists of vertebrae, on average there are 20-23, but there are also cases when there are 15-25 vertebrae. The shape, size and fit of the tail depends on the characteristics of each breed.
senses
The major organ systems of a dog, such as the circulatory, nervous, respiratory, and digestive systems, are similar to those of humans. The biggest difference is the work of the sense organs. Dogs have six of them: smell, touch, balance, sight, hearing and taste.
Smell. Unlike a person who receives basic information about the world through sight, the main sense organ of a dog is the sense of smell.
Just imagine: in the nose of a person there are about 5 million receptors that help us distinguish between smells, and in the nose of a dog there are about 150 million of them! The sense of smell of hunting and service breeds is even better: such animals can find a trace that is several days old.
Vision. Despite the fact that the structure of the dog’s eye is similar to the structure of the human eye, the pet sees much worse. It is believed that puppies have the highest vision in the first year of their life, and then it begins to deteriorate. In the end, older dogs are practically blind. However, it has been proven that pets see much better than humans in the dark.
Hearing and balance. Like humans, dogs have an outer, inner, and middle ear. In the inner is the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for the balance of the animal.
Of course, a dog’s hearing is much better than a human’s. For comparison, the range of frequencies heard by pets is from 12 to 80 Hertz, while humans are able to hear vibrations with a frequency of 000 to 16 Hertz. By the way, dogs also recognize ultrasound.
Touch. The pet also receives information about the world around it through the organs of touch: skin and whiskers – vibrissae. With the help of skin receptors, he feels temperature and pain. And the vibrissae, located near the nose, eyes and on the paws, perform a tactile function. The dog can understand the location of objects without touching them, by air currents.
Taste. It is not known for certain whether dogs can taste. Probably, the animal judges the edibility or inedibility of an object by its smell. Research confirms this: while there are about 9000 taste buds on the human tongue, only 1700 on the dog’s tongue.
Understanding how pets are arranged allows you to more sensitively monitor the health of the animal.
It is also important to pay due attention to all changes in the behavior and well-being of the pet and seek the help of a veterinarian in time.
Photo:
October 29 2018
Updated: January 17, 2021