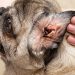
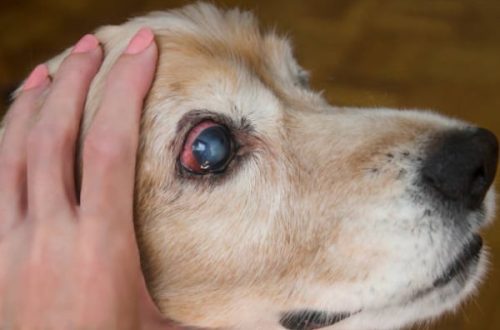
Dermatitis in dogs: types, causes, symptoms and treatment
Contents
Why does the disease develop?
Many factors lead to the development of dermatitis in dogs. Among the main reasons are:
- damage to the skin of varying degrees (insect bite, comb, wound);
- medicines (most often, these are external preparations used for a long time, for other purposes or in high concentration);
- thermal effect;
- infection of different origin;
- parasites (fleas, lice and others);
- internal disorders (often of an endocrine nature);
- allergies to internal and external influences (food, medicines, hair care products, and so on).
Often, dermatitis in dogs is a consequence of the simultaneous influence of several factors. For example, with a flea bite, bacteria enter the wound – an inflammatory process develops. The owner, without contacting a veterinarian, uses a drug that “always helps everyone.” As a result, the dog gets an allergy, the process is delayed, becomes chronic.
Common Symptoms of Dermatitis in Dogs
There are general signs of pathology that you need to pay close attention to:
- redness of the affected area;
- increased skin temperature in the area of inflammation;
- damage to the hairline (thinning or breaking of hair, thinning, complete loss);
- thinning of the walls of capillaries (leads to their damage and bleeding);
- itching;
- swelling of the damaged area;
- pain
In the future, the focus of inflammation increases in size, spreading to other parts of the body. There are ulcers, crusts, suppuration. The dog’s behavior changes, sleep and appetite are disturbed, immunity is greatly reduced.
Photo of dermatitis in dogs
Diagnostics
During the appointment, the specialist will not be limited to one examination of the dog. The owner will need to talk about the conditions of detention, nutritional habits, prescription and frequency of occurrence of the pathology. Laboratory diagnosis of dermatitis in dogs includes blood and urine sampling, scrapings from injury sites for microscopic and bacteriological analysis. If a microbe is detected, it will be necessary to conduct a test for its sensitivity to antibacterial agents, which in the future will serve as a guarantee of successful treatment.
Treatment of dermatitis in dogs
Based on the laboratory results obtained, the veterinarian determines the type of dermatitis in the dog, makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. The therapeutic plan includes:
- medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- preventive measures for the addition of a secondary infection.
Before starting treatment, the pet is given a primary treatment of the affected areas. As a rule, this is done in the clinic in the presence of the owner, so that later he can independently carry out such manipulations. The procedure consists in cutting the hair from the area (and around it), treating the affected skin with an antiseptic, followed by removing the softened crusts, and applying a bandage. If necessary, the animal is given an anesthetic or blockade with novocaine.
Medication Therapy
Drug therapy for dermatitis in dogs consists in eliminating symptoms, treating the underlying disease (for example, fungus, parasites), and increasing the animal’s immunity. To do this, use the following groups of drugs in different forms (drops, sprays, tablets, ointments, and others).
Antibacterial
Penicillins, cephalosporins and other groups
Take a course with mandatory pre-selection of dosage
Antifungal
Fungin, Zoomikol and others
Additionally, shampoos with antifungal action are prescribed.
Antiparasitic
Scalibor, Sanofly and others
If necessary, the treatment of the dog must be repeated
Antiallergic
Suprastin, Allervet
Relieve itching in any type of dermatitis
Diuretics
Furosemide
For removing toxins
Immunostimulants
Gamavit, Glycopin
Increase the activity of cells of the immune system
Physiotherapy
Among physiotherapeutic procedures, ultraviolet and infrared irradiation are popular. UV and infrared rays accelerate skin regeneration, kill pathogenic microorganisms, and strengthen local immunity. The combined use of physio and drug therapy contributes to a more stable therapeutic effect.
Traditional medicine
As an additional remedy for the treatment of dermatitis in dogs, traditional medicine can be used. Ointments, compresses and lotions based on chamomile, celandine, willow-herb, burdock, plantain will help to alleviate the course of the disease, reduce the severity of symptoms. For example, a compress based on raw potato gruel or a decoction of pear leaves, from which lotions are made, is popular.
To prepare a medicinal ointment from herbs, take 1 tbsp. l. the desired plants (for example, chamomile, Ivan-tea and plantain), mixed with hay dust in a volume of 400 ml, poured with boiling water, kept in the “bath” for 5 minutes. Cake is removed from the resulting broth, mixed with 15 g of butter and kept on fire until the mixture takes on a uniform consistency. After adding the same amount of glycerin, the ointment is ready for use. It should be applied to damaged areas of the skin four times within a month.
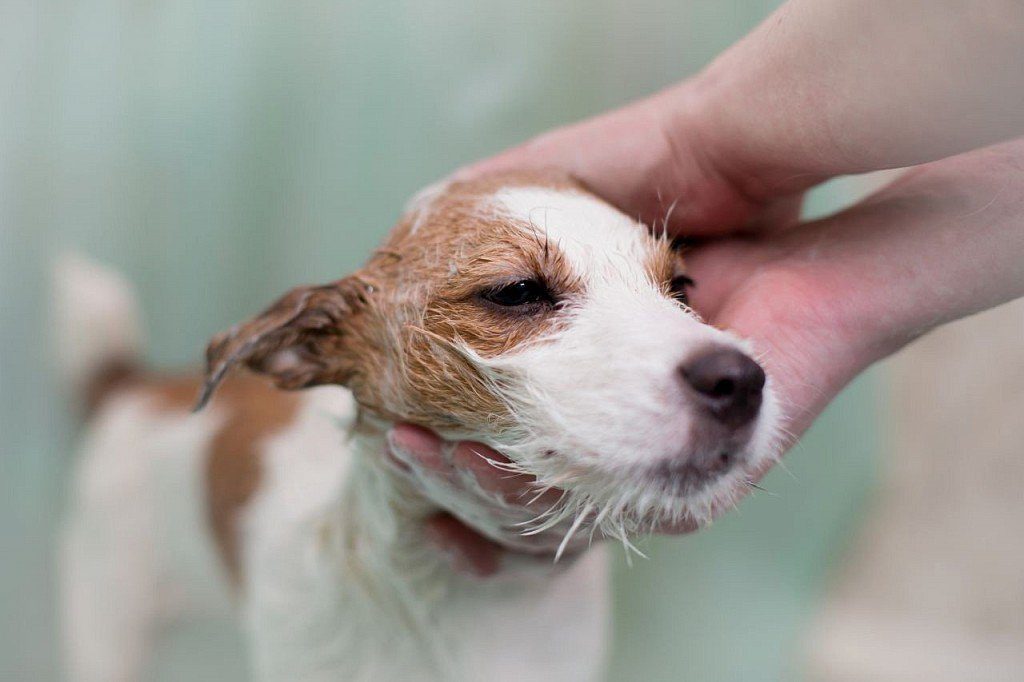

Regular hygiene measures as they get dirty are a good prevention of dermatitis
Treatment of dermatitis in dogs at home
It is rare that an owner manages to completely cure a dog of dermatitis on their own without visiting a clinic. However, if an appointment with a veterinarian is not possible in the near future, you can alleviate the condition of the pet by the following actions.
- Remove hair from the damaged area.
- Apply peroxide, wait until the dried scabs get wet. If there are no crusts yet or the stain is weeping, then remove excess peroxide with a dry swab, and then apply an ointment or cream with antiseptic properties, for example, salicylic emulsion.
- Itching with dermatitis is well eliminated by antihistamines. For example, you can give your pet a pill (having previously calculated the dosage) of Suprastin.
- If symptoms of intoxication are observed, furosemide should be given. The same drug will reduce tissue swelling with extensive lesions.
- Be sure to examine the pet for the presence of external parasites. If they are found, take appropriate action.
- Even if the dog’s dermatitis isn’t supposedly caused by a food allergy, switch it to a hypoallergenic diet – remove sweets, eggs, dairy products, and red vegetables.
- Replace your usual hair care products with ordinary laundry or tar soap.
If home treatment does not lead to improvement, then you should still try to find a way to contact the veterinarian.
The most common types of dermatitis in dogs
Since there are many causes of dermatitis and their combinations, the disease can be of different types. Each of them is characterized by its own, distinctive, symptoms and approaches to treatment. The most common types of dermatitis in dogs are briefly described below.
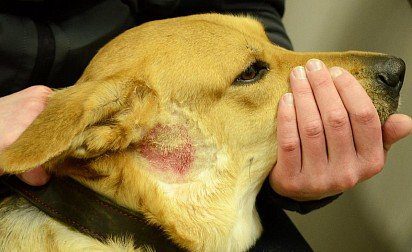
Pyotraumatic dermatitis in a dog
Pyotraumatic
In pyotraumatic dermatitis in dogs, the infection penetrates from the surface into the deeper layers of the skin, leaving behind plaques and a thickened stratum corneum. The deeper it penetrates, the more papules (pimples) and pustules (pustules) will appear on the pet’s skin.
Treatment is with the use of antibiotics.
Allergic
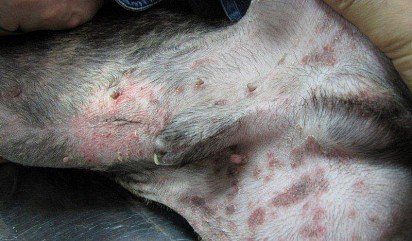
allergic dermatitis in dogs
Allergic dermatitis is considered the most common in dogs, since any object can serve as an allergen. Experts note that in most cases, skin allergies are provoked by external parasites, food and cosmetics for care. Among the symptoms: severe itching, redness of the skin, scratching, rashes, swelling.
The basis of treatment is the elimination of the allergen and symptomatic therapy.
atopic
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is one of the varieties of the previous form. The clinical picture is the same: dryness of the epidermis, rashes, very severe itching. Among the additional, characteristic signs, one can single out the development of otitis media and pododermatitis. Pathology develops mainly in dogs under 5 years of age with a similar heredity. It is noted that atopic dermatitis “loves” such breeds of dogs as: dachshunds, sharpei, bulldogs, setters, Dalmatians and a number of others. At the same time, anything can become an allergen.
Treatment consists in identifying and eliminating the allergen, conducting symptomatic therapy, and preventive measures to prevent otitis media.
Flea
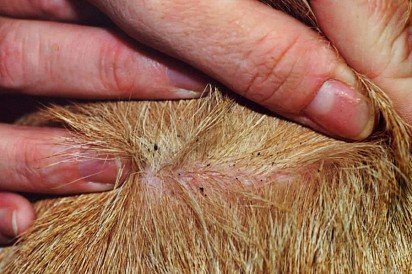
Flea dermatitis in dogs
The salivary secretion of fleas contains more than a dozen allergenic components that lead to flea dermatitis in dogs. The severity of symptoms depends on the individual susceptibility of the animal. Signs of pathology can be: alternating weeping areas and areas covered with crusts. In the chronic course of the disease, the pet reveals excessive skin pigmentation on the abdomen, hair loss. It is characteristic that the ears, muzzle and paws of the dog are almost not affected.
Treatment consists of getting rid of fleas and symptomatic therapy. Prevention is of great importance for recovery – the use of a collar from parasites, disinsection of the environment in which the dog lives.
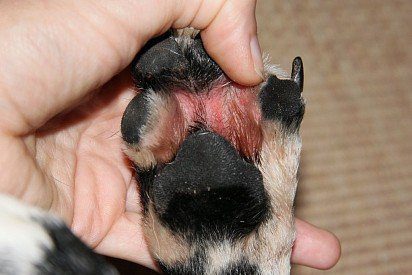
interdigital dermatitis in dogs
pododermatitis
Interdigital dermatitis in dogs, or pododermatitis, develops between the fingers of the animal, mainly on the forelimbs. If the lesions are single, it can be assumed that the disease is provoked by a wound. With extensive damage to the limbs, insects, allergies, and infections can become the cause. Symptoms: bleeding nodules, boils, pain leading to lameness.
Treatment is symptomatic.
Seborrheic
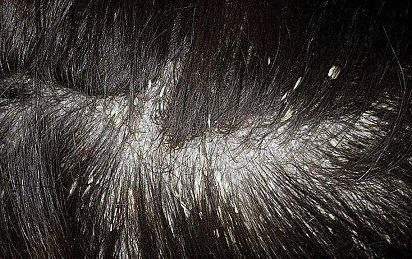
seborrheic dermatitis in dogs
Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by genetics. With this disease, the process of keratinization of the skin is accelerated, which is visually manifested in numerous scales, oiliness of the epidermis, but dry hair. The pet may have brittle nails; the inflammatory process on the skin is clearly visible, accompanied by severe itching. In the future, the disease is complicated by a secondary infection with all the ensuing consequences.
Treatment is carried out in two directions: local therapy and a systemic approach.
Akralny
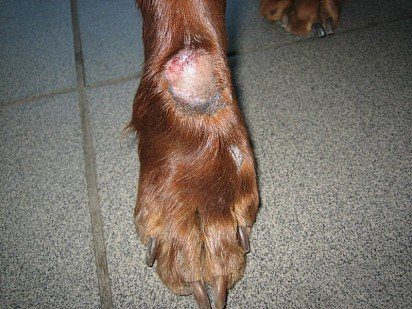
Acral dermatitis in a dog
Symptoms of acral dermatitis are hard, ulcerated patches of skin resulting from excessive licking of the area by the dog. Pathological behavior of an animal can be caused by allergies, parasites, infection and other factors that must be detected and eliminated before the skin can be treated.
Treatment consists in the initial elimination of the provoking factor, and the therapeutic effect on the damaged epidermis. Of great importance is the restriction of the pet’s access to the itchy place. In addition, antidepressant and psychotropic drugs are used in therapy.
Prevention of dermatitis
In many cases, the development of dermatitis in dogs can be avoided. The main preventive measure is the proper care of the pet’s coat and skin:
- regular hygiene measures as they get dirty;
- combing, preventing the wool from rolling;
- selection of combs in accordance with the characteristics of the animal;
- regular inspection for the presence of parasites, their removal if detected.
Proper nutrition will help prevent dermatitis, as well as deworming the dog every three months. In addition, a preventive measure will be a timely appeal to the veterinarian if any pathology is detected, and not an independent choice of medicines.