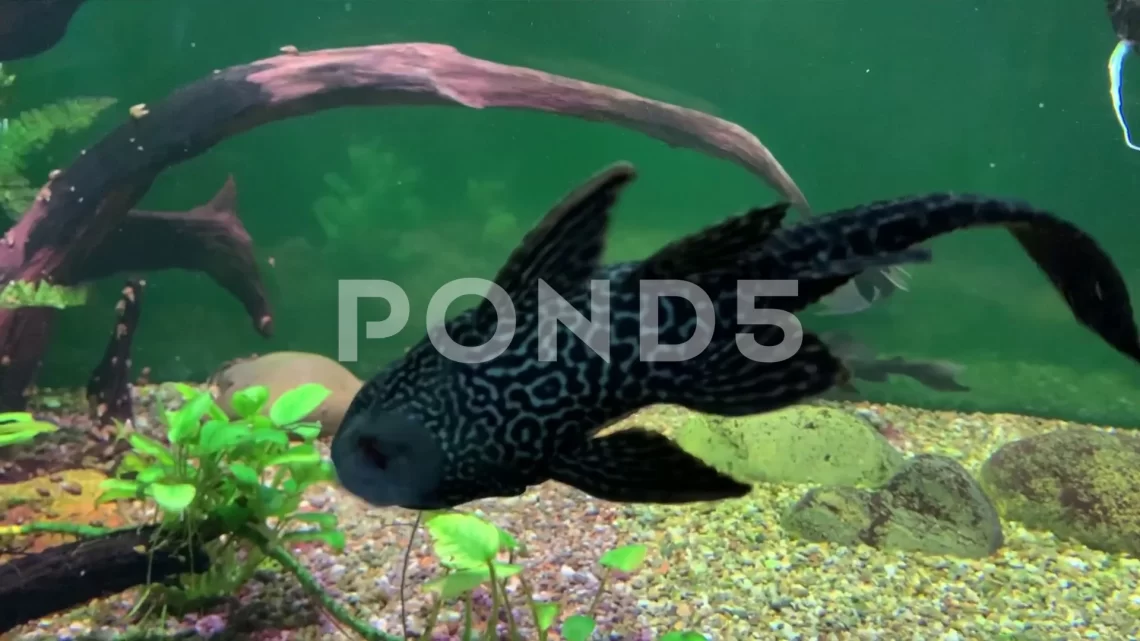
Brocade pterygoplicht – features of care and maintenance, compatibility with other fish and other features + photo
Some aquarists like nocturnal fish: sleeping during the day, active at night. But it is difficult to keep track of such fish, because they are awake when a person is sleeping. One of these fish is the brocade pterygoplicht. To figure out how to properly care for him, you need to study in detail the nature and needs of this fish.
Contents
History and features of the brocade pterygoplicht
Brocade pterygoplichthys (Pterygoplichthys gibbiceps) is a freshwater ray-finned fish (chain catfish family). It was first described by Kner and Günther in 1854. This species was assigned to pterygoplichts in 1980. And in 2003 it was classified as a glyptoperichthy. This chain mail fish is called differently: catfish, leopard glyptopericht, pterik, etc.).
Pterik is a strong, strong fish. Omnivorous, but feeds mainly on algae, so 1-2 fish can keep a large capacity aquarium clean. Since the catfish has a bottom lifestyle, it does not neglect carrion (in its natural habitat).

Brocade catfish love to lie on stones
This catfish is native to South America. Like other catfish, it occupies the shallows of rivers (Amazon, Orinoco, Xingu, etc.). Likes slow currents and flooded areas of land. If the dry season comes, then the catfish hibernates. For sleep, he chooses caves where he can hide in the mud. At the moment, many varieties of pterygoplicht are sold in pet stores (up to 100 species).
Appearance Description
Pterik is a large fish. In the natural environment, it can grow up to 50-60 centimeters. Such catfish are recognized as long-livers (life expectancy is more than 20 years). In aquarium conditions, the pterik lives up to 15 years. Its size depends on the volume of the aquarium. Pterygoplichts come in a variety of colors. The body of the fish is slightly flattened from above and covered with hard plates, for which the catfish was called chain mail. The belly of such a fish is smooth, without coating. Brocade catfish is distinguished by its high dorsal fin (length – up to 15 centimeters, consists of 10 or more rays). The eyes are high on the head.
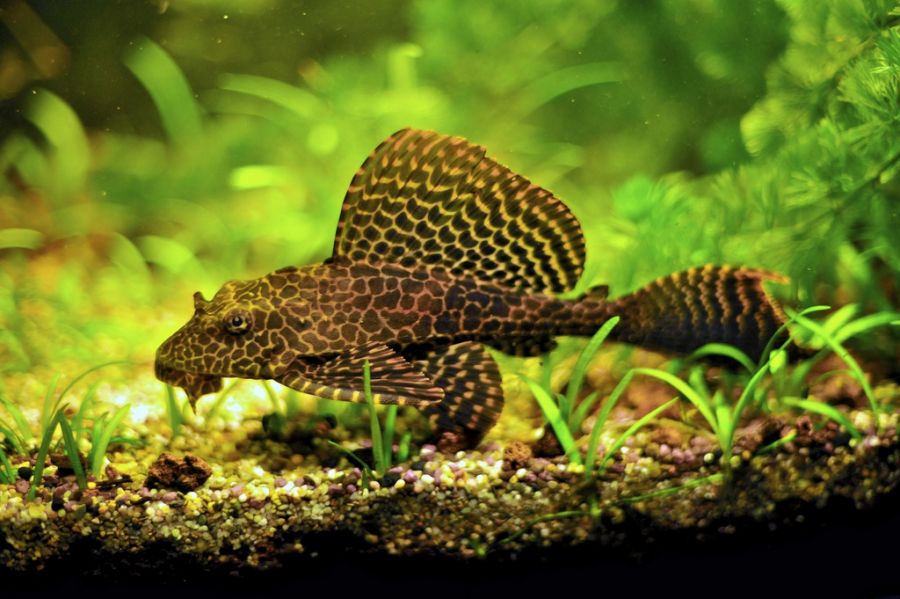

The muzzle of the catfish is flattened, elongated
By the way, young brocade catfish look very similar to adults. On the muzzle of the pterik there are large voluminous nostrils. The head is long (the length of the head is equal to the length of the first ray on the dorsal fin). The body color is brown, with lines and patterns of lighter tones (yellowish, gray and other shades). The pattern is very similar to the color of a leopard. The spots are larger on the body than on the head and fins.
The color and pattern on the body of the fish may change with age. Also, these changes are affected by the conditions of detention. The nature of fish is arranged in such a way that they adapt to the environment in which they live.
The mouth of the fish is in the form of a sucker. Catfish can cling so strongly to something that it will be difficult to safely tear it off. At the bottom of the mouth is an oblong skin fold, the edges of which smoothly pass into the antennae.

The eye of a catfish (except for the pupil) can also be spotted
Determining the sex of this fish is not easy, but possible (even at a young age). The size of the male is always slightly larger, and his fins are longer. In addition, the pectoral fins of the male have spikes, while the females do not. The color of the females is slightly duller. Professional aquarists can distinguish between female and male pteriks by sex (adult females have a genital papilla).
Varieties of pterygoplichtov
The most popular among spotted catfish lovers are red, golden and leopard pterygoplichts. But there are other equally beautiful subspecies that are popular with aquarists:
- reticulated pterygoplicht (Pterygoplichthys disjunctivus);
- Joselman’s pterygoplichthys (Pterygoplichthys joselimaianus);
- yellow sailing pterygoplichthys (Pterygoplichthys weberi);
- brocade pterygoplicht (Pterygoplichthys gibbiceps).
These catfish can be distinguished not only by experienced aquarists, but also by amateurs.
Table: main differences between subspecies of pterygoplicht
Photo gallery: different subspecies
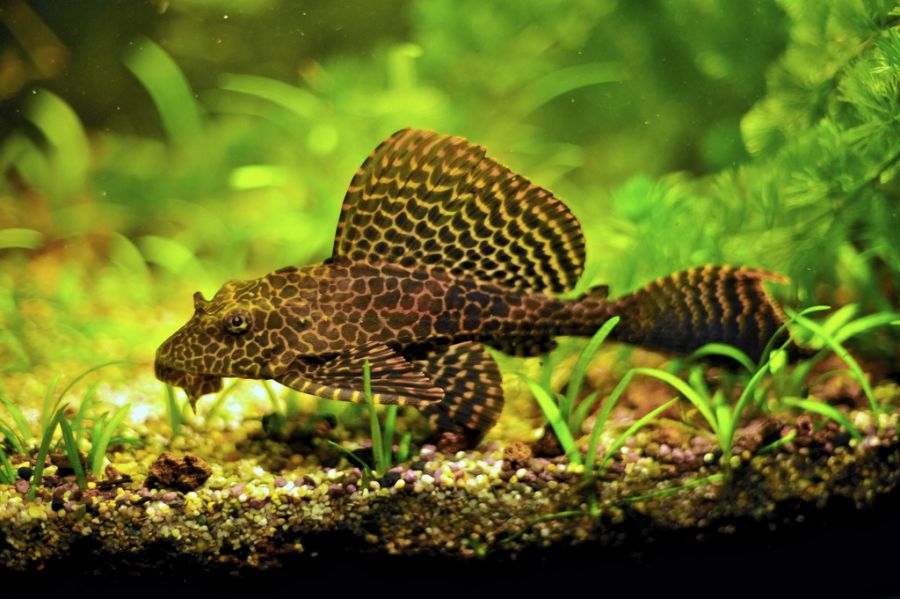

The pattern on the body of the brocade catfish is speckled, similar to brocade

Leopard catfish have a large pattern (black blurry spots on a light background)
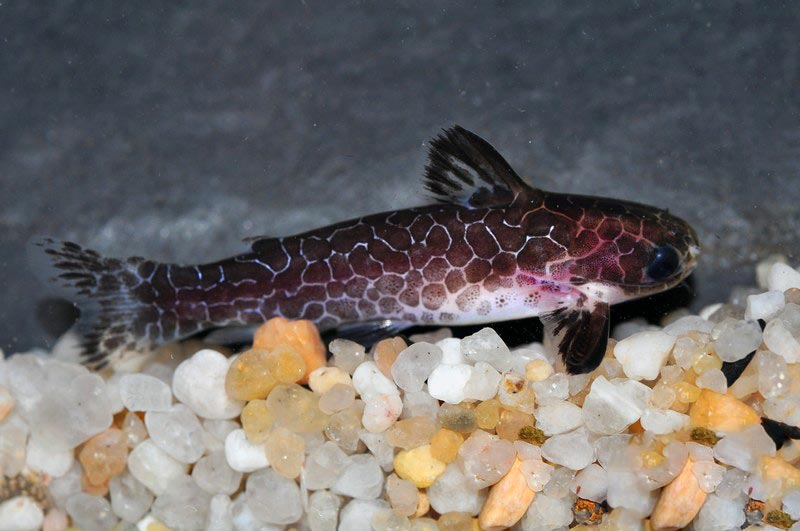

The pattern on the body of a reticulated catfish resembles a honeycomb

The yellow pterygoplicht is easy to distinguish from other catfish by the shape of the tail and the geometric patterns on the tail.

A distinctive feature of Pterygoplicht Yoselman is the shape of the spots (reminiscent of peanut pods)
How is pterygoplicht different from other species
Pterygoplichts are sometimes confused with other bottom fish species. This is used by unscrupulous breeders. However, if we take a closer look at catfish, we can notice the characteristic features for each individual species. Most often, the pterik is confused with the plecostomus (Hypostomus plecostomus).
The easiest way to distinguish these fish is when they lie at the bottom of the aquarium. In plecostomus, the antennae are thin and long, while in pteric they are cone-shaped. Also, Plecostomus does not have such a pronounced skin fold as in Pterygoplicht. You can also pay attention to the rows of small spikes along the body of the fish. There are two such rows in brocades, the upper one begins at the height of the eyes, and in plecostomuses only the lower row, which begins at the level of the pectoral fin, is clearly visible.

In plecostomus, you can see a line of spines on the side of the body
Catfish stuck to the transparent wall of the aquarium are distinguished by their whiskers. In plecostomus, the antennae are filiform, almost colorless, while in the pteric, the antennae are thick, dense. In addition, the gill covers of Pterygoplicht are brightly colored, which cannot be said of Plecostomus.
Brocade catfish is also confused with ancistrus (Ancistrus). Some amateur aquarists keep these fish in the same aquarium and may not notice the difference between them for several years. It is difficult not to confuse them without certain knowledge, especially if the fish are of a similar color. But you can distinguish them by the shape of the body and other details. If the age of the fish is approximately the same, then the difference will be in size. In pet stores, you can find young Ancistrus about 2 centimeters long, and Pteric – 3-4 centimeters. And there is also a bright spot above the tail of the ancistrus, while the pterygoplicht does not have such a feature.
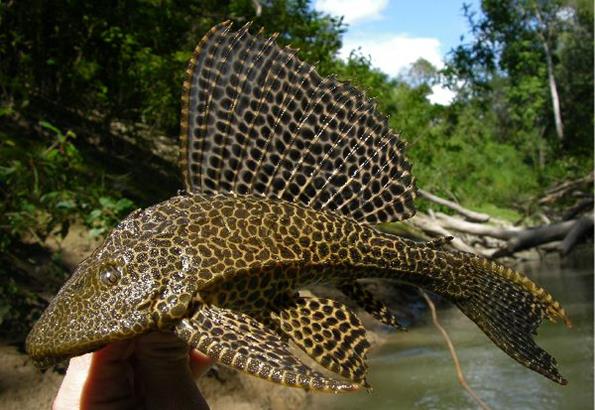

If you look closely, you can see that the body of the fish and the tail are, as it were, separated by a light transverse stripe.
In addition, brocade catfish have more open fins and a clear, “hard” outline. Ancistrus look softer, body shape is more streamlined.
Features of maintenance and care
Brocade pterygoplichts look very bright and spectacular, for which they are very fond of aquarists. By nature, these catfish are peaceful, but they can conflict with relatives. The cause of disputes is the struggle for leadership. Pteriks are active in the dark, and in the light of day they hide under snags and leaves of plants. Catfish needs a large aquarium (1 brocade catfish – 200 liters). The fact is that a pterik will not grow in a small aquarium. The organism will try to grow, but there will be little space. As a result, dystrophy can develop, and this is detrimental to fish and reduces life expectancy. In addition to size, some tricks also affect the growth of catfish.
The only way to get a fast enough growth is high (28 degrees) water temperature and frequent changes, combined with abundant (2 times a day) feeding. The food contained spirulina, krill, seafood fillets, etc., and the pterik ate everything for 4 young Astronotus. I didn’t stop cleaning the walls.
Alexander Kharchenko, owner of pterygoplicht
In brocade catfish, the circulatory system of the intestine is arranged in such a way that they can also absorb atmospheric air. If the fish does not have enough air, the catfish emerges and swallows an air bubble with its mouth. Nevertheless, you need to filter well and supply oxygen to the water. Aeration (air saturation) and filtration can be arranged using special devices that are sold at any pet store. In addition, it is very important to equip the aquarium with all kinds of shelters (grottoes, caves, etc.). If it is not possible to install such “houses”, then you need to take care of the presence of broad-leaved algae (catfish can hide in their shade).
Video: brocade catfish in a cozy aquarium
Water parameters
In the wild, pterygoplichts live in rivers, so they are used to gentle movements of water. Weak flow can also be done with a filter. Ichthyologists recommend mandatory water parameters:
- temperature — 24–30 °C;
- alkalinity – 6,5–7,5 pH;
- medium hardness.
It is also important to change the water at least once a week. A major water renewal is not necessary, it is enough to replace a quarter of the volume. Brocade fish themselves choose a comfortable place, so special lighting is not required. You can install a lamp for other fish, and the catfish will adapt to the proposed conditions.
Feeding rules
Aquarium catfish eat everything. In addition to algae, fish can eat simple plant foods:
- nettles;
- spinach;
- carrot;
- dandelion.
The body of catfish is designed so that they can also consume animal protein:
- earthworms;
- bloodworms;
- shrimp.
The correct balance of minerals and vitamins is observed in ready-made dry food for bottom fish. Brocade fish can also eat other fish. This is not a consequence of aggression, just a catfish sees food in a slowly swimming fish. Most often, discus and angelfish (flat and slow) lose scales from catfish suckers. The ideal diet for brocade catfish is a combination of carbohydrates (70–80%) and proteins (20–30%). If the pterygoplicht was taken already grown up, then there is no need to drastically change the usual diet for the “right” food. Otherwise, he may refuse food.
In addition, any fish may not take food that is unusual for it. For example, a ptera was fed with a bloodworm, and you give him pills – he may not eat. Maybe not eat for a long time.
Roman, an experienced aquarist
Due to the nocturnal lifestyle, the pterik eats little during the day. Therefore, if you spoil the fish with goodies, then you can give, for example, frozen live food for the night. Everything that will not be eaten, including other fish, will settle on the ground. At night, the catfish will pick up the leftovers and eat. Some brocade fish, having reached adulthood and increased in size, begin to pull out even large plants. Therefore, you need to install algae with a strong root system.
If you like delicate algae with weak roots, you can plant them in pots. At the bottom of the dishes you need to make small holes so as not to close the space. After transplanting, the soil in the pot should be sprinkled with pebbles. The entire pot must be wrapped with a fine mesh (for example, a mosquito net), leaving a hole only for the plant to exit. Catfish cannot bypass such a trick.

Coconut shells are a convenient substitute for driftwood
Catfish really need snags. Such elements are overgrown with small algae, and pterygoplichts eat them. This top dressing will not replace a full meal, but is important in the diet. Brocade and other catfish receive the necessary trace elements from these algae, which affects the functioning of the digestive system, color brightness and immunity in general. Bottom fish are very slow, so they often do not eat up (other fish swallow all the food). Therefore, you need to make sure that all the other inhabitants of the aquarium are full, and after that pour some more food. Satiated fish will ignore the new supply of food, and the catfish will eat calmly. You can determine malnutrition by examining the belly of the fish (a dense, rounded belly indicates satiety).
Compatibility with other fish
In the wild, if the catfish is in danger, it spreads its fins to become larger in size and the enemy could not swallow it. During hibernation, the pterik, buried in the mud, hisses. So nature provided for the catfish “alarm”, which is triggered when the fish is sleeping and has poor control over what is happening around. In an aquarium, such a critical danger does not threaten the fish, so conflicts arise only between males of any kind of catfish. The fish spreads its ray-finned fins in order to intimidate the opponent.
If two catfish of the same species do not conflict, they may be of different sexes.
Since the pterygoplicht can grow up to half a meter, the neighbors must match its size. Cichlids, gourami, polypterus, etc. can be attributed to “convenient” neighbors. However, catfish cannot be added to absolute vegetarians. The catfish will eat or pull out everything it can, and the herbivorous neighbor will starve.
Pterygoplicht is distinguished by its meek disposition and friendliness. But sometimes disputes between fish can arise in cases where an already grown catfish has been planted in a common aquarium. Males of even other species can see a future rival in a newcomer.
Video: cichlid fish attacks new pterygoplicht
A pteric may ignore or fear a person, but over time, the fish will get used to the one who provides food. If a catfish lives with one person for several years, then over time it will be given into hands.
Breeding
At the age of three, the brocade catfish will become sexually mature. Often, aquarists, knowing this, begin to prepare for the addition (they buy another catfish of the opposite sex, prepare a jigger, etc.). But at home it is almost impossible to breed pterygoplichts. The fact is that in the wild, the female lays eggs in burrows. The recesses in the ground should be silty and of such a size that an adult male can hide in them (he guards the eggs).
Therefore, all the fry that are sold in Russian aquashops are brought from fish farms. Breeders place pairs of brocade catfish in specially equipped ponds with a muddy bottom and soft ground. There are commercial pterygoplicht farms in America, Australia, and southeast Asia.
Pterygoplicht diseases
Brocade catfish is a fish resistant to various kinds of ailments. But if the conditions of detention are violated (poor nutrition, lack of driftwood, dirty water, etc.), the immunity of the fish may weaken. The most common health problems in catfish are digestive disorders and infectious diseases.
Bottom fish are predisposed to infection with protozoa. But a healthy pterygoplicht does not get sick just like that, so it is important to maintain the immunity of the fish (proper nutrition, cleanliness of the aquarium, etc.). Catfish can get sick with ichthyophthyroidism (colloquial – “semolina”), the causative agent of which is the infusoria shoe. If the water is not changed for a long time and other conditions of detention are violated, then the infection can be transmitted to other inhabitants of the aquarium. This sore is brought in with new fish (so you need to remember about a three-week quarantine for beginners). You can detect the disease by white spots on the body of the fish. If your pterik is covered with “mold” in places, you need to urgently go to the veterinarian. The prescribed medicine will need to be given by planting a sick fish in a separate container.
If there is only one spot and has recently appeared, then you can try to cure the catfish yourself. To do this, the temperature in the aquarium (jigging tank) is raised to 30 °C. The water is made slightly brackish. It is hoped that the causative agent of the disease will not survive the drastic changes and leave the body of your pet. If that doesn’t help, go to the vet immediately. It is important to treat pterygoplicht, because, despite their size, catfish, like other fish, can also die from the disease.

If the fish lies limp and does not move, it may be sick
Inexperienced aquarists may think that unpretentious bottom fish need not be looked after, but this is not so. If the conditions for keeping the catfish are violated in any way, the fish will get sick, and this will manifest itself in the form of symptoms:
- behavior has changed (hides even at night, beats against the walls of the aquarium, etc.);
- the body or individual parts have brightened (abdomen, fins, back);
- catfish looks emaciated (lost weight, sunken mouth, etc.);
- whitened or bulging eyes;
- holes appeared between the rays of the fins or the fins look “tattered”;
- a light film appeared on the surface of the water, light flakes appeared in the water (not from food) or light threads of mucus “hang”;
- the fish lost its appetite;
- the pet lies at the bottom.
Pteriki most often get sick from the accumulation of organic matter. Metabolic products, remaining in the water, cause an increase in the level of harmful substances (nitrites, ammonia, etc.). But one should not despair and put up with such a state of affairs. There are various quick tests on the market that you can use at home (you don’t have to buy expensive ones).
You need to choose tests to recognize different salts (nitrites, nitrates), chlorine and pH levels at once
Each test comes with instructions. So you will understand what exactly rolls over. One of the ways to deal with a harmful substance is air conditioning. These are special additives that can neutralize the poison. The air conditioner is selected for use in a specific volume of water. You also need to replace part of the water (1/4). This also requires air conditioning (for example, Akutan or Aquasafe). New water must be treated with this agent, if necessary, heated to the desired temperature and poured into the aquarium. If it is not possible to buy such an additive, then you can treat the water in a more troublesome way (boil and cool).
When the water returns to normal, the immunity of the catfish will begin to recover. Then there will be a chance that the fish will recover. Pterygoplicht usually swims low, touching the ground with its fins. If the pectoral fins do not move, and the fish just lies (and does not eat anything), the owner begins to panic. In addition to the reasons listed above, this catfish behavior may be due to stress. For example, when a pterik is new to an aquarium with other fish (or a catfish has a new aquarium). If all the conditions of detention are normal, then you can wait a couple of days. When the brocade gets used to the new conditions, it will definitely start to swim and eat.
Brocade pterygoplicht is a catfish whose body is covered with hard plates. These fish eat vegetable and protein foods, lead a bottom lifestyle and do not sleep at night. Pterygoplicht can live up to 20 years in aquarium conditions.