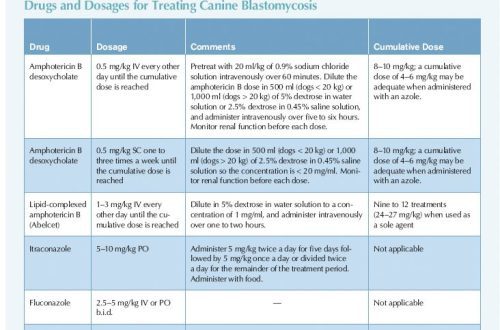
Babesiosis in dogs: diagnosis
Diagnosis of canine babesiosis is based on taking into account the epizootic state, season of the year, clinical signs, pathomorphological changes and the results of microscopic examination of blood smears..


Decisive in the diagnosis are the positive results of microscopic examination of smears of peripheral blood. When staining blood smears according to Romanovsky-Giemsa, Babesia canis can have a different shape: pear-shaped, oval, round, amoeboid, but mostly they find a para-pear-shaped form of the parasite (A.A. Markov et al. 1935 T.V. Balagula, 1998, 2000 S. Walter et al., 2002). All forms can be associated differently in one erythrocyte. Also, according to the literature data, diagnostics can be carried out: RDSC, RIGA (X. Georgiou, 2005), ELISA, etc. A frequently used method of serological diagnostics is the enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) and its modifications (slide-ELISA, two-site ELISA, sandwich-ELISA). This method is often used in various modifications. Its advantages are the ability to store the constituent materials for this method for a long time, ease of setup, a minimum of instruments used in setting up the reaction, the ability to evaluate the results in the optical range, as well as visually. In recent years, PCR has begun to be used in studies on canine babesiosis. With this highly sensitive test, it has become possible to determine the genotypic relationship between Babesia species and determine the taxonomic position of the parasites of this genus.
Babesiosis is differentiated from leptospirosis, plague, infectious hepatitis.
With leptospirosis, hematuria is observed (erythrocytes settle in the urine), with babesiosis – hemoglobinuria (upon standing, the urine does not clear), bilirubin protein is also present. In the urine sediment, mobile leptospira are detected using the “hanging drop” method. With plague, lesions of the digestive and respiratory systems, conjunctivitis and lesions of the nervous system come to the fore. Infectious (viral) hepatitis occurs with persistent fever, anemic and icteric mucous membranes, urine is often light brown due to the presence of bilirubin.
See also:
What is babesiosis and where do ixodid ticks live
When can a dog get babesiosis?
Babesiosis in dogs: symptoms
Babesiosis in dogs: treatment
Babesiosis in dogs: prevention