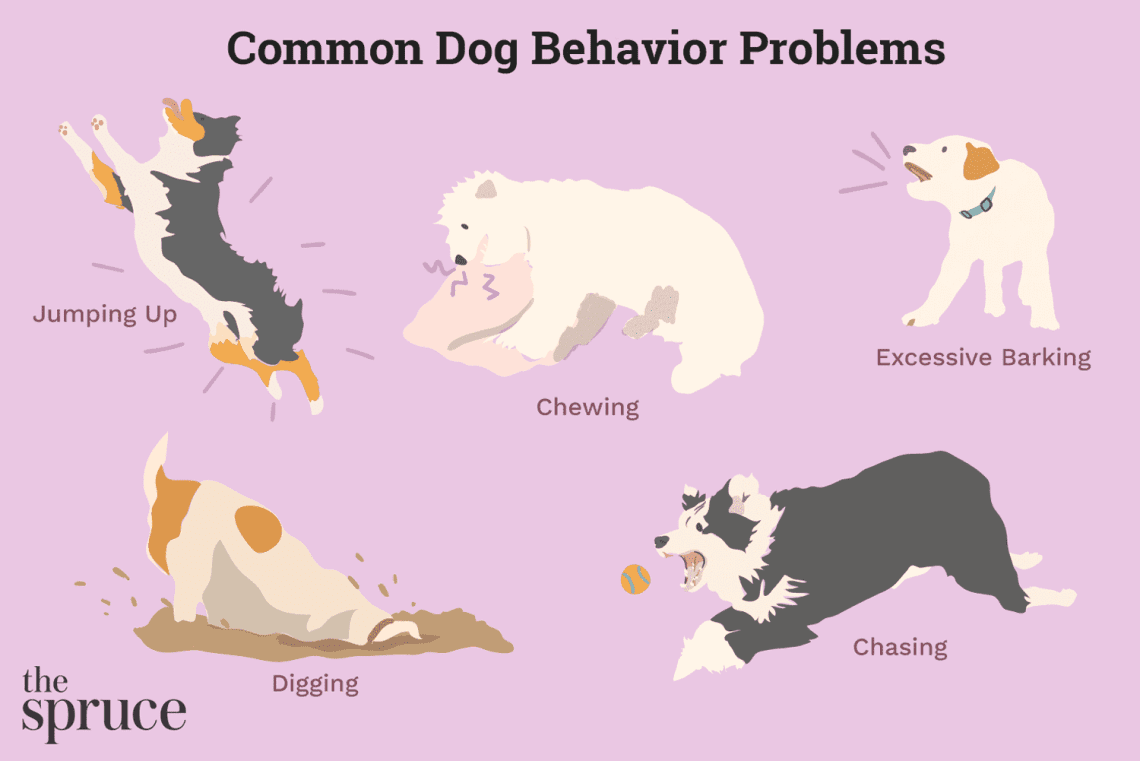
8 Common Dog Behavior Problems
excessive barking
Dogs make various sounds: they bark, howl, whine, etc. But mostly the owners are worried about the pet’s barking too often. Before you can fix it, you must determine why your dog is constantly barking.
The most common causes of barking are:
The dog wants to warn you about something;
The dog is trying to get your attention;
This is how her playfulness manifests itself;
Something is bothering her;
She’s just bored.
What to do?
Learn to control excessive barking. Together with the dog handler, try to teach your pet the “Quiet” and “Voice” commands. Be consistent and patient. Eliminate the root causes of barking.
Spoiled things
Dogs need something to chew on, this is normal. But if instead of special chew toys, the pet gnaws on your things, then this can become a serious problem.
Most often, a dog chews on things because:
She is teething (this applies to puppies);
She is bored and has nowhere to put her energy;
Something is bothering her;
This is how curiosity manifests itself (especially in puppies).
What to do?
Buy plenty of chewable toys and praise your dog when he plays with them. When you leave your dog alone at home, limit his movement to areas where there are the fewest things that he can ruin.
If you catch a pet at the moment when he nibbles on something inappropriate, stop him with a sharp sound and replace this item with a toy. And, of course, walk more and play with your pet so that he directs his energy in a peaceful direction and does not make a mess in the house out of boredom.
excavated earth
Some dogs (like terriers) love to dig in the ground, following their hunting instinct. And if your pet spoils the lawn in your country house, then, of course, you will not like it.
As a rule, most dogs dig the ground for the following reasons:
Boredom or excess energy;
anxiety or fear;
hunting instinct;
The desire for comfort (for example, to cool off in the heat);
Wanting to hide things (such as bones or toys)
An attempt to escape.
What to do?
Try to determine the cause of the excavation, and then try to eliminate it. Spend more time with your dog, play with it and train it. Alternatively, you can designate a place where the dog can dig, and only allow it to do so there.
separation anxiety
This problem manifests itself in the following: as soon as the owner leaves the dog alone, she begins to howl, gnaw things, go to the toilet in the wrong places, etc.
How to understand that all these negative manifestations are connected precisely with the fear of separation?
The dog begins to worry when the owner is about to leave;
Bad behavior occurs in the first 15–45 minutes after the owner leaves;
The dog follows the owner with a tail.
What to do?
This is a serious problem that requires work with a specialist – it is best to consult with an animal psychologist to correct this behavior.
Urination and defecation in the wrong places
It is very important to discuss this with your veterinarian first to rule out health problems. If the reason is still not medical, try to determine why the pet is behaving this way. This is usually associated with something from this list:
Urination due to overexcitation;
Territorial behavior;
Anxiety;
Lack of proper upbringing.
What to do?
If this behavior is observed in a puppy, then this is normal, especially under the age of 12 weeks. Older dogs are a completely different matter. It is worth consulting with a zoopsychologist to correct such undesirable behavior.
begging
This is a habit that dog owners themselves often encourage. But you should not do this, because begging can lead to digestive problems and obesity. Dogs ask their owners for food because they love to eat, not because they are hungry. However, the leftovers of your food are not a treat, and food is not love. Of course, it can be difficult to resist a pleading look, but even giving in “just once” will create problems for you in the long run. So the dog will understand that she can beg, and it will be extremely difficult to wean her from this.
What to do?
Every time you sit down at the table, send the dog to his place – preferably somewhere where he cannot see you. Or close it in another room. If the dog is behaving well, treat him only after you have left the table.
Jumping
Jumping is a common and natural behavior for dogs. Puppies jump up and down to greet their moms. Later, they may jump up and down to greet people. But when the puppy becomes an adult, his jumping on people can become a serious problem.
What to do?
There are several ways to stop a jumping dog, but not all of them may work for you. The best method, which always works, is to simply ignore the dog or walk away altogether. Don’t look the dog in the eye, don’t talk to it. When she calms down and stops jumping, praise her. Soon the dog will understand that jumping on you is not worth it.
bites
Puppies bite to explore their environment. Mother dogs teach babies not to bite too hard. The owner also needs to show the puppy that you should not bite.
In adult dogs, the desire to bite is also not always associated with aggression. A dog bites for a variety of reasons:
Out of fear;
on the defensive;
Protecting property;
Experiencing pain.
What to do?
Any dog needs socialization and proper education. Puppies need to be taught from childhood not to bite. If you do not wean the dog from this habit in time, you will need the help of a cynologist in its re-education.