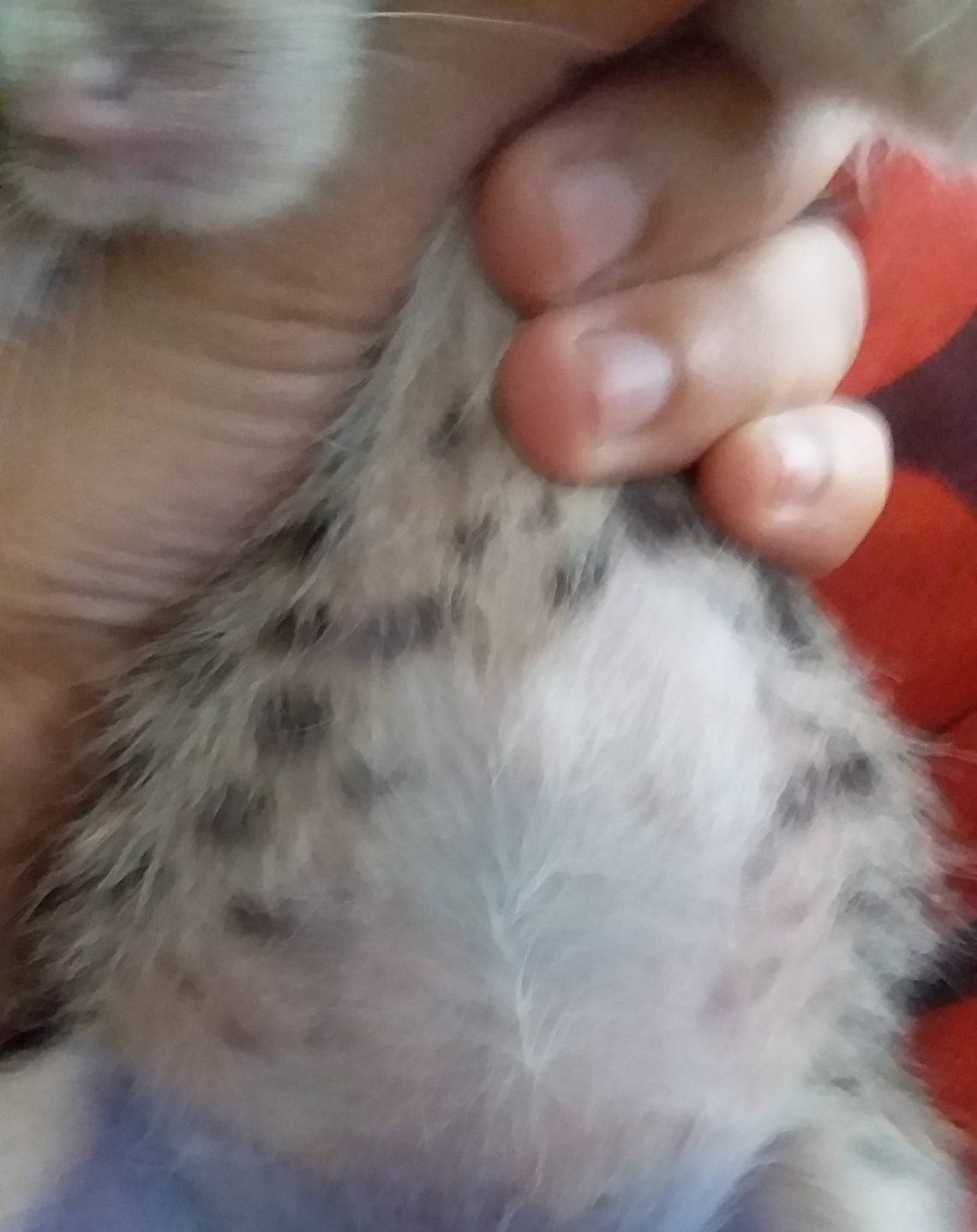
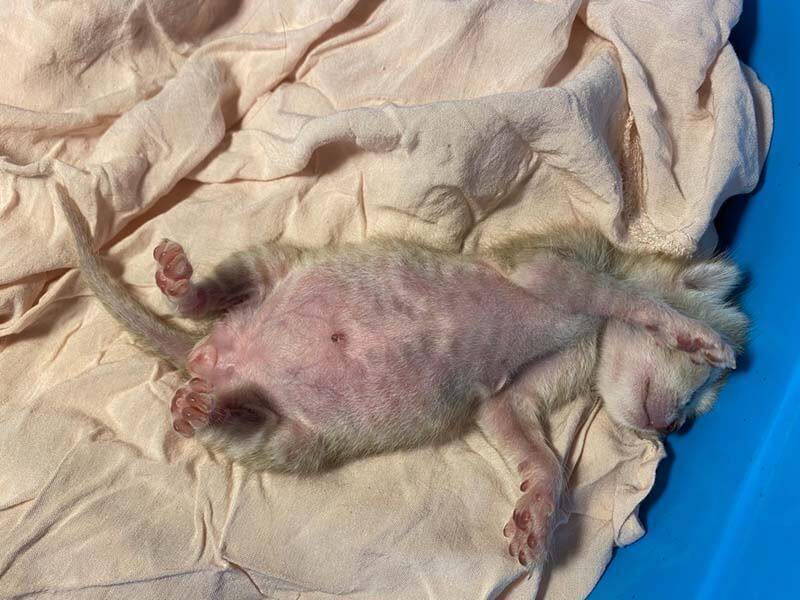
Why does a kitten have a big belly?

Contents
The main causes of a large belly in kittens
Variant of the norm
A large belly in a kitten up to 3 months old can be considered normal. This is due to the fact that while he has little muscle mass. As cats get older, their belly tightens.
Signs that a kitten has a large belly is normal:
the stomach becomes smaller after going to the toilet;
the kitten has a good appetite;
he regularly (at least twice a day) goes to the toilet;
the abdomen is neither painful nor hard when pressed;
no belching, gas, diarrhea, vomiting.

Constipation and bowel obstruction
Decreased peristalsis (hypotension) is most often associated with nutrition. Lack of fiber, bones can cause hypotension and cause constipation. It all starts with the fact that the kitten goes to the toilet less than 2 times a day, his stool is dry, and his stomach becomes tight. The baby sits in the tray for a long time and strains, drops of blood may appear in the feces. Over time, this can lead to megacolon.
With complete intestinal obstruction, cats become restless, may refuse to eat, and vomiting will appear. If appetite is maintained, vomiting will occur with undigested food.
Diseases of the digestive tract
Inflammation of the digestive tract (gastroenterocolitis, pancreatitis, IBD, etc.) occurs due to infections, helminths, and improper feeding. The abdomen becomes painful, hard. Additional symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, decreased appetite.
Flatulence
Flatulence in a kitten is not uncommon. The abdomen at the same time increases, becomes dense, there may be pain. With a gentle massage of the abdomen, the animal becomes easier, it can let out gases. They are formed due to the vital activity of certain microorganisms in the intestine. Most often, the reason lies in nutrition.
Helminths
Helminths (worms) can even be found in animals living in an apartment and not going outside. Cats are extremely clean creatures, they actively lick their fur, paws, and tail. You can bring the eggworm home on clothes or shoes, and the baby, rubbing against you, will become infected with them. If there are too many parasites, the kitten will have a bloated stomach and digestive problems, there may be vomiting or diarrhea, refusal to eat, lethargy.
Ascites
Ascites (dropsy) is an accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. The most common cause is feline viral peritonitis (FIP).
Also, ascites occurs against the background of diseases of the heart, liver, with protein loss, due to perforation of the intestine, with pyometra (inflammation of the uterus).
With ascites, the kitten’s abdomen becomes voluminous, round, the abdominal wall characteristically springs when pressed. As the fluid accumulates, the kittens have difficulty moving, the stomach becomes painful, constipation appears, vomiting, as a rule, the skin and mucous membranes become pale or icteric.
liver disease
The liver is the body’s main detoxification organ. It occupies a fairly large volume of the abdominal cavity. With excessively active work or inflammation (infection, injury), it will increase, the stomach will grow noticeably.
In addition to an increase in the abdomen, there may be the following symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, yellowness of the mucous membranes, lethargy, pain in the right hypochondrium.
Urinary retention
The cause of urinary retention in kittens may be an abnormal structure of the urinary tract
(congenital anomaly), secondary hyperparathyroidism (occurs against the background of improper
feeding) or inflammatory diseases such as cystitis.
If the urethra is obstructed, the bladder will increase in volume, and the stomach will become large and dense. As a rule, the process is accompanied by unsuccessful attempts to urinate, vocalization, pain in the lower abdomen. If help is not provided on time, symptoms of acute renal failure will begin (vomiting, shortness of breath, refusal to eat). This is a dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Diseases of the uterus
In cats older than 5 months, the first signs of estrus begin to appear, which means they become susceptible to diseases of the uterus and ovaries (cysts, endometritis, pyometra). With these pathologies, pathological processes can begin in the horns of the uterus, and fluid (pus, exudate) will accumulate in it. Additionally, there may be signs of incessant estrus, discharge from the loop, fever, thirst, lethargy, vomiting. Sometimes the disease is almost asymptomatic, and the owners do not notice anything but a voluminous belly.
Polycystic/neoplasm
Kittens can also have tumors and cysts in their internal organs. Most often they are localized on the kidneys and liver. The disease can occur in absolutely any cat, but there are breeds at risk (Persian, Exotics). In the early stages, there will be no symptoms, but as it progresses, there may be: refusal to eat, thirst, lethargy, vomiting, bad smell from the coat and yellowness.
Diagnostics
Visit doctor
To understand why the kitten has a large and hard belly, you need to conduct an examination in the clinic
and take a thorough history.
The doctor will evaluate if there is pain, fever, paleness or yellowness of the skin. The doctor will need to provide all the information about the pet – about the treatment for parasites, vaccinations, nutrition, maintenance, etc.
Ultrasound diagnostics
Ultrasound will be required to diagnose any of these diseases.
Laboratory research
A clinical blood test will be required if there is a suspicion of infectious and inflammatory diseases: peritonitis / ascites, inflammation of the uterus.
Blood biochemistry is needed for the diagnosis of diseases of the kidneys, liver, as well as for ascites.
PCR testing for antibodies to feline coronavirus infection (FIP) should be done with signs of peritonitis and ascites.
Exudative fluid with ascites should be examined for infectious peritonitis and its cytology should be performed.
Treatment
Constipation, bowel obstruction
With a decrease in peristalsis, the treatment consists in correcting the diet. For constipation, antispasmodics and laxatives (for example, lactulose) are prescribed.
In case of partial obstruction, symptomatic therapy is carried out (droppers, antiemetics, painkillers). If the obstruction is not eliminated, then the problem is solved surgically.
Diseases of the digestive tract
As a rule, first of all, a diet is prescribed. Depending on the location of the inflammation and its cause, antibiotics, painkillers, antiemetics, gastroprotectors, prebiotics, droppers, antihelminthics can be prescribed.
Helminths
Kittens, regardless of the size of their bellies, need to be treated for parasites once every 1.5-2 months. If there are symptoms of helminthic invasion (worms in the stool, vomiting), then the treatment should be carried out in therapeutic dosages, which the doctor will individually calculate at the reception.

Flatulence
Gas in a kitten may be due to improper feeding. Treatment consists of nutrition correction, abdominal massage and the use of carminative drugs.
Ascites
The treatment of ascites depends on its cause, but it is always an alarming symptom.
Viral peritonitis has a poor prognosis. In recent years, there is information about the treatment with an antiviral drug from human medicine (GS), it shows high efficiency. But there are still few studies, and the drug is difficult to use because of its high price and dosing regimen. Antiviral pills from a regular pharmacy (acyclovir, etc.) will not only not help in treatment, but can be dangerous for cats.
If the cause of ascites is in diseases of the internal organs, droppers, intravenous albumin, tonic drugs, hepatoprotectors, antibiotics may be required.
With an abundant accumulation of fluid, it is aspirated (pumped out).
liver disease
In liver diseases, hepatoprotectors and symptomatic treatment (antiemetics, antispasmodics) are first prescribed. After diagnosis, antimicrobial, choleretic drugs, diet, drip infusions can be recommended. Sometimes surgery is required.

Urinary retention
Treatment of acute urinary retention can only be provided in the clinic. To drain urine, a urethral catheter is placed or a cystocentesis (puncture through the abdominal wall) is performed.
Depending on the cause of urinary retention, it is prescribed: pain relief, diet, antibiotics, drip infusions, drinking regimen, supplements. With the formation of large uroliths or with an anomaly in the structure of the urinary system, an operation will be required.
Diseases of the uterus
Conservative treatment of uterine diseases in cats has been developed, but shows its effectiveness only with early diagnosis. In addition, the risks of relapse in the next estrus remain. Therefore, sterilization (OGE) is done much more often. During this operation, the uterus and ovaries are removed.
Polycystic and neoplasms
Neoplasms of almost any nature are recommended to be removed and sent to the laboratory. Based on the histological findings, chemotherapy may be prescribed. Cysts, as a rule, even after removal appear again. Their effective treatment has not been developed. They use symptomatic therapy, do regular examinations and ultrasound to control the size of the cysts.
Prevention
Balanced diet
For the prevention of flatulence, constipation and dynamic intestinal obstruction, first of all, it is important to properly feed the kitten. The correct ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates is only a small condition for a balanced diet. Equally important is the content of fiber, vitamins, trace elements. If you feed your baby with food, then it’s enough just to choose a diet according to age and breed. However, if you are feeding your pet as a natural diet, then it is important to balance all the nutrients, a nutritionist will help you with this.

Regular treatments for parasites
As we discussed earlier, deworming in kittens should be done every 1.5-2 months. But there is not a single drug that acts absolutely on all parasites, so it is recommended to change the drug every 1-2 treatments in order to capture a larger spectrum of pathogens.
Sterilization
If you are not planning on kittens, then it is best to have a scheduled spay. Cats undergo such operations from 4 months. This will protect against the appearance of cysts on the uterus and ovaries, and early castration (from 4 to 8 months) prevents the formation of tumors of the mammary glands.
Limit contact with sick animals
Ascites often occurs due to the peritonitis virus. The only way to prevent infection is to keep your pet away from sick and potentially dangerous animals. Don’t let him out unsupervised. Quarantine for at least 2 weeks when introducing new animals.
Bloated belly in kittens: the main thing
The reasons for the appearance of a large belly in a kitten can be: helminths, improper feeding, infections. And sometimes a big belly in a small kitten is normal.
For diagnosis, a doctor’s examination and ultrasound are needed. Blood tests or exudative fluid may be required (for peritonitis, infections).
For treatment, depending on the cause, diet therapy, antibiotics, carminative, antihelminthic, laxatives and other drugs are used.
Prevention consists of a balanced diet, limiting contact with infected animals, and regular treatments for parasites.
Answers to frequently asked questions
December 9 2021
Updated: December 9, 2021