
Why does a guinea pig lose hair, causes and treatment of baldness
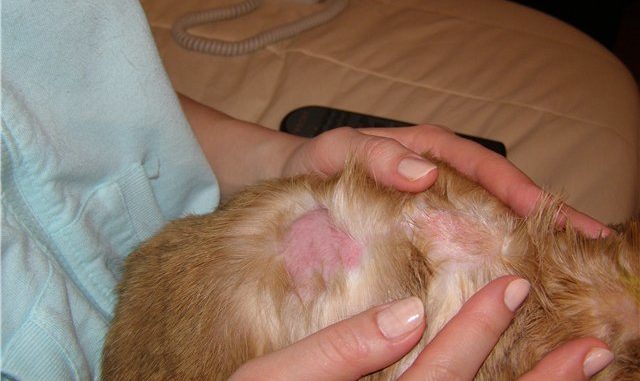
The quality of an animal’s fur is an accurate indicator of its health. If a guinea pig’s hair falls out, the pet needs additional attention and a thorough examination. Immediate assistance can save your pet’s life, as well as avoid serious consequences.
Contents
Natural hair loss
The temperature in the apartment is the same all year round, so the wool of rodents can fall out constantly and in small quantities. If there are no other symptoms, the pet is most likely shedding.
Bald patches behind the ears are normal for guinea pigs. If both areas are symmetrical and do not grow over time, and the skin does not peel or itch, there is nothing to worry about.

Hair loss may indicate the aging of the animal. This is usually accompanied by decreased activity and weight gain. Pigs at a respectable age pay less attention to hygiene, which is reflected in the quality of wool.
If changes are found in the behavior and appearance of the animal, then the hair that has fallen out indicates problems with the health of the pet.
Baldness reasons
Natural physiological processes do not cause discomfort in the pet and do not affect the appearance. Any changes require additional attention of the owner.
Signs of diseases:
- nervous and frequent scratching;
- bald spots;
- baldness;
- apathy;
- decreased appetite;
- anxious behavior;
- skin defects in the form of papules, abscesses, scratches, scabs;
- erythemal nodes;
- dry skin and dandruff;
- traces of parasite activity.
If you notice unpleasant symptoms, you should consult with your veterinarian.

There are common cases of combined disorders that are difficult to identify for a non-professional.
Inappropriate Diet
Nutrient and vitamin deficiencies in the diet can cause tufts of hair to fall out in guinea pigs.
With beriberi, the guinea pig goes bald, gnaws on limestone walls and dirty bedding.
The rodent’s immunity is reduced, so symptoms are often accompanied by conjunctivitis and colds.
With beriberi, you should change the pet’s diet. It is necessary to use special complexes of trace elements, including:
- vitamins A, C, D;
- potassium;
- calcium;
- phosphorus.
Lack of roughage can cause animals to eat their own wool. The animal should be provided with access to fresh hay.

Particular attention should be paid to nutrition in winter and early spring. A weakened body needs additional sources of nutrients. Avitaminosis can develop in mumps during breeding. The period of gestation and care of the young depletes the body of the female.
Parasite infestation
If your pet has lost hair, it is worth checking the fur for the presence of parasites. The larvae can get on the skin of a pet while walking on the street. This is due to poor quality hay or contact with other pets.

Traces of vital activity of most species can be identified during the inspection. Fleas leave a scattering of dark dots on the coat. When combing with a fine comb, insects and brown granules remain on the teeth.
In a similar way, lice can be calculated. The pear-shaped larvae are attached to the hairs. Parasites prefer hard-to-reach areas with thick fur. When examining animals, it is convenient to use a magnifying glass. It will help to identify uninvited guests in the early stages of infection.
Scabies mites cause intense itching. The animal becomes restless, scratching the skin to form wounds with grayish scabs. Possible alopecia, coarsening of the cover, the formation of papules and abscesses. The tick prefers to settle on the back, head and sides. A scraping is needed to diagnose it.

The fur mite lives in the fur on the pope and around the crotch. When infected, the guinea pig’s hair falls out and the skin flakes off, redness is possible. Itching is not so strong, but the rodent constantly licks the hair, which makes it dull. Ticks can be detected with a microscope.
Vlas-eaters live at the root of the hairs.
They are visible to the naked eye, reminiscent of white dots that quickly move through the fur of the animal. They form bald spots and scratches.
Treatment for parasites includes treatment of the animal with insecticides and disinfection of cells. All tissue must be removed from the cell. Rinse hard surfaces thoroughly under running water after treatment.

Worms can cause nutritional deficiencies in the body, which affects the animal’s appetite. The animal becomes lethargic, it has increased thirst and symptoms of poisoning. The coat of the animal looks like with beriberi.
The parasite can be seen with the naked eye among the excrement of a rodent. Treatment at home is not recommended. Preparations must be selected in accordance with the subspecies of the parasite, otherwise, it will survive and adapt to adverse conditions.
Fungal infections
Guinea pigs are prone to fungal infections. The disease is contagious, it can be obtained through contact with other individuals. Most often this occurs from poor care, high humidity, dirty bedding and heat. Fungal infection can be transmitted to humans.
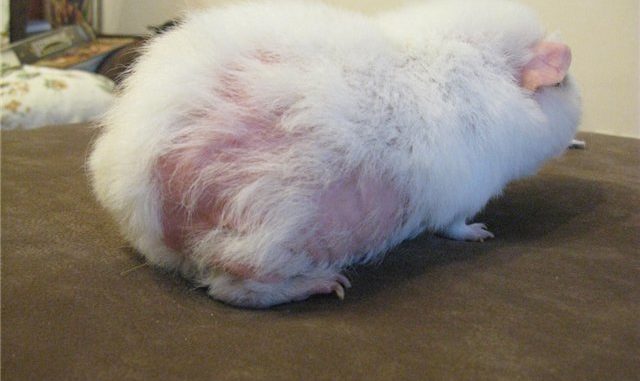
The most common problem is lichen. A sick guinea pig actively itches, her hair falls out. Large bald patches form among the fur. In areas where there is no hair, redness and flaking of the skin are noticeable. In most cases, the disease spreads from the tip of the ear.
Treatment of a fungal infection is prescribed by a veterinarian. A scraping may be needed to determine the type of bacteria. The owner should take preventive measures so as not to get infected from the pet.
Other factors
Hair loss on the abdomen and flanks is observed in pigs with an ovarian cyst. The disease can pass without symptoms. Occasionally it is accompanied by anorexia and lethargy. The guinea pig has an enlarged belly. Diagnosis and assistance can only be provided by a veterinarian.
Hair climbs in stressed guinea pigs.
Alopecia often develops due to increased anxiety. A cramped cage and a nearby source of loud sounds have a negative effect on the psyche of the animal.

Prevention
In order for the coat to be thick and shiny, it is necessary to provide the animal with good care. The guinea pig should have a spacious and clean room with a suitable temperature regime. Nutrition must be balanced.
Do not allow animals near the guinea pig. When moving in, a new individual must undergo a two-week quarantine in a separate cage.
All purchased feed must be inspected, checking the quality. Accessories from the pet store should be washed thoroughly before installation. Before going outside, it is better to use a pest control spray.

A soft brush for wool and a double-sided comb with different tooth frequencies are indispensable in caring for wool. With their help, you can comb out dirt and dead flakes of the epidermis, which favorably affects the coat. Regular combing allows you to quickly detect infestation with fleas and lice.
Video: bald patches in guinea pigs behind the ears
What to do if the guinea pig’s hair falls out and the skin flakes off
3.3 (65.13%) 39 votes





