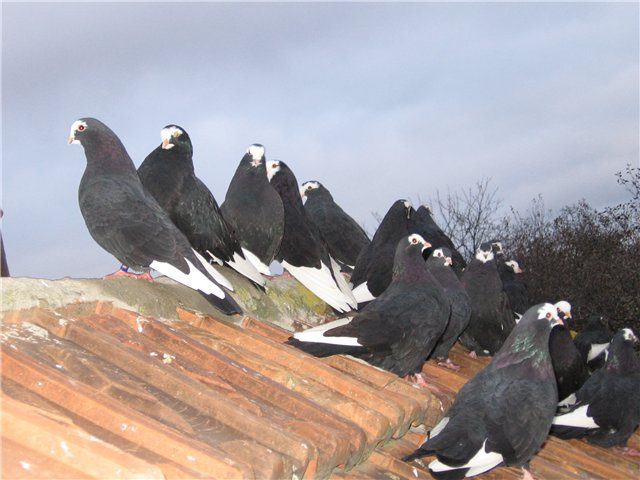
Who are Kursk pigeons, where did this name come from and the main differences
Kursk pigeons – this is one of the popular breeds of high-flying pigeons, the old name is Kursk Turmans.
The origin of this breed is still unknown. In space, Kursk birds are very well oriented and therefore get lost quite rarely. The flight of Kursk birds is carried out mainly by a group. Kursk pigeons are tied to the house.
Bird features
They rarely fly alone. If there is no wind, the pigeons slowly gain altitude by flying in circles. They begin to fly “the flight of a lark”, that is, flight in place, as soon as they pick up the necessary air currents. rise to the height, spreading tail and wings. They slowly land in vertical flight. Many of the Kursk pigeons are in flight for 5-6 hours, and more enduring ones can be 8-10 hours.
Following the flock, one can notice behind the Kursk Turmans that they seem to freeze in the air at a certain height. At this point, only the movements of the pigeons’ wings can be seen. After some time, one of them curls up into a ball and flies sharply down. This is then repeated by another, then a third. After that, the pigeons again gain height and continue to fly in a flock. This doesn’t happen just once.
Kursk pigeons are bred in the same way as other breeds. You just need to know that flight is important for this breed and a strict feeding regime is necessary, as well as the correct selection of food. Peas, wheat or corn are considered “heavy” food for them, and the birds will quickly lose their main flight qualities. These feeds simply need to be added in small quantities to barley and oatmeal.
History of occurrence
Previously, the German fascists issued an order to destroy pigeons and, due to this, they hoped to eliminate the postal service of the partisans. But still, people saved the birds and hid them anywhere. The breed was almost completely exterminated, but those that could be saved were mixed with each other. The focus was on flight. That’s why color changed, tails and wings have changed.
The date of creation of a new breed of these birds is the 2th century. As you know, such a breed was bred in the city of Kursk, by crossing 20 breeds of pigeons. These are pure Voronezh chegrashs and local tumblers. As a result, Azar pigeons were formed. A. Bityukov studied these pigeons well. The plumage of the Azar pigeons was very diverse, but many individuals of this breed had a magpie color. Beltless pigeons of light gray color were still known in Yelets in the 1950s. In Lipetsk, Yelets and many other cities, Kursk pigeons have been bred since XNUMX. And they also had a forty color. Due to their excellent flight capabilities, simplicity and unpretentiousness of keeping birds, they have become very popular in Russia.
Basic Types
One of the pigeon breeders singled out four types. For Kursk pigeons:
- strong, strong body, they have well-developed muscles;
- black, bluish plumage, a dark ribbon across the tail, red plumage is rare;
- wide convex chest, strong back;
- excellent flying qualities.
- The first type of Kursk includes pigeons with a dense, strong body. White feathers on the ventral part, mandible, undertail, on the tail between the tail feathers. The forehead and cheeks are also white. Close to the body stiff feathers. Round shape big head. Yellow-gray eyelids with black eyes. Their short beak is thinner and flesh-colored.
- The second type includes these representatives with a smaller, elongated and low-set body. Dense black plumage with a bluish tint. The head is small and convex. Mostly silver eyes, but sometimes dark brown. Light beak of medium thickness. Graceful, thin, slender neck, refined throat. Wide wings with red limbs. Soft flesh-colored claws. There are 12-14 tail feathers on the long tail. In this type of pigeon, the black tail is especially important.
- The third type of this bird breed is similar to the second body. Plumage light gray, the neck is dark steel with a green gloss. The head is larger, the forehead is white. Dark brown eyes on a white head or silvery on a colored head. Short and pinkish beak. The flight feathers on the wings are white. Dark gray tail with a dark band across
- The fourth type includes pigeons with an ordinary body. Large, rough head. Magpie color, white plumage on the cheeks, forehead, wings, undertail and abdomen, black shoulders and chest with a green sheen, light black or grayish tail with a wide transverse stripe. Large, slightly rough head. The beak is short, flesh-colored, thick. Bulging chest. Thick strong neck. Long, wide wings are located on opposite sides of the tail. Large featherless limbs with light claws.
A sign of the health and strength of a bird is long flight. The height of the departure of birds uphill and their stamina in height are valued. But not all hunters train to stay in the air for quite a long time.