What is the heart of turtles and what color is their blood?

The turtle belongs to reptiles and has a circulatory system similar to lizards and snakes, while in crocodiles the blood supply system has some distinctive features. The body of a turtle is supplied with mixed blood. This is not a perfect blood supply system, but it allows the reptile to feel great in a particular habitat. Consider how the circulatory system of an exotic inhabitant of deserts and seas functions.
Contents
turtle heart
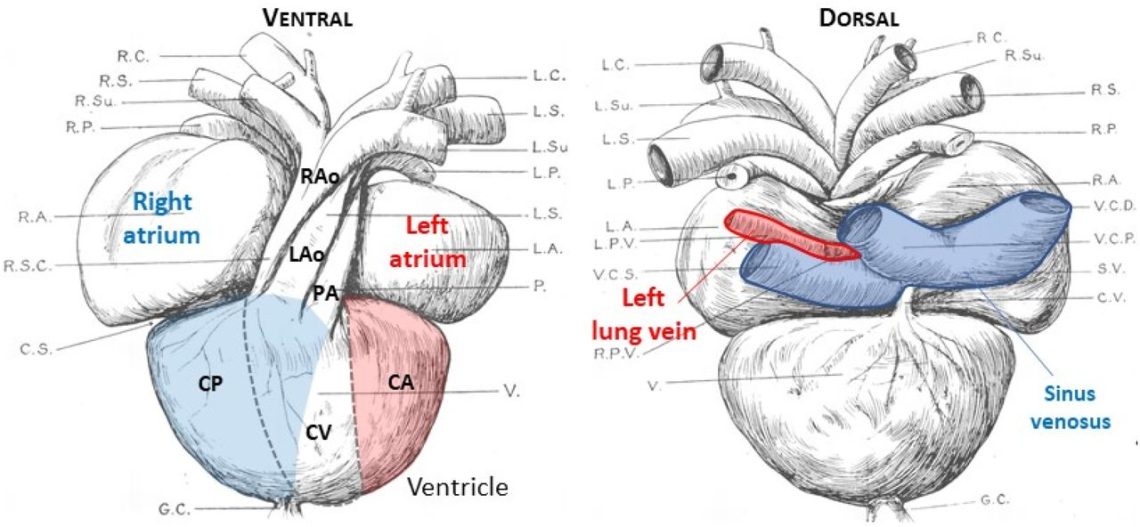
The heart of a turtle is located in the central part of the body between the sternum and abdomen. It is divided into two atria and one ventricle, it is three-chambered in its structure. The chambers of the heart function by filling the body of the reptile with oxygen and nutrients. The ventricle is also provided with a septum (muscular ridge) but does not completely overlap.
The chambered heart allows you to evenly distribute blood, but with this structure it is impossible to avoid mixing the arterial and venous fractions. The system of entry of turtle blood into the heart is as follows:
- The oxygen-poor composition enters the right atrium from various organs. It enters the atrium, passing through 4 veins.
- The “living water” from the lungs, which is saturated with oxygen, passes into the left atrium. It is supplied by the left and right pulmonary veins.
- From the atria, when they contract, the blood is pushed into the ventricle through the disconnected openings, so initially it does not mix. Gradually, a mixed composition accumulates in the right side of the ventricle.
- Muscle contractions push the “nutritional mixture” into two circles of blood circulation. The valves stop it from returning to the atria.
Important! The blood in the normal state and breathing of the turtle moves from left to right due to the difference in pressure. But if breathing is disturbed, for example, when immersed in water, then this movement changes and goes in the opposite direction.
Heart rate
The turtle’s pulse can be determined by placing a finger between the neck and forelimb, but it is poorly palpable. As the ambient temperature rises, the heart rate increases noticeably so that heat is absorbed as quickly as possible. When it gets colder, the heartbeat slows down, which allows the reptile to keep warm as much as possible. How many beats per minute the heart produces depends on age, species characteristics, body weight.
The turtle’s pulse, its norm is related to the temperature at which the animal feels comfortable (in nature it is + 25- + 29C).
The pulse per minute ranges from 25 to 40 beats, depending on the type of animal. During the period of complete rest (anabiosis), in some species, the heart rate is 1 beat per minute.
Important! The speed of the heartbeat and the movement of blood changes even before the body temperature has changed, which indicates the presence of thermoreceptors on the skin.
Work of circulatory circles
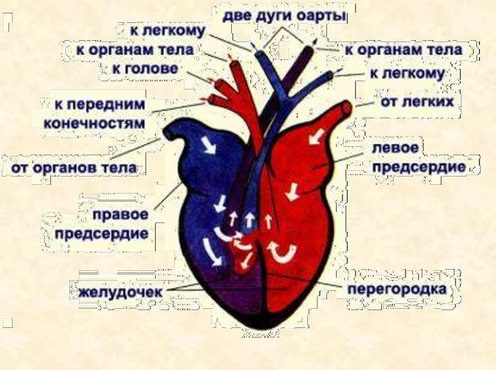
The circulatory system of a turtle forms two circles of blood circulation: small and large. This allows you to clean the turtle’s blood from carbon dioxide and deliver it to the organs, already saturated with oxygen. The movement in a small circle is as follows:
- the ventricle contracts in the area where the venous cavity is located, pushing the nutrient fluid into the pulmonary artery;
- the artery bifurcates, going to the left and right lung;
- in the lungs, the composition is enriched with oxygen;
- the composition returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
The large circle of blood circulation is more complicated:
- when the ventricle contracts, blood is ejected into the right (arterial) and left (mixed) aortic arches;
- the right arch is divided into carotid and subclavian arteries, which supply the brain and upper limbs with a nutrient mixture;
- the dorsal aorta, consisting of mixed blood, nourishes the pelvic region and hind limbs;
- the composition enriched with carbon dioxide returns to the right atrium through the right and left vena cava.
This structure of the heart allows you to control the work of the vascular system. It has its drawbacks: getting into the bloodstream of mixed blood.
Important! In aquatic species, the return of arterial blood is higher, their cells are better supplied with oxygen. This is due to the state of hypoxia during diving, when the blood fraction is retained in the capillaries. Such a process is an adaptation to specific environmental conditions.
Video: turtle circulatory system
What color is turtle blood?
The composition and role of blood cells in turtles and mammals is the same. But the composition can change in turtles and depends on the time of year, pregnancy, diseases. All blood components contain nuclei, which is not typical for more highly organized groups of animals.
The color of the blood of the reptile is red and does not differ in appearance from the human. The volume is 5-8% of body weight, and the color of the arterial composition may be slightly darker, as the composition is mixed. The blood of the red-eared turtle, which is often kept in an apartment, does not differ from its relatives.
Important: Turtles are slower and get tired faster, they have slower metabolic processes, because the cells suffer from a lack of oxygen when they are fed with a mixed blood composition. But at the same time, lizards and snakes are quite mobile and show great activity at certain moments or periods of life.
The circulatory system of turtles, like other reptiles, is more advanced than that of amphibians (frogs) and less advanced than that of mammals (mouse). This is a transitional link, but it allows the body to function and adapt to specific external environmental factors.
The cardiovascular and circulatory system of turtles
3.3 (65.61%) 57 votes





