What is the difference between a mouse and a rat (photo) – comparative table

Some people don’t know the difference between a mouse and a rat. Others believe that the difference between them is only in size. Still others even argue: a rat and a mouse are one and the same animal at different ages. But it is not.
What do rats and mice have in common
These mammals are included in the order of rodents of the mouse family. There are other common features as well. Because of them, these two species are often confused.
Mice and rats: general features of life
Both of them are cosmopolitan species. That is, these rodents inhabit all corners of the Earth except for Antarctica and the Far North, they are not even high in the mountains.
These rodents are considered synanthropic, that is, associated with humans. Wild subspecies live in human dwellings, utility rooms or intended for keeping domestic animals. Although in warm regions they can live away from human habitation.
Rodents are animals with a nocturnal and twilight lifestyle. They are most active at sunset. However, when kept in captivity, animals adapt to the rhythm of the owner’s life, get used to being awake in the light and reduce activity during human rest.
These types of rodents are very mobile. They are great at climbing, running, jumping and swimming. Possessing high plasticity of the body, the animals can “leak” into very small cracks.
Mice prefer to live in nature in colonies in which they maintain a hierarchy. Adult males can arrange fights among themselves. In families, aggression sometimes extends to the grown offspring, which the parents expel from their territory.
Rodents are clean creatures. They maintain cleanliness and order in their homes. The droppings and urine-bound piles of dust that they leave during the journey are special marks for determining the route.
Both species of rodents not only live in nature, but also take root in captivity, are easily tamed. To date, breeders have bred their domesticated subspecies of various colors, which many lovers are happy to keep as companion animals.

similarity in appearance
The mouse really looks like a smaller copy of the rat:
- The house mouse and rat have long tails covered with horny scales and sparse short hairs. Only the black rat stands out here. Her tail is covered with thick hair.
- Both species have a sharp muzzle, rounded small ears, round black eyes (in albinos they are red or dark ruby).
- The main features of these two species of rodents are long sharp incisors that grow throughout life, the absence of fangs. With their teeth, animals can gnaw through very hard materials, even concrete.
Important! Keeping in mind the peculiarities of the teeth of these rodents, it is necessary when keeping animals to give them the opportunity to grind their incisors. For this, twigs with a diameter of 2-4 cm, pieces of charcoal are placed in the cages for pets.
What is the difference between a rat and a mouse
Despite the commonality between these rodents, they differ greatly from each other:
- The main differences are due to the different number of chromosomes. There are 22 of them in rats, and 20 in mice. Therefore, it is impossible to cross these mammals in order to obtain offspring.
- Decorative rats reach 30 centimeters in length, excluding the tail. Mice do not grow more than 9 and a half centimeters. By weight, large rodents reach 650 grams. The mouse is never heavier than 30 grams.
- Despite the fact that the number of newborn rats and mice in one female is from 5 to 12, the number of nipples in rodents varies. The rat has 12 of them, while the mouse has fewer nipples – only 10.
- Due to the rapid metabolism, the activity of mice differs from that of rats by polyphasic activity. The animal falls asleep 15-20 times a day. Each activity phase lasts from 25 minutes to an hour and a half. The rat lives more “slowly”: it sleeps once a day, if it is not disturbed.
- There is a difference between them in nutrition. Although both of these species are omnivores, they can attack and eat other living creatures, but in a rat the predatory instinct is more developed. Mice are seed eaters. Predatory instincts appear only when absolutely necessary, which is why they are even considered vegetarians.
Important! It is recommended to feed domesticated species of rodents with grain, fruits, protein is given to them in the form of boiled low-fat chicken, cottage cheese, boiled egg white. It is impossible to feed raw meat, cheese, smoked meats, lard to animals.
Rodents-hunters
The rat is more aggressive than the mouse. When danger approaches, they show miracles of courage, they can even attack a person, defending themselves. In nature, rats often hunt in packs. Animals can attack in a group even on mammals that exceed their size.
Mice prefer to hunt alone. Therefore, only insects, smaller animals, become their victims. These animals are shy, extremely cautious.
Because of such character traits, these animals are natural enemies. Large rodents attack small ones, kill them, they can even eat them. Therefore, the instinct of self-preservation dictates that mice beware of their larger relatives. Smelling the smell of a rat, small rodents leave their habitat.
Important! Where a population of mice has developed, you can get a pet – a rat, which is allowed to run around the house, leaving its smell. Small uninvited rodent residents will leave their homes very soon.
For the same reason, individuals of these two species cannot be kept together. It is not recommended even to put cages with them in the same room.
Comparison of rodent intelligence
Rats are smarter, smarter than their small counterparts. Catching a wild specimen is troublesome. They are careful, attentive, cunning. If the loser suddenly falls into a trap, she lets the rest of the colony know about the danger. Never again will a single animal appear here.
There are many stories about how these clever thieves opened bottles of wine, closed with polyethylene corks, one of them lowered the tail into the neck, pulled it out, and others licked the delicacy from it.
Or how rodents, moving through a wide crevice, grappled into the path, biting the tail of the animal in front of them with their teeth. On such a living bridge, the entire colony easily got over the obstacle.
Companion rats, living next to a person, also show their remarkable abilities. They are easily trained, respond to the name, even come up with their own games, inviting the owner to join.
There are no such stories about mice. However, these sweetest creatures can give their owners a lot of pleasant moments of communication. They also become attached to a person, touch those who observe their life with their habits.
Who grows faster: a mouse or a rat
The metabolism of mice is higher than that of a rat, so their lifespan is shorter. The average life span of small rodents at home is 1,5-2 years, while their large relatives live up to 2-3 years.
Rats and mice grow the same way. At the age of 1-1,5 months, young rodents are capable of reproducing their own offspring.
External differences between a mouse and a rat
To distinguish a mouse from a rat, you just need to carefully examine the animal:
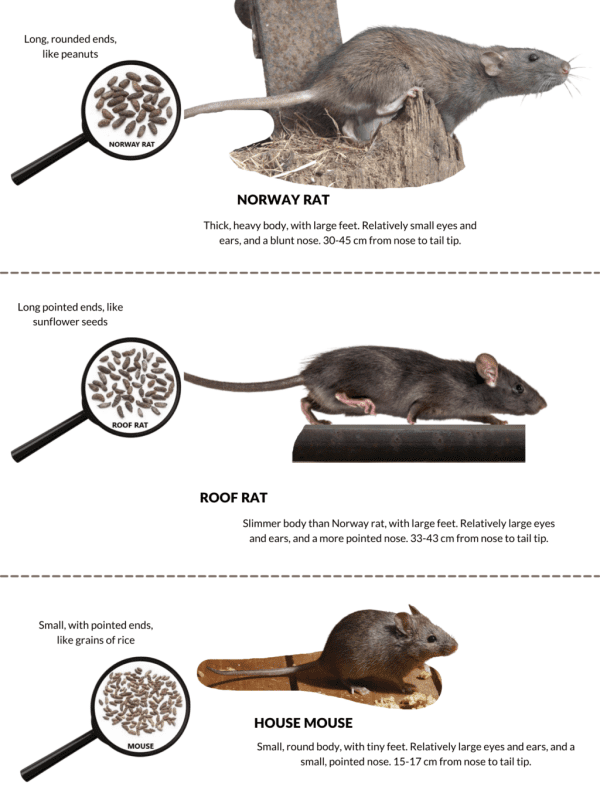
- rat tails are longer than those of mice. They are equal in size to 70-110% of the body. Mouse tails are shorter. They can reach no more than 60% of the body;
- the tails of large rodents are thicker than those of mice, more powerful (with the exception of the tailless rat);
- the muzzles of rats are sharper and more oblong. Mouse heads are rounder and less pointed;
- the body of small rodents is more round. Animals rarely straighten up, preferring to sit, huddled together. And their species relatives can rest, lying on their tummy, stretching their hind legs, like cats;
- mouse fur is soft, silky, while rat hair resembles a coarse pile;
- the hearing organs of rodents are arranged differently. Mouse ears are thinner, rounded. They look like folded petals. Rat ears are thicker, sharper, not wrapped.
Table of the main differences between domesticated rats and mice
| Distinction | Rat | Mouse |
| Chromosomes | 20 | 22 |
| body size | 30 см | 9,5 см |
| Weight Limit | 650 g | 30 g |
| Life time | 1,5-2 years | 2-3 years |
| Daily phases of sleep | 1-3 | 15-20 |
| Tail compared to body length | 70-110% | 30-60% |
| Muzzle | More elongated, pointed | Rounded |
| Body | elongated | rounded |
| Number of nipples | 12 | 10 |
| Wool | Rough, lint-like | Soft, gentle |
| Ears | More pointed, even | Rounded, thin, rolled up |
The difference between a rat and a mouse
4.2 (83.44%) 64 votes