Urolithiasis in cats: treatment, main signs and causes
Urolithiasis is a common disease in cats associated with metabolic disorders. Such a serious pathology with untimely treatment can be a danger to the life of the animal. To stabilize the condition of the pet, you need to choose a special diet and start complex therapy.
Urolithiasis is chronic illness. It is manifested by the formation of sand or stones in the kidneys and ureters, as well as the bladder. At first, salt deposits do not make themselves felt, but they gradually increase in size. As a result, even small stones can damage the urinary tract, causing severe pain in the cat. In some cases, blockage of the ureters occurs, due to which fluid stagnation and intoxication are observed. To alleviate the condition of the animal, emergency assistance will be required, otherwise a fatal outcome is possible.
Contents
Main reasons
It is almost impossible to establish the exact cause of the appearance of such a pathology. Most often, the disease in cats leads to an unhealthy lifestyle, lack of care and an unbalanced diet.
Possible reasons:
- congenital pathology of the development of the genitourinary system, as well as anatomical features, including a curved or too thin urethra;
- poor quality drinking water, which contains a lot of minerals (it is for this reason that tap water should not be given);
- a diet based on an insufficient amount of liquid;
- various disorders in the development of the body, due to which the metabolism slows down;
- dysfunction of the digestive system;
- mixing or frequent alternation of natural food and dry food;
- regular feeding of the animal with fish or fatty foods;
- the use of low-quality feed;
- constant overfeeding, which leads to obesity;
- insufficient motor activity;
- injuries of the pelvic bones;
- streptococcal, staphylococcal and other infections;
- neoplasms in the urinary tract.
Urolithiasis and castration
It is believed that KSD is most often observed in neutered cats, but scientists do not always agree with this opinion. In any case, there is some connection between urolithiasis and castration. So, after the removal of the testes, the hormonal background of the cat changes. He becomes more calm and loses interest in cats, and it is precisely the lack of mobility that leads to urolithiasis.
There is an opinion that cats replace interest in the opposite sex with a passion for food. Because of this, obesity develops, which is a causative factor in KSD. To avoid this pathology, it is necessary to give cats low-calorie food in small quantities. It is also necessary to castrate animals that are at least six months old, and preferably 8-10 months old, because during the operation at an earlier age, the urethra stops developing and remains narrow.
The main signs of urolithiasis in cats
If the animal has just begun to develop urolithiasis, then it rather difficult to diagnose., because at an early stage the symptoms are mild. As a rule, the cat becomes less active. She does not eat well and may experience discomfort while urinating. However, such signs are characteristic not only for urolithiasis.
If left untreated, the size and amount of salt deposits increase. Over time, the stones separate and travel down the ureter. At this stage, the diagnosis of the disease does not cause difficulties.
Common symptoms:
- during urination, the animal meows loudly, which is explained by severe pain;
- the cat often sits in the tray, because it feels the urge almost all the time;
- after the animal goes to the toilet, pink or reddish stains can be seen in the tray, which is explained by the presence of blood particles in the urine;
- urination may stop completely, while sometimes there is a prolapse of the rectum;
- with the help of palpation, it is possible to notice that the cat’s stomach has become tight;
- even the most well-mannered pets start going to the toilet in the wrong place;
- cats behave fussy and try to either attract the attention of the owner, or hide in a corner;
- the animal has rapid breathing;
- The cat’s appetite is almost non-existent.
Diagnostics
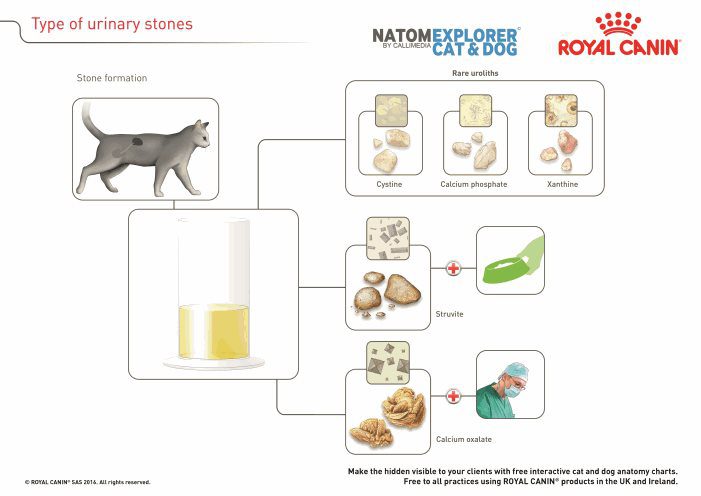
If urolithiasis in a cat is suspected, take to veterinary clinic. The specialist will take into account all the symptoms, as well as prescribe special procedures. For the diagnosis of urolithiasis, ultrasound, x-rays and examination of urine sediment are used. It is also important to determine the type of salt deposits, because thanks to this it is possible to choose the right treatment. For more accurate studies, X-ray diffraction and polarized light microscopy are used.
Treatment
If during the examination it was found that the cat is really developing urolithiasis, complex treatment is prescribed. Thanks to him, it is possible to remove the exacerbation and improve the condition of the animal. This takes into account the degree of damage, the general condition of the cat, the stage of the disease, as well as the sex and age of the pet.
To solve the problem, both conservative therapy and surgical intervention can be used. Sometimes the removal of deposits using a catheter or their removal under anesthesia is prescribed.
Conservative treatment
Various procedures are used to restore the outflow of urine and eliminate inflammation. At the same time, treatment is also aimed at prevention, which helps to avoid possible complications and relapses.
cat select a range of drugs, which will help restore the patency of the urinary tract and eliminate the stagnation of urine. So, antispasmodics and sedatives are prescribed, including baralgin and neotropin, antibiotics and homeopathic remedies, namely cantharis and magnesia.
After stopping the attack, the cat’s condition improves. For recovery to come sooner, a lumbar novocaine blockade is used. Also, the pet must be kept warm.
Operative therapy
To cure urolithiasis, removal of stones is often prescribed. If for some reason a decision is made to refuse the operation, acute pyelonephritis, hematuria, hydronephrotic transformation and severe pain syndrome may develop.
Depending on several factors, the specialist prescribes a urethrostomy or cystostomy. The first option involves the creation of a channel to remove salt deposits, and the second is a serious abdominal operation. It is carried out in the case when the size of the stones exceeds the size of the urethra.
After the operation, urination is restored, however, to normalize the condition, the cat is additionally prescribed a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Diet
In addition to treatment, the veterinarian must prescribe a special diet for the animal. It is selected taking into account the violation of salt metabolism. Thanks to proper nutrition, it is possible to restore metabolic processes and maintain homeostasis.
Natural food
If the cat eats natural food, you should consult a veterinarian and pick up certain products. In addition, vitamins A and group B are prescribed. Food should be prepared immediately before feeding. The cat’s diet should include boiled lean meat, cottage cheese, boiled eggs, carrots, rice and cheese.
Animals should not be given pork, fish, sausages, and canned food. Food should be non-spicy and non-greasy.
Dry food
If the cat eats ready-made food, then special varieties intended for animals with KSD should be preferred. This food contains the optimal amount of minerals. Cheap food related to the economy class cannot be bought.
It is necessary to ensure that the animal consumes enough water. If the cat drinks little, then it is better to pre-soak dry food or give special canned food.
Prevention
Even if the treatment of the animal was successful, it is necessary to follow preventive measures, which will help to avoid relapses. These are the recommendations:
- Proper nutrition, which involves the use of medicated foods designed specifically for cats with KSD. You can also give natural food, taking into account all the recommendations of the veterinarian.
- Pet weight control. The cat must weigh no more than 4,5 kg.
- Phytotherapy with the use of diuretics.
- Use of filtered clean drinking water.
- Regular pet play.
- Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys every six months, as well as regular urinalysis.
Thanks to these simple rules, the pet will remain active and cheerful.
Urolithiasis gives cats a lot of discomfort. Moreover, in advanced cases pathology leads to death.. If there are suspicions of KSD, it is urgent to consult a veterinarian, because only timely treatment, proper care and a balanced diet can restore the cat to health.