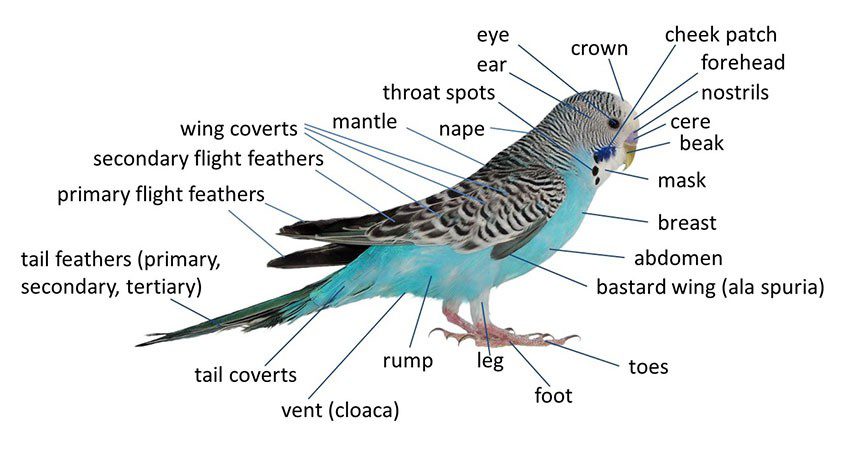
The structure of the budgerigar
For lovers budgerigars this article can be very helpful.
The budgerigar belongs to a small species, its body length is only 18 cm, but if we are talking about exhibition Czech budgerigars, then here the size of the bird is 24 cm. The length is measured from the crown to the tip of the tail.
Contents
Visual representation of the structure of the budgerigar in the photo:

Anatomy of a budgerigar
Bones in a budgerigar, like in other birds, they are hollow, light and durable. Strong pectoral muscles are attached to the keel bone.
Skull large.
Neck long, consisting of 10 vertebrae. Allows the bird to rotate its head nearly 180 degrees.
Jaws. The upper part of the beak of the budgerigar is not fused to the skull (unlike other birds), it forms a mobile connection with a wide range of action. This is due to the fact that the upper jaw of the parrot is connected by a tendon to the frontal part.
Beak. Budgerigars have a strong, rounded beak. It is covered with a strong stratum corneum. A cere with nasal openings is located at the base of the beak (mandible). The beak of budgerigars is much more mobile than that of other birds.

Language. Wavy are smooth-tongued parrots, the tip of their tongue is covered with a stratum corneum. The tongue itself is thick, short and rounded.
Eyes. Budgerigars see the world in color, with tints, and at a wide angle (monocular vision), that is, they observe two “broadcasts” at the same time. When a bird wants to examine an object, it tilts its head to the side and looks at it with one eye.
The bird also has a third eyelid (flashing membrane) that protects the eyeball from contamination and drying out.
Budgerigars do not have eyelashes; they are replaced by small half-feathers.
Ears. The organs of hearing in budgerigars are hidden by feathers. They help birds navigate and communicate.
Birds perceive sounds in the range from 120 Hz to 15 kHz.
Paws budgerigars are strong, they allow birds to deftly move along branches, run on the ground, hold, carry and throw food or objects.
Fingers. The wavy has 4 long toes on each foot.

Claws sharp, tenacious and curved.
Leather in budgerigars, it is hidden under dense plumage. If you push / inflate the feathers, you can see a thin, like a film, skin, under which there is a network of blood vessels.
The body temperature of a budgerigar is about 42 degrees.
Respiratory system. The wavy has two pairs of “air sacs”. When inhaling, air is directed through the lungs into the air sacs of the neck and head; When you exhale, air from the abdominal sacs passes through the lungs. Enrichment of oxygen in the body of a parrot occurs by constantly driving air through the lungs.
Because of this feature, the bird is very vulnerable to harmful impurities in the air.
Budgerigar breathing rate: 65-85 breaths per minute.
Vote. Budgerigars do not have vocal cords. Playing sounds is a very complex process. Sound is created by the vibration of the Eustachian tube, which sets the air in motion.
In the chest cavity is the organ “syrinx” (lower larynx), it is located in the place where the trachea is divided into the right and left bronchi. The syrinx consists of membranes, folds and muscles that can change shape, size, degree of tension, which forms the bird’s voice.
Why is the parrot talking? Parrots can copy sounds and speech, they are very good imitators. All this they get thanks to the influence of the brain on the lower larynx.
The cardiovascular system. Birds, like humans, have arterial and venous circulatory systems. But interestingly, birds have rather large hearts, this is due to the high metabolic rate (especially when flying).
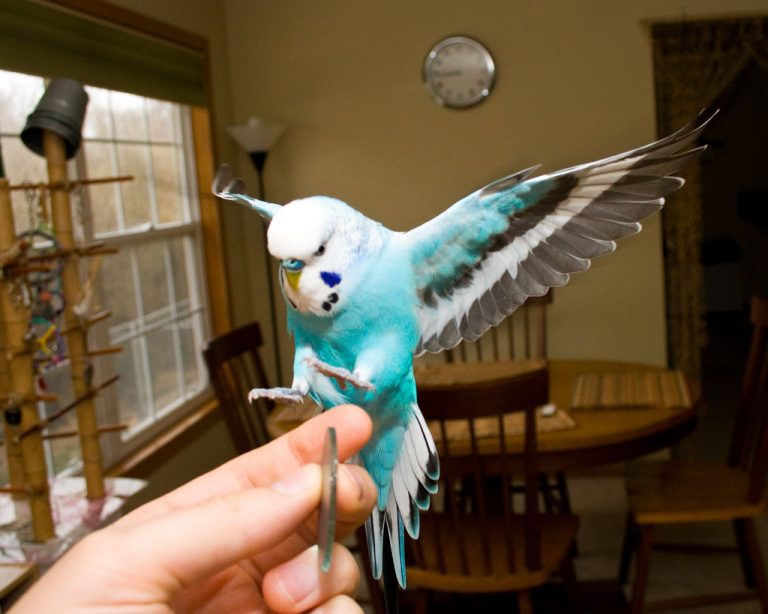

The pulse rate of a budgerigar during the rest period is about 400-600 beats per minute, in flight it exceeds 1000 beats.
Under such conditions, the blood pressure of the parrot will necessarily be high.
Digestive system. Birds have food receptors in the sky. They are much smaller than those of a person, so you can’t call a budgerigar a gourmet.
There is no saliva in the bird’s mouth, the food is moistened, getting into the esophagus, and then into the stomach. Next – the duodenum and intestines. Recycled residues are excreted through the cloaca.
Birds do not have a bladder and urethra, the kidneys form urine, which is excreted through the cloaca.
Nervous system similar to human. It regulates and coordinates the activity of all parts of the parrot’s body.
The brain is more complex in structure than the brain of reptiles. It is larger, the large hemispheres of the brain are smooth without convolutions and furrows. Within them are centers of coordination for instinctive forms of brain activity, including singing and feeding. Behind the hemispheres is the cerebellum, on which the balance in flight depends.
The higher parts of the brain control the spinal cord.
The autonomic nervous system regulates the functioning of the digestive, circulatory, excretion and reproduction organs. It is also responsible for controlling the entire muscle group, including the heart muscle, as well as the iris.
The structure of a budgerigar, like the structure of any creature, is a very complex system. Ornithologists carefully study birds and analyze not only their behavior, but also professionally understand the work of the feathered organism.

Many hobbyists mistakenly project their needs onto those of the budgerigar, sometimes it can be just a waste of time and money, and sometimes a serious mistake can be made in keeping a bird.
For lovers of budgerigars, a more in-depth study of your pet is individual and optional. But even a cursory knowledge of your bird’s anatomy can help you understand behavior your pet and his needs.





