The dog’s muzzle is swollen – why and what to do with swelling

Contents
Possible Causes of Facial Swelling in Dogs
The main causes of edema can be divided into two groups:
General reactions – for these reasons, the entire muzzle or most of it swells. These are allergies, reactions to insect and snake bites, poisoning, post-vaccination reactions and reactions to medications, infectious diseases.
Local edema is manifested by severe swelling in one place: on the nose, lip, under the eye or on the cheek of the dog. And its causes are: neoplasms, inflammation of the roots of the teeth, chemical burns, trauma.
Let’s take a closer look at each of the reasons.
Food or contact allergies
Quite often, the reason that the dog’s muzzle is swollen is an allergy. The rate of development of edema depends on the amount of the allergen that has entered the body. The more allergen, the faster and brighter the edema appears. Usually the swelling due to allergies is symmetrical, spreads over the entire head, often accompanied by itching, but in general the animal feels good, eats and behaves as usual. Most often, an allergy in a dog is manifested by swelling of the muzzle to foods rich in chemistry, shampoos, cosmetics of the owner, plant pollen.

Reaction to insect and snake bites
Snakes, stinging and blood-sucking insects, when bitten, release poison in the form of an active protein. The animal’s body perceives this protein as foreign, and an acute allergic reaction begins. If the bite was in the head area, the dog’s muzzle swells, the nose swells. The bite site is hot and painful, the dog constantly scratches it, soft tissue necrosis may develop at the bite site.
Poisoning
Some plants have toxic components – oxalates, which cause a sharp swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, and the pet’s muzzle swells upon contact with them. Toxin poisoning is an emergency condition, you should immediately consult a veterinarian. If possible, try to recognize the toxin and tell the doctor (name and photo of the plant or poison packaging). Also, in addition to swelling, other symptoms may appear: heavy breathing, vomiting, confusion, diarrhea.

Post-vaccination reaction
The reaction is very similar to that of an allergy. This is the most dangerous complication in vaccination, as it develops rapidly and can occur at any age and in any dog. Most often in dogs, ears, nose, eyes swell. Salivation, asthma attacks, and loss of consciousness may also begin. At the first symptoms of an allergy, a veterinarian provides first aid. Usually, the reaction passes as quickly as it comes, so within a few minutes after the administration of the drugs, the dog will feel better.
Infectious diseases
The lymphatic system of dogs reacts to any infection that enters the body. And often the lymph nodes, as a result of this invasion, begin to swell and cause inflammation in their places of accumulation. The head and neck are no exception, inflammation of the muzzle and neck begins. Edema can be on one side or both, depending on the volume of the inflamed lymph nodes.
Reaction to medications
It proceeds according to the type of reaction to vaccination or allergies. It also appears a few minutes after the administration of the drug. Clinical signs can be different: swelling of the head and neck, bumps on the body, active breathing, redness of the mucous membranes, salivation.

Neoplasms
A tumor on the face of a dog, as a rule, does not appear abruptly. The edema grows gradually and may not cause discomfort to the pet for a long time. Just like in humans, there is no clear cause of cancer in dogs. Various types of sarcomas are the most common tumors. In the neoplastic process, soft tissues and bones can be involved, so the clinical picture will be different.
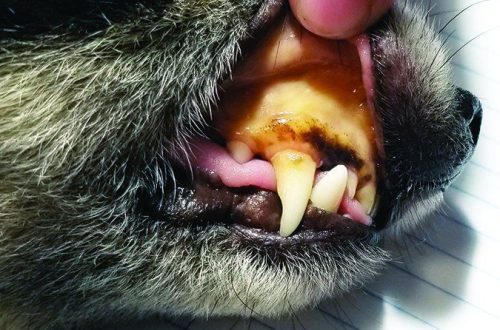
Inflammation of the roots of the teeth
If a dog has a sharp swelling of the cheek or swelling under the eye, then it is unlikely that she has a tumor. Most likely, the reason is in the teeth. When the teeth are inflamed, the roots are exposed or broken, then, just like in humans, purulent inflammation can occur – an odontogenic abscess. Dogs have a rather narrow jaw bone, so when the root of the tooth becomes inflamed, the swelling quickly grows under the eye or on the cheek in the projection of the diseased tooth.
Injury
Also, the cheek may swell sharply due to blunt trauma. After extensive blows, the blood vessels are injured and burst, resulting in hematoma and edema. Usually in a dog, swelling of the eye is most noticeable with injuries. When providing first aid, you can cool the injury site so that the vessels spasm and stop the formation of a hematoma.

Bacterial infections
If the injury is punctured or bitten, an abscess may form. An abscess is a limited cavity with purulent contents, its development is provoked by bacteria that have penetrated through the wound. It is distinguished from a tumor or hematoma by the presence of severe pain. It grows gradually, over several days, and every day becomes softer and hotter, until it bursts and pus flows out of it.
Concomitant symptoms
With swelling of the muzzle, the animal may have accompanying complaints that will help determine its underlying cause:
itching indicates an allergy or a bite;
pain indicates injury or bite;
depression and loss of appetite indicate an increase in temperature due to the development of inflammation or infection;
salivation, confusion, redness of the mucous membranes are formed due to an acute allergic reaction.

Diagnostics
Often, with swelling of the muzzle in dogs, to determine its cause, it is enough to take an anamnesis and remember that the new preceded the development of symptoms. Has the pet been in contact with something – plants, cosmetics, insects. Or he had a fight the day before, and there were injuries, bites. Diagnosis in the form of x-rays will be required if dental disease is suspected. To make a diagnosis, it is enough to examine the oral cavity, first determine the diseased tooth, take an x-ray and assess the degree of inflammation. If an oncological process is suspected, visual diagnostics is used – x-rays and computed tomography, as well as cytological examination of tissue samples. If you suspect the development of an infectious process, you will need to conduct a clinical blood test, examination and temperature measurement, tests for infections may be prescribed if there are specific complaints – diarrhea, vomiting, nasal discharge, cough.
Treatment
If the cause of complaints is an allergy, it is necessary to exclude the allergen from the life of the pet and give an antihistamine. If the cause of the edema is a bee sting, it is necessary to remove the sting, treat the bite site with chlorhexidine, peroxide or, in extreme cases, any alcohol solution and apply cold to the bite site. When bitten by a snake, you must try to suck out the poison and disinfect. Make sure that the dog does not scratch the bite and drink more. With the development of inflammatory processes due to the penetration of bacteria and viruses, treatment with antibacterial drugs is carried out, and symptomatic treatment is also prescribed, depending on the existing complaints.
One of the longest and most complex treatments is carried out with the development of the oncological process. Cancer treatment is not always possible, surgery and chemotherapy are prescribed. The stage at which the owner asks for help is very important. The longer treatment is left untreated and the larger the tumor grows, the less likely it is that treatment will be successful.
A considerable amount of treatment is also carried out with diseases of the oral cavity – dental procedures and antibiotic therapy are necessary.
If an operative visit to the veterinarian is not possible
Before helping at home, determine where exactly the swelling of the muzzle occurred, whether it prevents the dog from breathing, whether it is conscious. Try to remember what preceded the swelling – did you walk in the field, did you give something new from the food, or maybe the dog had a fight with someone. Examine the head for injuries, bites, pus, blood, signs of scratching. Once the preliminary cause has been determined, you can try to help.
For example, treat wounds if there are any, remove the sting if it is a bite. And give an antihistamine drug – it is best to keep it in the first aid kit (“Tavegil”, “Tsetrin”, “Zodak”).
When do you need urgent veterinary care?
Some causes of edema require urgent veterinary attention. If, in addition to swelling of the muzzle, you observe additional symptoms in the dog, such as discoloration of the mucous membranes, blue or pallor, repeated vomiting or diarrhea, a sharp change in body temperature, outflow from swelling, difficulty breathing, convulsions, confusion, you must urgently contact a veterinarian. clinic. In these cases, it is impossible to independently provide first aid at home, and every minute counts.

Prevention
Examine the pet after active games with other dogs and treat all wounds found.
Regularly inspect the mouth for the integrity of the teeth and the presence of tartar. Also, do not forget about the prevention of tartar – brush your teeth regularly.
Feed your dog the right way. Avoid allergens and too much variety of food components.
Avoid contact with poisonous plants and chemicals.
Regularly treat for external parasites.
If you decide to walk your dog in a new area, keep it on the leash and explore the local flora and fauna.
Have an annual checkup with a veterinarian.
Answers to frequently asked questions
October 22 2021
Updated: November 7, 2021