The cat’s coat turns yellow. Why and what to do?
However, it often happens that the coat of cats changes color, and this is most noticeable if your pet’s coat is white. So what can be the reason for the change in coat color?
The effect of food on wool
Do not underestimate the effect on the coat of an animal of the products that it feeds on. Very often, owners of white cats note that the coat begins to turn yellow from a new food or, if the animal is on natural food, and not on ready-made dry food, immoderate consumption of carrots or pumpkins.
Most often, if you change the food or limit the consumption of vegetables or fruits, from which the color of the coat changes, everything returns to normal, and after molting the cat pleases with its snow-white color.
Diseases
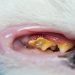
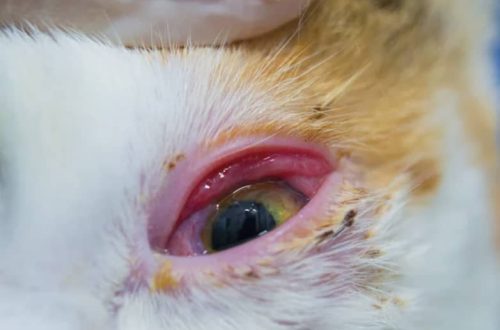
The situation is much more complicated if the color of the coat has changed due to illness. Cancerous tumors, especially skin cancer, jaundice, which usually occurs with liver diseases, allergic reactions, bacterial infections, can lead to a change in color, weakening or strengthening of skin pigmentation. Also, the formation of age spots – lentigo or loss of pigmentation – vitiligo leads to a change in coat color. Such changes are most often due to heredity.
Features of caring for the snow-white six
Another, very prosaic reason for changing the shade of fur in cats is banal dirt. Especially often the coat can change color if the cat has access to the street.
If dust and dirt can be overlooked on the dark coat of a pet, then every speck is visible on the snow-white coat. It is best to remove any dirt from the wool as soon as possible. How to do this depends on the degree of contamination. Sometimes, in order for the cat’s coat to become snow-white again, it is enough to brush off the dust with a damp brush and let the pet brush itself. However, if the pollution is serious, then in order for the coat to shine, a full bath is required.
The haircut of the animal can also lead to a change in the intensity of the color and color of the coat. Due to the fact that the hair grows back and the cat could experience severe stress during the haircut, pigmentation may be disturbed.
However, as well as the structure of wool. Instead of the rather stiff hairs that the cat had before shearing, soft, “cotton” hairs can grow. Before cutting a long-haired cat, it is worth weighing the pros and cons well. Perhaps, after the very first haircut, it will no longer be possible to return the coat to its original state, both its structure and the color of the pet will change.