Staphylococcus aureus in dogs: treatment, symptoms, danger to humans
Contents
- Features of the disease
- What contributes to the development of staphylococcus aureus in dogs
- Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in Dogs
- Complications of the disease
- How to identify pathology: diagnosis
- Treatment of staphylococcus
- Can a person get infected
- Home security measures
- Is there a vaccine against staphylococcus
- preventive measures
Features of the disease
Staphylococcus in dogs is caused by spherical bacteria – representatives of the genus Intermedius. They are present everywhere, therefore they are on the surface of the body of animals and humans and are normal. Any damage to the skin leads to increased reproduction of microbes. If the body’s immune system is strong, its cells quickly cope with the infection. Otherwise, the activity of bacteria causes an acute inflammatory process, accompanied by necrotic phenomena, the formation of pus.
Staphylococci are characterized by:
- resistance to external environmental factors due to the special structure of their cell membrane;
- the ability to synthesize enzymes and toxic compounds that facilitate penetration into the animal or human body;
- resistance to many antibiotics.
Most often, the disease occurs in the hot season. The risk group includes young, elderly and weakened dogs.
What contributes to the development of staphylococcus aureus in dogs
The cause of the development of staphylococcus aureus in dogs can be any disorder in the body that leads to a decrease in defenses, for example:
- malnutrition with a minimum content of vitamins;
- damage to the skin and / or mucous membranes;
- disruption of the liver;
- high blood sugar;
- internal and external parasites;
- past illnesses;
- hormonal changes.
If staphylococcus develops on its own, it is called primary. If it is a consequence of another violation, then they speak of a secondary form.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in Dogs
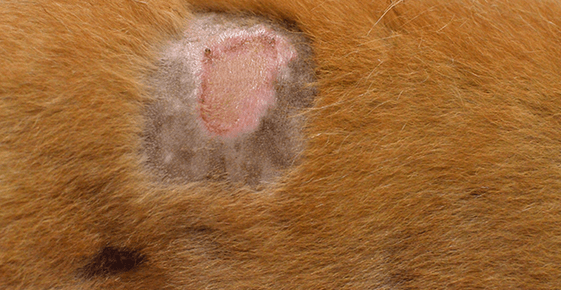
At the very beginning of infection, the symptoms of staphylococcus aureus are concentrated on the skin or mucous membranes. These include:
- round spots of pinkish or red color;
- pus;
- hair loss in the area of spots;
- severe itching;
- bleeding of damaged areas (the pet gnaws spots due to severe itching);
- boils (when bacteria penetrate into the deep layers).
Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous – in addition to the above symptoms, it causes disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. The clinical picture is manifested in vomiting, intestinal upset, the rapid onset of dehydration.
Complications of the disease
If even a small infected area is found, urgent action must be taken. Ignoring the disease can cause serious complications.
- The development of inflammation in the ears. The animal develops an unpleasant odor from the ear canal, and pressure on the auricle leads to a squelching sound. Simultaneously with the ears, the organs of vision, the nasal mucosa can become inflamed: characteristic discharge, swelling, redness appear.
- In bitches, staphylococcus is complicated by vaginitis, endometritis, pyometritis. Males suffer from inflammation of the prepuce. Pathologies quickly become chronic, which further complicates treatment.
- The spread of staphylococcus through the bloodstream is fraught with the formation of numerous boils, carbuncles, and inflammation of the follicles. Being located in the area of interdigital folds on the paws, they especially worsen the condition of the dog.
How to identify pathology: diagnosis
The basis for diagnosing staphylococcus aureus in dogs is an examination. After determining the symptoms and receiving information from the owner, the veterinarian can take smears for bacteriological culture. However, in most cases, the results of the study of the material do not provide accurate information about the microorganism, since, in addition to staphylococcus, it also contains other microbes. Among the additional methods used tests for the presence of allergies, detection of systemic disorders.
Treatment of staphylococcus
Treatment of staphylococcus in dogs is carried out in a complex. First of all, it is necessary to destroy the pathogen. To do this, the pet is injected with a staphylococcal bacteriophage. In addition, they activate the animal’s own immune system using non-specific and specific methods. In the first case, the use of immunostimulants is shown, causing an increase in the number of immune cells. With specific treatment, staphylococcal toxoid (active immunotherapy) or anti-staphylococcal serum (passive immunotherapy) is administered. The latter option is applicable only at the beginning of the development of pathology. Both cannot be used at the same time.
The complex of therapeutic measures necessarily includes antibacterial agents. Staphylococci quickly develop resistance to antibiotics, therefore, as a rule, several drugs are prescribed one after another or in combination (according to indications). Widespread in the treatment of staphylococcal infections received means: Enroxil, Ciflox, Enrosept, Quinocol, Baytril. In some cases, antibiotics continue for about a month or more.
Simultaneously, symptomatic treatment is carried out.
- To dry the wound surface, it is irrigated with various solutions. For this, enzymatic and antibacterial preparations are used: potassium alum, dermalot, tribask, lysozyme.
- Dimexide or novocaine lotions help relieve itching. For the same purpose, suprastin or tavegil is used.
- If the infection has spread to the inner ear, a powder mixture of novocaine and dermatol is instilled into the ear canal. With a high intensity of symptoms, novocaine is used intramuscularly.
- Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa requires not only taking antibacterial drugs, but also restoring microflora agents – probiotics, for example, lactobacterin.
- The introduction of vitamin complexes into the diet contributes to strengthening the immune system and increasing the body’s resistance.
If the cause of staphylococcus in a dog is diabetes, thyroid disease or allergies, then the appropriate medications are prescribed in parallel.
Can a person get infected
Is canine staphylococcus dangerous to humans? Expert opinions differ. Some argue that a sick pet is not infectious for the owner and animals living nearby. Others believe that the dog should be isolated from others.
Mainly, staphylococcal infection poses a danger to weakened organisms. If the family has small children, the elderly, those who have recently suffered or have any disease, then, of course, the risk of catching an infection is much higher. The same applies to our smaller brothers.
Healthy people and animals have nothing to fear, as a strong immune system quickly copes with a bacterial invasion. This explains the fact that staphylococcus aureus is normally located on the surface of our skin, but does not lead to illness.
Home security measures
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of staphylococcus infection from a dog to others, as well as to avoid the development of complications in it, if appropriate measures are taken from the very beginning of the disease:
- ensure the isolation of the pet;
- several times a day to process the room where the animal is kept with disinfectants;
- regularly replace the bedding with a clean one; when washing, use boiling for at least half an hour;
- wipe the dog during the day with a solution of tar soap (lightly, over the wool), do the same with nasal discharge – soap particles remaining on the surface of the animal’s body prevent further reproduction of pathogenic microbes.
Is there a vaccine against staphylococcus
To prevent the development of staphylococcal infection, a vaccine is used – ASP (polyvalent staphylococcal toxoid). Injections are given to whelping females 3 and 6 weeks after birth. This reduces the chance of infection of the puppies and the mother.
preventive measures
Unfortunately, it will not be possible to completely prevent the development of staphylococcus aureus in dogs, since any injury to the integumentary tissues provokes the growth of bacteria. However, through preventive measures, it is possible to reduce the likelihood of illness to a minimum.
- To reduce the risk of microbes penetrating deep into the body, the bloodstream and lymph, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system by all means: provide a diet rich in vitamins (if necessary, give them additionally) and regular long walks.
- If there are sick animals in the house, it is important to limit contact between them as much as possible. Dogs should not communicate with stray homeless relatives and cats.
- Follow your dog’s vaccination schedule carefully. Timely vaccinations will not only prevent many diseases, but also increase the immunity of the pet.
- Pay attention to the condition of the skin and coat of a four-legged friend: regularly carry out hygiene procedures, prevent the formation of crumpled wool, the appearance of adhering particles (grass, feces, and others), inspect the skin for injuries, especially in folds.
- It is necessary to identify and destroy external and internal parasites in time, use prophylactic agents against fleas and ticks, and regularly carry out planned deworming.
- If even minor damage to the skin or mucous membrane is found, immediately treat them with antiseptic preparations.
- In the summer, do not allow your pet’s body to overheat.
Stress can lower immunity, so it is recommended to protect your pet from negative situations as much as possible.
Attentive attitude to the pet and a quick response in case of detection of the disease will serve as a guarantee of the destruction of microbes and the prevention of their spread to others.