Staphylococcus aureus in dogs
Contents
Causes and causative agents of the disease
Staphylococcus aureus is a genus of bacteria widely distributed in the world. The reasons for the spread of this disease include the high resistance of these bacteria to drugs, the ability of staphylococci to synthesize a variety of toxins, each of which can act separately. All this complicates the use of various means of protection and prevention. Also, various scientific studies to the causes of the spread of staphylococcus aureus include environmental degradation, unbalanced feeding of pets, and most importantly, the uncontrolled use of antibiotics by animal owners.
As for specific pathogens, there are such types of staphylococcus in dogs as:
- saprophytic staphylococcus (Staphylococcus saprophyticus);
- epidermal staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus epidermidis);
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus);
- hemolytic staphylococcus (Staphylococcus haemolyticus);
- but most often in dogs coagulase-positive staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus intermedius) occurs.
It was previously believed that all of the above types of staphylococcus can cause disease, but thanks to the achievements of modern science, in particular phylogenetic analysis, it was found that in most cases it is Staphylococcusps eudintermedius, which is a subspecies of Staphylococcus intermedius, that causes clinical manifestations.
Old literature indicates that the disease can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, but at the moment it is believed that the confusion was due to the fact that pathogens are morphologically similar and old methods of laboratory diagnostics did not allow them to be distinguished from each other.
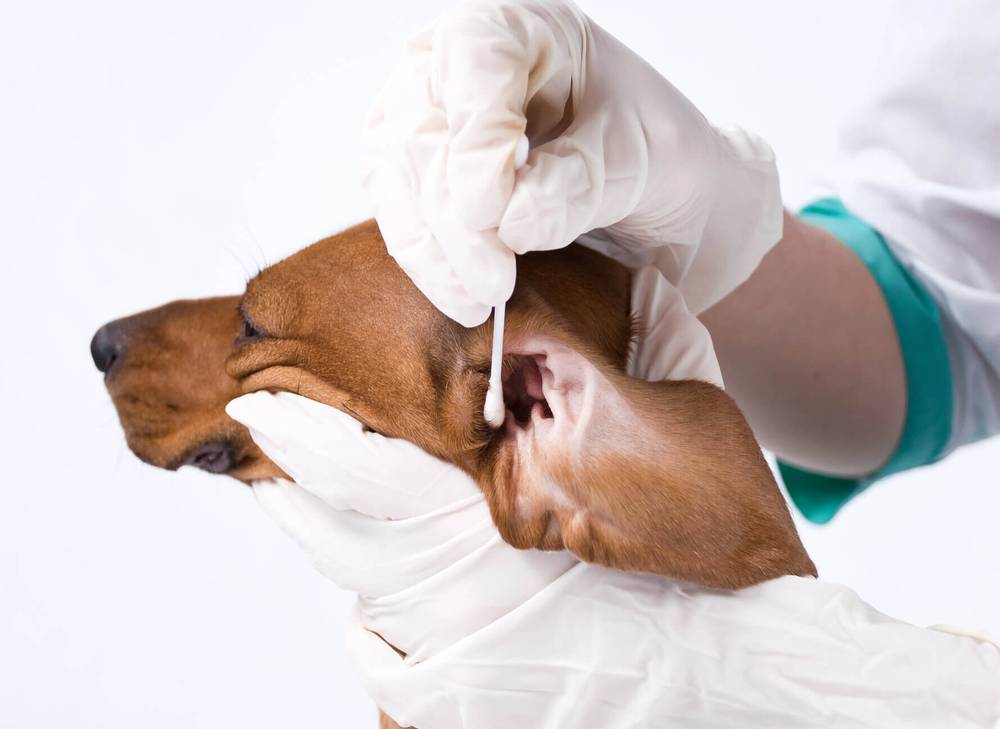
Fact: Staphylococcus aureus does not occur in dogs! (pictured is a pet with otitis media – one of the possible manifestations of the disease)
Hemolytic staphylococcus aureus in dogs deserves special mention. Hemolytic Staphylococcus is a bacterium that causes infectious and inflammatory reactions in the human body. The hemolytic microorganism got its name because of its ability to hemolysis, that is, to destruction. Hemolytic staphylococcus is a conditionally pathogenic bacterium for humans, it is capable of causing various purulent processes. Sometimes in the results of bacteriological culture, the owner meets such an expression as “hemolytic coagulase staphylococcus aureus positive in a dog.” But it only means the presence in the sowing of a microorganism that is part of the normal microflora of the dog, that is, it cannot cause infection, and you should not worry about such a result.
Can staphylococcus be transmitted from dogs to humans?
The most frequently asked question to a veterinarian is: is it possible to get staphylococcus aureus from a dog? Is a special type of staphylococcus aureus in dogs dangerous for humans – intermedius? Unfortunately, in this case, the answer is yes. Despite the fact that according to recent data it has been found that in dogs the disease is mainly caused by the colonization of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, and in humans by Staphylococcus aureus and epidermal, colonization of multidrug-resistant “canine” Staphylococcus aureus can also occur in humans. In this case, people with weakened immunity, vitamin deficiencies, as well as young children and the elderly should be careful.
To avoid infection during treatment and after contact with a sick animal, wash your hands thoroughly. You should be careful during the treatment process and not allow unwashed hands of a person to come into contact with his mucous membranes and wounds on the skin.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a staphylococcal infection depend on the type of microbe and the affected organ. At the moment, staphylococcosis is focal and generalized. The generalized form deserves special attention, which can lead to sepsis and death of the animal.
It is noted that staphylococcal infections can occur with a wide variety of symptoms: from chronic septic processes, accompanied by the development of abscesses on the internal organs, to various skin lesions that can manifest as conjunctivitis, cystitis, otitis media, rhinitis, pyometra, polyarthritis, gingivitis, etc. But it is worth noting that often the cause of the disease is not the very presence of staphylococcus in the body, but other causes.
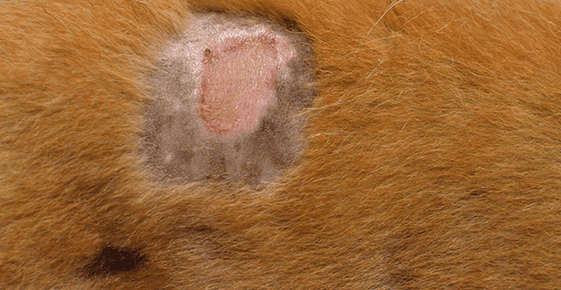
However, the most common manifestation of staphylococcus in dogs at the moment is a symptom of pyoderma, or purulent inflammation of the skin, that is, the dog will have cocci on the skin. This disease, depending on the severity, is divided into superficial and deep, and purulent otitis is also isolated separately. In young animals, pyoderma usually manifests itself in the form of pustules on the abdomen, chest, head and ears (acute and chronic otitis media with purulent discharge). With otitis, a fetid odor from the ears is noted, dogs itch, shake their ears. It should be noted that otitis media may be the only manifestation of the disease.
The generalized form may be the result of a lack of treatment of focal processes or develop against the background of other diseases with severe violations of the integrity of the skin and vascular permeability. Also, the generalized form can develop against the background of incorrect therapy – for example, when high doses of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are combined in combination with corticosteroid drugs, which leads to a pronounced decrease in the body’s resistance.
Diagnostics
In the modern world, it is not difficult to diagnose “staphylococcosis”. In skin forms of the disease – for example, in the presence of staphylococcus aureus in the dog’s ears or in case of skin lesions (when staphylococcus is found only on the skin), it is enough for a doctor to take a smear imprint cytology to make a diagnosis. But with systemic lesions, as well as with inflammatory diseases of the bladder (that is, when staphylococcus is found in urine tests), a comprehensive examination of the pet is required: a complete blood count, blood biochemistry and sampling from the affected organs for bacteriological culture with mandatory titration of the results to antibiotics.
Treatment of staphylococcus
How to cure staphylococcus aureus in dogs? It is important to understand that for the treatment of staphylococcus, it is imperative to use an integrated approach that includes both local and systemic therapy. Of course, one cannot do without a course of antibiotic therapy for this disease, but the owner must understand that it is simply impossible to choose a drug, dosage and course of antibiotic therapy at home – this should be done by a veterinary specialist. Also, in many cases of the disease, especially given the problem of the development of resistant strains of staphylococci, to determine the type of antibiotic, it is necessary to perform bacteriological culture with the determination of subtitration to antibiotics.
But in some diseases (for example, in the treatment of skin infections), empiric antibiotic therapy is also used, that is, symptomatic, when bacteriological sensitivity is not determined. The fact is that on the skin of dogs there is a large amount of microflora, including absolutely safe, so the results of sowing are very often false positive. In such cases, the doctor decides on the use of a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Also, unfortunately, in some cases, antibiotics have to be used for a long time (up to one or even two months in a row) to treat recurrent staphylococcal infections.
In addition to antibiotic therapy, drugs such as corticosteroid hormones or antihistamines (for example, to stop pyoderma due to food allergies), hepatoprotectors, choleretic drugs for the treatment of liver diseases, vitamin preparations for diseases associated with malnutrition of the animal are used to treat staphylococcal infections in dogs. , as well as specialized diets (for example, feeds with protein hydrolysate).
Topical therapy is used for skin manifestations of staphylococcus aureus and is always necessary in combination with systemic therapy in order to reduce treatment time and reduce the spread of surface bacteria. Local treatment includes the use of antiseptics with drying and disinfecting properties. One of the most popular drugs is a 0,05% solution of chlorhexidine, as well as miramistin, furacillin. With extensive skin lesions, the use of special veterinary shampoos containing a 4-5% solution of chlorhexidine is justified. With purulent dermatitis, antibiotic sprays, such as terramycin spray or chemi spray, have a good therapeutic effect. In the presence of staphylococcus aureus in the ears, ear drops with antibiotics are used. But it is important to remember that the use of local remedies in many cases is not enough.
Of course, dogs that develop staphylococci in the background of other diseases need to receive appropriate specific treatment for the underlying disease in addition to the treatment of staph infection. For example, with purulent inflammation of the uterus (pyometra), surgical treatment of this disease is used.
It is interesting to note that the treatment approaches for S. aureus in humans and S. intermedius in dogs are not significantly different.
Possible complications
Possible complications of staph infection in dogs include the development of antibiotic resistance. Unfortunately, at present, there is a tendency for the widespread spread of multi-resistant staphylococcus aureus, that is, resistant to conventional antibiotics, throughout the world. As a result of research, it has been proven that in dogs affected by such staphylococcus a multidrug-resistant staphylococcus aureus can be isolated for a whole year after recovery, therefore, such pets should be considered as a potential source of the spread of this dangerous infection.

staphylococcus aureus in puppies
Special attention deserves staphylococcus aureus in puppies. The symptoms of staphylococcus aureus in a puppy include both systemic disorders (vomiting, diarrhea) and local manifestations (dermatitis). The development of the disease in puppies is primarily associated with the age-related characteristics of the immune system and metabolism, which contributes to the development of various infections.
Systemic disorders are accompanied by gag reflexes, frequent loose stools, which can lead to severe dehydration of the dog’s body. Even death is possible. Cases are described when outwardly absolutely healthy litter of puppies suddenly died. In some cases, a rash is noted in the abdomen and groin, an increase in visible lymph nodes.
It is also worth noting that the mechanism of action of drugs in puppies is significantly different from adult animals. For example, it is not recommended to give puppies oral antibiotics because they can negatively affect the intestinal microflora. Also, unfortunately, it must be taken into account that a common skin infection in a puppy can lead to a systemic disease (sepsis). Therefore, the treatment and prevention of diseases in puppies should be treated with particular care. The only positive point is the fact that with proper treatment, puppies recover much faster than adult animals, and accordingly, they need a shorter course of antibiotic therapy.
It was also previously believed that the cause of the development of purulent conjunctivitis in puppies is Staphylococcus aureus, since it was found in crops from the conjunctival sac. But recently it has been proven that bacteria are not the primary cause of the development of conjunctivitis, it is always necessary to look for another etiological factor – it can be an allergy, mechanical damage, anatomical features (for example, ectopic eyelashes), etc.

Methods of prevention
For the prevention of staphylococcal infection, it must be understood that this bacterium belongs to the conditionally pathogenic microflora, that is, all healthy animals normally have staphylococcus aureus. It leads to the disease only under certain circumstances. Therefore, proper maintenance of dogs is especially important, including complete nutrition (industrial food or homemade food balanced on consultation with a nutritionist), hygiene, sufficient walking, and sterilization of animals that are not involved in breeding.
Unfortunately, at the moment there is evidence of long-term survival of multidrug-resistant staphylococcus on environmental objects (up to 6 months after recovery of pets). Therefore, in addition to treating the patient himself, special attention should be paid to the disinfection of the environment.
And remember that only correctly performed diagnostics and well-prescribed treatment will allow you to cure your pet and not encounter antibiotic-resistant microflora!
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
11 September 2020
Updated: February 13, 2021





