Skin diseases in dogs: photos of diseases and treatment

Consider the main skin diseases in dogs with descriptions and photos of diseases.
Contents
Skin Diseases in Dogs: Essentials
Skin diseases in dogs are very common in veterinary practice.
Many diseases have very similar clinical symptoms, so it is impossible to make a diagnosis only by visual examination.
Often the treatment is lifelong and requires regular monitoring by the attending physician.
The main symptoms are red spots on the skin, pimples, pustules, scratching, bald patches, peeling.
Before examining a doctor, you should not carry out any skin treatments on your own, as this will blur the picture and make it difficult to make a diagnosis.
To prevent skin diseases, it is required to keep the pet in a clean room, carry out regular treatments for parasites, and avoid contact with animals suspicious of skin diseases.
Popular symptoms
There are some of the most common symptoms that will indicate a skin condition in a dog.
Red spots on the dog’s belly
Red spots on the abdomen in dogs can be found very often. In the abdomen and groin, they are especially noticeable, since the hair there is not so thick. Often they can be observed in allergic conditions as a response of the skin to the entry of an allergen into the body. We will discuss the different types of allergies in more detail below. Ring-shaped red spots on a dog’s body will indicate bites from parasites such as mosquitoes and midges, especially they prefer hairless areas of the skin.
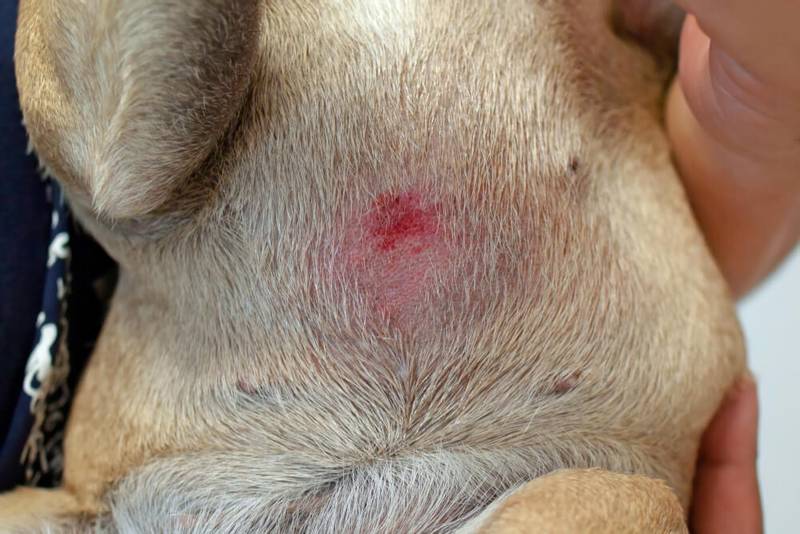
dog skin ulcers
An ulcer is a deep inflammatory lesion of tissues with a violation of their integrity, the ulcer heals mainly with the formation of a scar. Sores on the stomach, back and other parts of the dog’s body, similar to ulcers, will most likely indicate a deep infection of the skin. Also, ulcers are possible due to chemical burns, impaired blood supply or nerve conduction in this area. Malignant tumors can often look like ulcers.
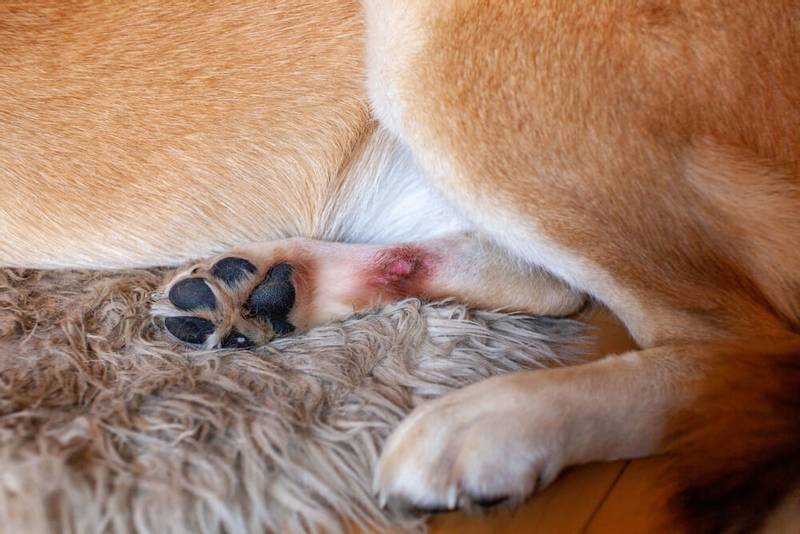
Irritation in the dog’s stomach or groin
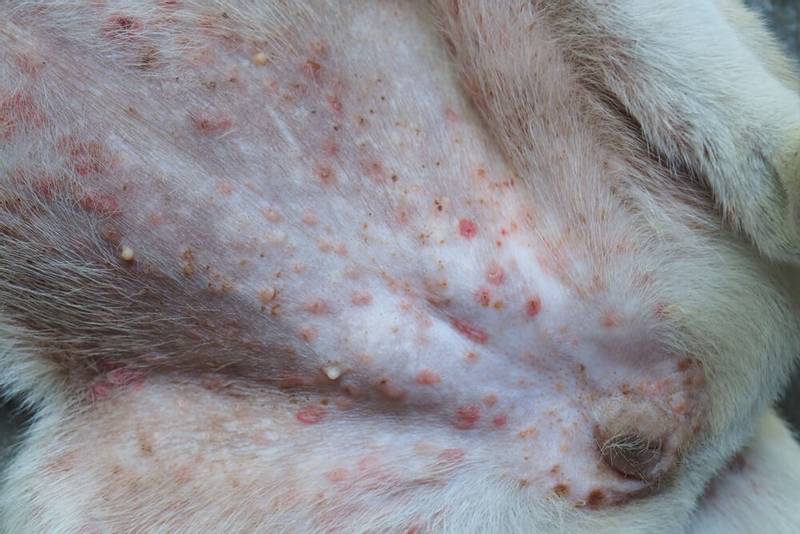
Irritation should be understood as the presence of papules (pimples) and pustules (pustules) on the skin. Most often, the appearance of acne on the dog’s body is a sign of superficial bacterial inflammation of the skin. But this can also be the case with a parasitic disease, an autoimmune process. In atypical cases, even lichen may look like this. Diaper rash can appear in overweight dogs with a large number of folds (shar pei, bulldogs) due to infection in the folds of the skin. Sometimes the only treatment is plastic surgery.
Dog has white patches on nose
A change in the color of the nose to white can be due to several reasons.
“Winter nose”
Some dog breeds are prone to lightening of the nose in the winter season, these include the Labrador, Husky, Golden Retriever, Shepherd Dog, Bernese Mountain Dog and some others. This condition is popularly called the “winter nose”, and it is associated with a reduction in daylight hours and a restriction in the production of melanin by the skin. During the summer months, these dogs’ noses return to their normal color.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is an immune system disease in which pigment cells stop being produced in certain areas of the body. This condition is irreversible, but does not require treatment, as it does not harm the body.
Lupus
An autoimmune disease such as discoid lupus erythematosus may be the cause of the discoloration of the nose. With lupus in a dog, you should expect other symptoms on the skin, crusts on the nose, scrotum and pads. This condition requires serious treatment.
Uveodermatological syndrome
This condition is also related to the dog’s immune system and occurs due to the destruction of skin pigment cells by immune cells. The dog has a whitening of the nose, skin and hair around the eyes, lips, and then other parts of the body. This is accompanied by eye damage with inflammation of the choroid.
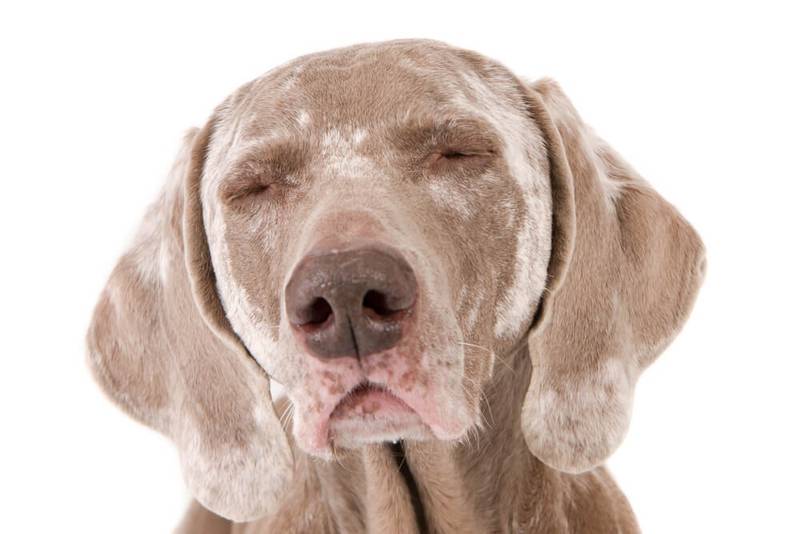

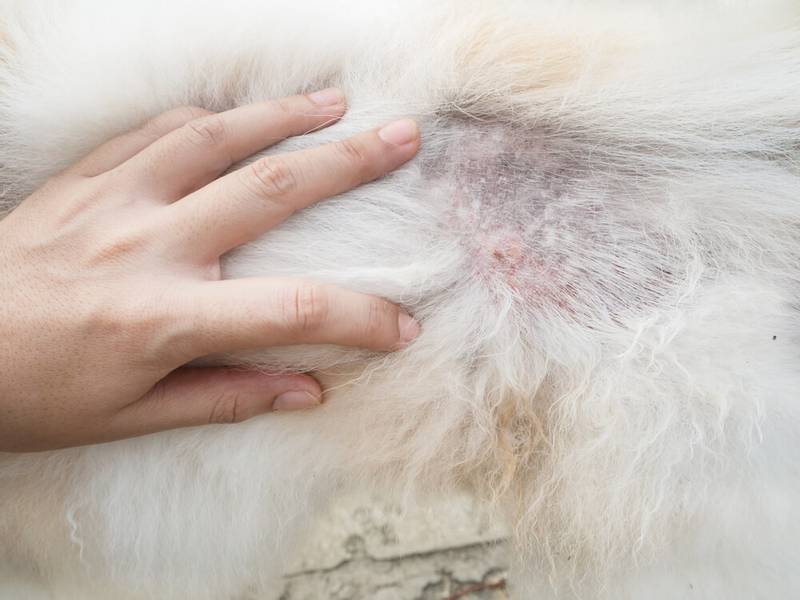
Dog’s skin is flaky and hair is falling out
Hair loss, which is accompanied by peeling, is often a sign of dermatophytosis (lichen). Usually the lesions are localized at the onset of the disease, but without treatment they begin to spread throughout the body. We will discuss this disease in more detail below. Also, hair loss with peeling is characteristic of various endocrine diseases, while bald patches will most often be located symmetrically throughout the body. In dogs with plush coats such as Spitz, Chow Chow, Husky, hair loss should be suspected of Alopecia X.
Bacterial skin diseases in dogs
superficial pyoderma
Superficial pyoderma in most cases is not actually a disease, but only a manifestation of some other root cause. Most often, the primary disease in dogs with pyoderma will be allergies, endocrinopathies, minor injuries. The main causative agent of pyoderma is staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus pseudintermedius), even on normal skin, a small amount of this bacterium can be found. Under favorable conditions, staphylococcus begins to multiply and cause changes in the skin. Diagnosis is based on characteristic clinical signs and results of cytological examination from the lesions.
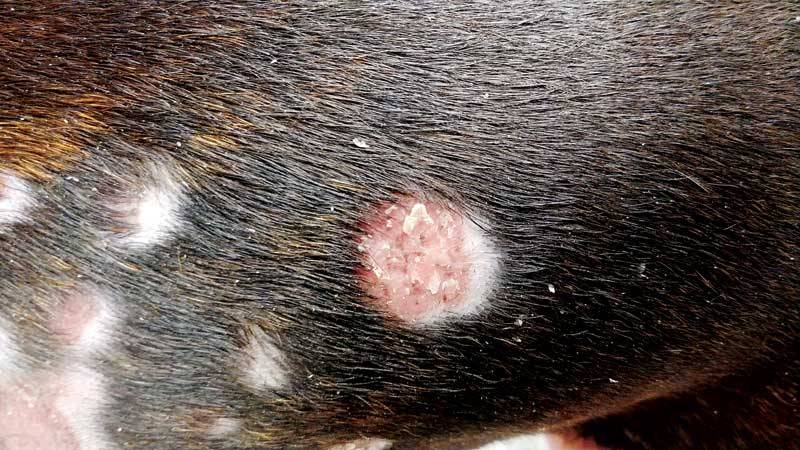
Symptoms
With superficial pyoderma, dogs often have pimples on the body, pustules, hairless skin, crusts, scales, and discoloration of the skin. Lesions similar to prickly heat in a dog will also indicate a bacterial infection in most cases. Often the dog will itch intensely, scratching himself, causing damage and further aggravating the situation.
Treatment
For the treatment of pyoderma, it is first necessary to find the cause that caused it. To cope with bacterial overgrowth, antibacterial drugs are used. First of all, local remedies with chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide, such as shampoos, gels, solutions are prescribed. If the lesions are extensive, then systemic antibiotic therapy with a long course may be prescribed.
deep pyoderma
Deep pyoderma is also a secondary disease, but differs in damage to the deeper layers of the skin. Here, the root cause can often be the defeat of the dog with demodicosis, since this mite multiplies in the hair follicles. Also, the deep layers are involved in the process if the treatment of superficial pyoderma was not started on time. Chemical, thermal burns and other injuries contribute to deep infection of the skin.
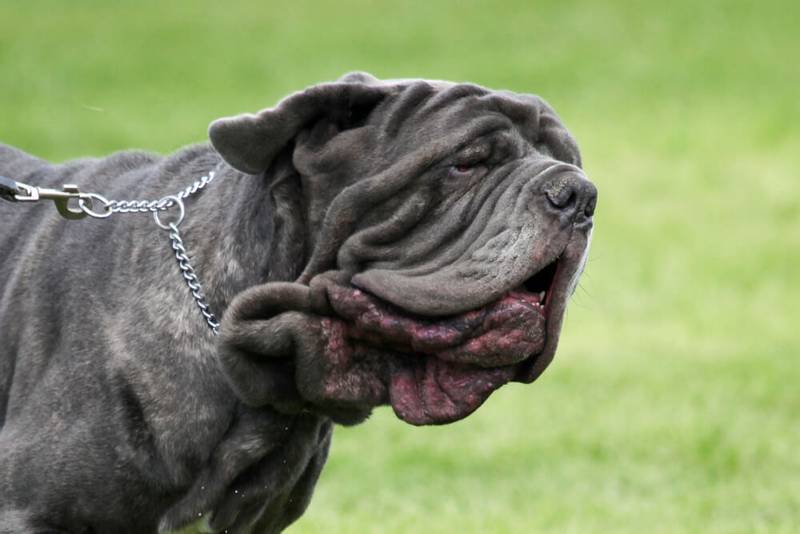

Symptoms
The lesions will be more pronounced than with a superficial infection. In addition to the typical rash on the dog’s abdomen, one can note the appearance of boils, ulcerations, fistulous openings with expiration.
Treatment
Treatment usually combines the use of topical agents and systemic drugs. Shampoos, solutions, gels are used. Of the systemic drugs, antibiotics are prescribed based on the result of a cultural study. Antibiotics should be taken in dermatological, that is, in higher dosages, the course is usually at least 4 weeks and another 2 weeks after complete recovery. Anti-itch and anti-inflammatory drugs may be used.
Skin diseases in dogs caused by parasites
Demodecosis
Demodicosis is a disease caused by the canine skin parasite Demodex canis. It is a mistake to call Demodex a subcutaneous parasite, since this mite lives in the hair follicles of the skin of dogs, and not under the skin. Normally, this mite is found in single quantities on the skin of all dogs, but it begins to multiply intensively and cause disease only under favorable conditions, most often against the background of a decrease in the overall immunity of the body. The diagnosis is confirmed by conducting deep scrapings from all lesions.
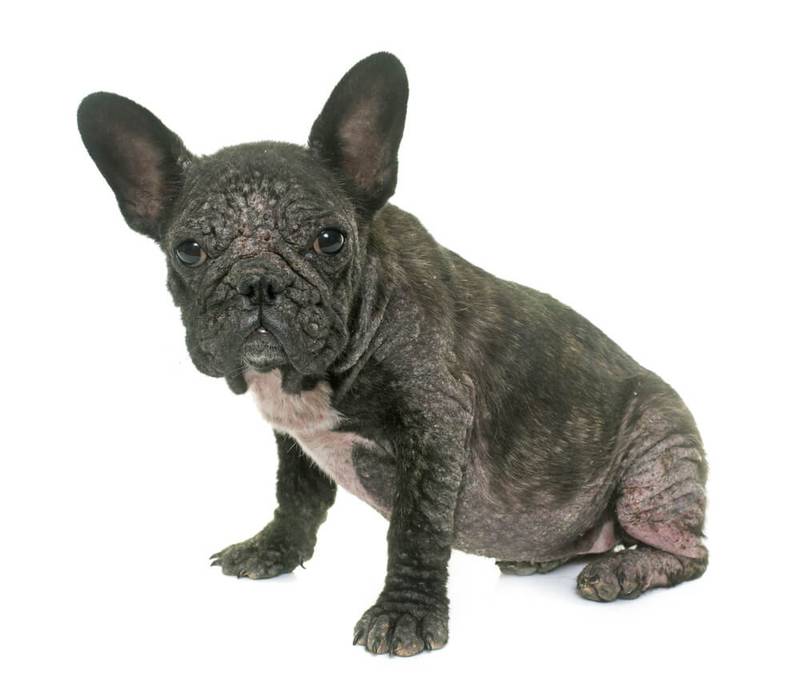

Symptoms
The main symptoms are patchy hair loss and peeling. Often you can find hair loss around the eyes, the so-called “glasses”. Black dots on the body (comedones) are clearly visible on hairless areas of the body. At the initial stage, the dog will not itch, but without treatment, a secondary infection joins demodicosis, and it will already cause itching. Then it will be possible to notice the appearance of pimples, pustules, scratching, redness of the skin, the dog will behave restlessly.
Treatment
In mild cases, treatment of demodicosis is not required, since when immunity is restored, it is able to go away on its own. With a generalized form, treatment is required. Recently, modern drugs from the isoxazoline group have been used, even a single dose of them can defeat this disease. Sometimes taking drugs is required longer, as well as additional use of antibacterial agents locally or systemically. All dogs that have ever been ill with generalized demodicosis should be withdrawn from breeding, as there is a high probability of transmission of this disease to offspring.
Sarcoptic mange
Sarcoptic mange in dogs is caused by the scabies mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It is highly contagious between dogs and is widespread among street dogs. Diagnosis is often made on the basis of clinical signs alone, since the detection of a tick in a scraping is not very likely. Successful treatment can also confirm the diagnosis.
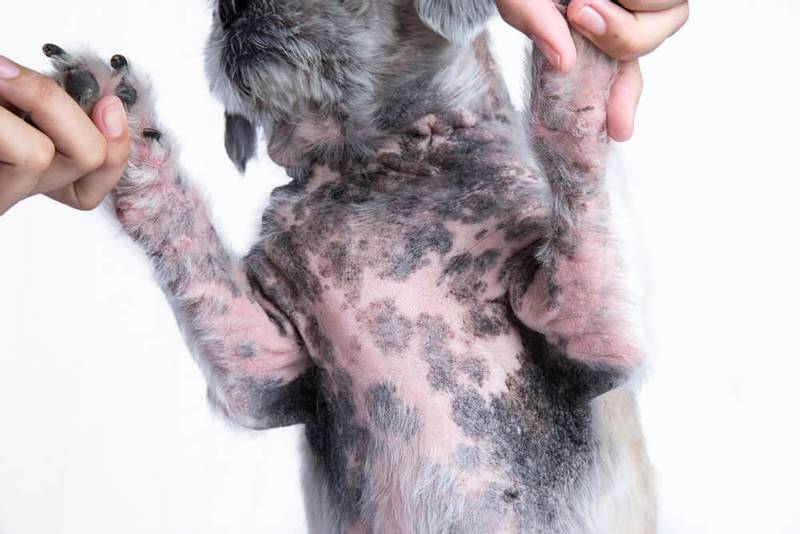
Symptoms
Favorite breeding sites for this tick on a dog are the areas of the ears and muzzle. The skin in these places becomes dark, dense, covered with crusts and scabs, hair falls out. The dog experiences severe itching, combs itself. Without treatment, the tick spreads to other parts of the body and is able to capture the entire skin of the animal.
Treatment
For treatment, the same means are used as in the fight against demodicosis. These are isoxazoline preparations, topical antibacterial agents, and exfoliating shampoos to remove crusts. Prevention is the absence of contact with sick animals and regular treatments with agents against external parasites.
Fungal skin diseases in dogs
Dermatophytosis
Dermatophytosis, or simply lichen, is a fungal skin disease of dogs. Common in street dogs, but not highly contagious. Infection will depend on the immunity of each individual animal. There are four main causative agents of lichen in dogs: Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Microsporum persicolor. Diagnosis is by fluorescent imaging, trichoscopy, PCR testing, and culture.
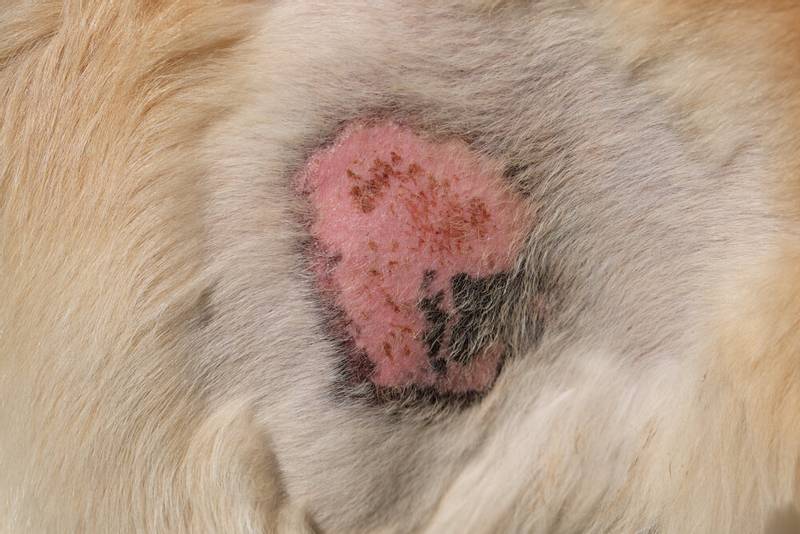
Symptoms
Most often, with lichen, foci of bald patches with peeling will be noted. Localization may be different; once on some part of the body, the fungus spreads further along the skin, and as a result, the dog may become completely bald. There is an atypical form of lichen in dogs – kerion. Kerion looks like a rounded, pink plaque raised above the skin surface. Often it is located on the nose of a dog and can be mistakenly called a pimple. Itching at the initial stages is absent. After some time, the secondary bacterial flora joins the fungus, the lesions may turn red, with a lot of pimples, the dog will begin to scratch himself.
Treatment
Most often, local and systemic treatment is used simultaneously. Of the local preparations, solutions of hydrogen sulfide lime and enilconazole are used. Of the systemic drugs, the choice falls on itraconazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine. It is also imperative that the premises be treated to eliminate the spread of spores in the environment. Means in the form of smoke bombs with an antifungal active ingredient are well suited. Smoke settles in all the smallest cracks, which improves the quality of cleaning.
Malassesious dermatitis
Malassezia dermatitis is caused by the yeast fungus Malassezia spp. Most often, this is a secondary disease that occurs against the background of allergies, endocrine diseases, demodicosis, seborrhea. Malasseziozny dermatitis very often accompanies atopic dermatitis. Normally, all healthy dogs have these fungi in single quantities. But under favorable conditions, they multiply and cause certain symptoms. The diagnosis is made by performing a cytological examination of skin lesions.
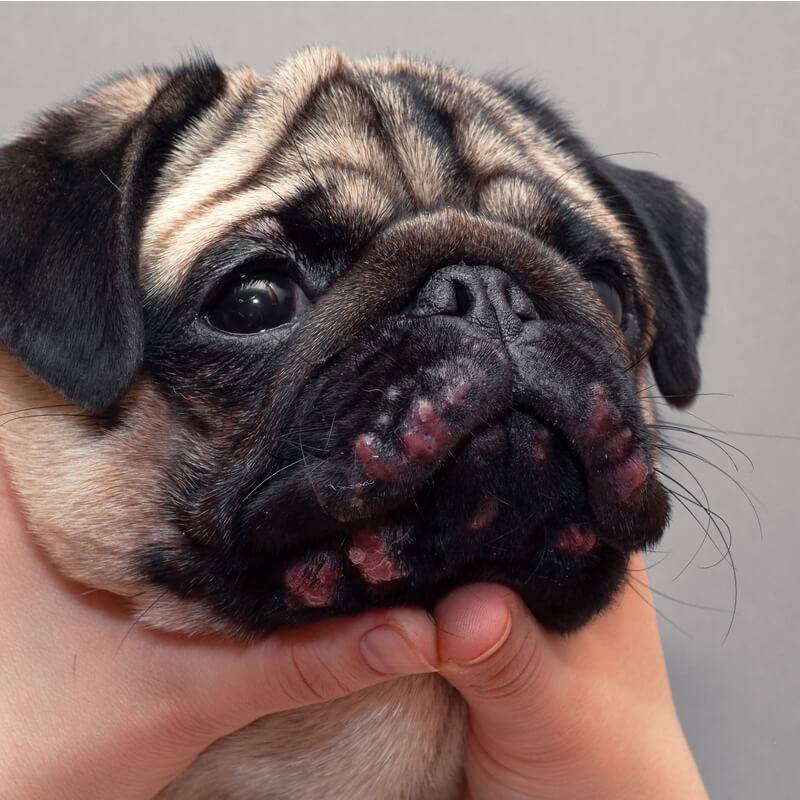
Symptoms
In most cases, Malassezia dermatitis will be itchy and the dog will scratch and lick the affected area. A rash in a dog with fungal dermatitis is rare, unlike bacterial dermatitis. The characteristic signs of this particular disease should be considered a change in the color of the skin and coat to rusty, thickening of the skin, as well as a specific sweet smell.
Treatment
First of all, it is necessary to establish the disease, against which Malassezia dermatitis developed, and take it under control. For the treatment of fungal overgrowth, local preparations are used, most often in the form of shampoos. A 3% vinegar solution may be used. With a significant lesion, systemic antifungal drugs are added.
Other skin conditions
Allergy
There are three types of allergies in dogs:
Allergy to flea saliva;
food allergy;
Atopy.
Allergy to flea saliva, or flea allergy dermatitis, is the most common type of allergy in animals. Flea saliva is a protein, and in sensitive animals, if it enters the bloodstream, it causes characteristic symptoms. At the same time, finding a flea on a dog can be extremely difficult, since their habitat is not the skin of animals at all, but the environment. Only 1 flea bite can cause a reaction. Food allergies, on the other hand, are the rarest type of allergy. Despite the common misconception about the high allergenicity of chicken in the diet of animals, dietary protein very rarely causes any reactions. Atopy is the second most common type of allergy. Allergens are various air components – dust, pollen, bed mites, etc. There are no tests that can confirm the type of allergy. The diagnosis is made only by exclusion.
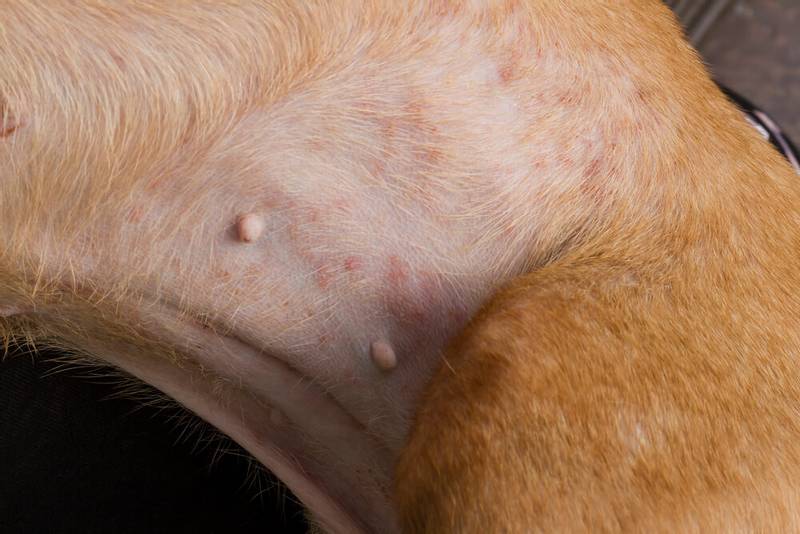
Symptoms
For all three types, the symptoms will be extremely similar. The first sign of an allergy is itching. They will be accompanied by 80-90% of all cases. On the body of the dog, redness, bald patches, scratching, pimples, pustules, crusts, scales can be noted. Brown spots on the dog’s abdomen, that is, darkening of the skin, will be the result of a post-inflammatory reaction already.
Treatment
Treatment in most cases is both a method of diagnosis. Antiparasitic treatments are used to treat and exclude allergies to flea saliva. Most often, drops are used at the withers, preferably with a repellent effect. For diagnostics, drops are used for at least 2-3 months without interruption, with a good treatment effect, they remain permanent. Also, at the same time, the premises where the dog lives are treated, since fleas like to settle in the genital crevices, in rugs, under the baseboards. To treat the premises, special solutions are used for washing floors and surfaces, as well as antiparasitic sprays. If, against the background of these manipulations, the effect is weak, the dog still itches, there are lesions on the skin, then the exclusion of food allergies begins. For this, a special elimination diet is prescribed. It includes either foods that the dog has never eaten before, or foods based on protein hydrolyzate. If the animal improves, and after the return of the old food, a relapse occurs, then the diagnosis of food allergy is established. Now you need to pick up a new food, and on this the symptoms in the animal will disappear.
If all of the above measures fail, the dog is diagnosed with atopy. Its treatment is extremely difficult, basically all measures are only supportive in order to eliminate itching, inflammation, infection and dry skin. Allergen-specific immunotherapy can also be used for treatment. An individual vaccine is made for the animal, which will help the body not react to the identified allergens. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to achieve 100% effectiveness, and such vaccination must be constantly repeated throughout life.
Autoimmune diseases
There are many different skin diseases in dogs caused by autoimmune processes, most of which are still not fully understood. Some of the most common conditions can be noted:
Pemphigus foliaceus
A disease of the immune system in which one’s own immune cells attack skin cells. It is more common in Akita and Chow Chow dogs, although it can occur in other breeds.
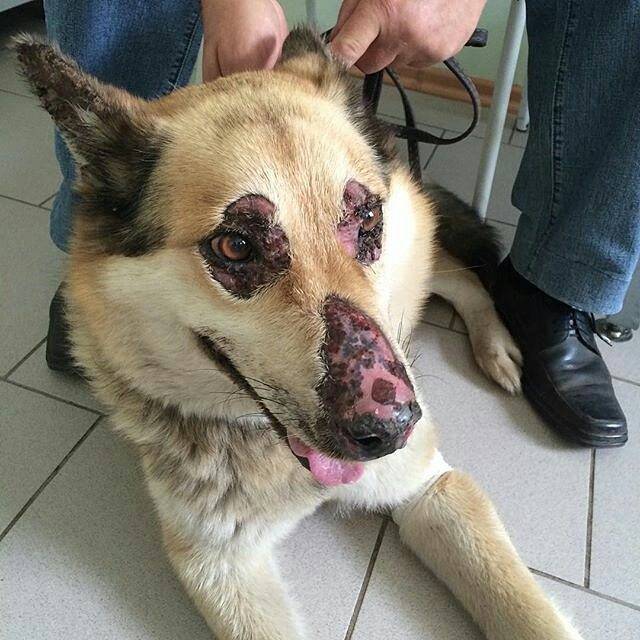
Symptoms
The main symptom of this disease is the detection of pustules throughout the body. Often this is difficult to do, since the pustules are covered with thick hair and burst easily. Secondary lesions are noted more often – crusts, scales, bald patches. Typical localization around the eyes and on the nose. Sometimes the only sign is thickening of the paw pads with crusts.
Treatment
The main treatment is to suppress the body’s immunity, for this, glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants are prescribed. Antibacterial shampoos are used topically to soak the crusts and eliminate the infection. With a serious infectious process, antibiotics are prescribed orally.
Discoid lupus erythematosus
It also occurs due to a malfunction in one’s own immune system, there is no breed predisposition.
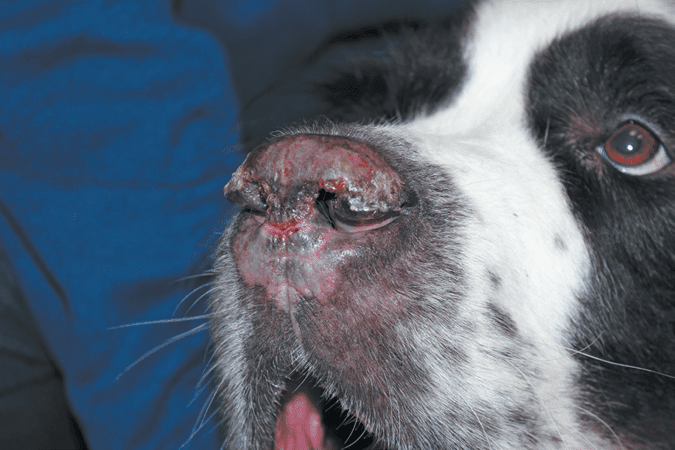
Symptoms
The main symptoms include whitening of the nose, the formation of crusts and sores on it and next to it. The skin and hair around the eyes, lips, and fingertips may also lighten.
Treatment
Treatment also consists of suppressing the immune system and ruling out infection. If the lesions are very small, you can try to get by with only local creams.
Can dogs get skin diseases?
First of all, a contagious disease common to dogs and humans is lichen. In order not to get infected, you must wash your hands before and after communicating with an infected dog, try to contact it only when necessary, do not let the dog into your bed and limit its movement around the apartment as much as possible. If you find any lesions on your skin, immediately consult a doctor.
Bacterial skin infections are dangerous only for people with reduced immunity; it is almost impossible for healthy people to get an infection from a dog. Sarcoptic mange can cause pseudo-scabies in humans, but it cannot multiply on human skin and does not need treatment. Allergic and autoimmune skin diseases cannot be contagious, but can be inherited in dogs. It is necessary to think before letting such animals into breeding.
August 18 2021
Updated: September 16, 2021