Pulmonary edema in cats and cats
Contents
Pulmonary edema – what is it
Pulmonary edema is not an independent disease, it is a consequence of other pathologies. Normally, the alveoli of the lungs (thin-walled bubbles that come into contact with the capillaries) are filled with air: oxygen when inhaling and carbon dioxide when exhaling. Between them and the capillaries there is a constant exchange of gases, due to which the blood is continuously saturated with oxygen.
Under various pathological conditions, the alveoli are filled with fluid, which disrupts gas exchange and prevents oxygen saturation of the blood. The tissues do not receive the right amount of oxygen, hypoxia develops. All cells of the body are sensitive to oxygen deficiency, but the nervous and cardiovascular systems are especially affected. Prolonged hypoxia as a result of pulmonary edema can lead to the death of a significant number of brain neurons, and later to the death of the animal. In some cases, this process occurs rapidly.
Types of pulmonary edema in cats
According to the nature of progression, the following types of pulmonary edema in cats and cats are distinguished:
- lightning fast – develops rapidly, often causes the death of a pet;
- acute – also characterized by a rapid course, but, unlike the previous one, timely treatment and treatment can save the life of a cat;
- subacute – it is characterized by alternating episodes of impaired lung function and remission;
- chronic – can persist for years.
It must be borne in mind that the nature of the development of edema cannot be predicted, since this process depends on many conditions: the age of the cat, the characteristics of immunity, the characteristics of the provoking disease, living conditions and other parameters. Sometimes the pathology develops so quickly that only a few minutes remain for first aid.
Causes of pulmonary edema in cats
Causes for which a cat or a cat can experience pulmonary edema are divided into cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic. The first group includes congenital and acquired pathologies of the cardiovascular system: malformations, hypertension, cardiosclerosis, pulmonary embolism, heart failure, heart valve dysfunction, and others.
The second group of factors that provoke pulmonary edema in cats include:
- chest injuries (when falling, for example, from a balcony or from a window);
- allergic reactions to medicinal substances, plants, poor-quality feed;
- intoxication with toxic compounds from the external environment or internal, arising from certain diseases (neoplasms, pathologies of the urinary system, viral and bacterial infections);
- lack of protein in the body due to errors in the pet’s nutrition, diseases of the liver, kidneys, metabolism;
- hormonal pathologies, often with obesity.
Also, pulmonary edema can occur as a reaction to anesthesia, for example, during castration.
Symptoms of pathology
It is important that the owner notices the symptoms of pulmonary edema in time and quickly delivers the animal to the clinic. You need to be wary if the cat has the following signs of pathology:
- frequent breathing, shortness of breath;
- breathing is carried out by the stomach, which is visually very noticeable (the mouth is most often open);
- the mucous membrane of the oral cavity (sometimes the skin) acquires a blue tint;
- the cat coughs, expectorating a liquid secret;
- the pet breathes, widely spreading the limbs, over time, there is heavy abdominal breathing in the position lying on its side;
- wheezing is heard during the cat’s breathing.
Especially clearly the symptoms are determined in the acute form of pulmonary edema. Even with complete immobility, the cat is worried about coughing and severe shortness of breath. In severe cases, the pet may develop a foamy discharge from the mouth with an admixture of blood or a reddish color. The animal needs urgent veterinary care!
If the pathology is chronic, its detection is associated with certain difficulties. In the supine position, there are no signs of a violation, but they appear only with active movement. In this case, the cat, most often, has an open mouth, nostrils are swollen. She can suffocate, stop to rest, take a breath of air. If you notice similar symptoms in your pet, immediately take him to the veterinarian, as the pathology can worsen at any moment.
First aid
If your cat begins to choke, foam comes out of the mouth, the mucous membrane suddenly becomes bluish, do not panic. Of course, ideally, an animal needs an oxygen mask, but not everyone has one. You can simply open the window and bring your pet to it.
Calling the veterinarian or going to the clinic yourself, lay the cat on its side, do not let it rise so that oxygen, which is already supplied in insufficient quantities, is not wasted on unnecessary processes. On the way to the clinic or while waiting for the doctor, stroke your pet, talk to him.
Do not give your cat any medication without a prescription. It is often advised to give the animal a diuretic, such as furosemide. You should not do this – if the body is dehydrated, then such remedies will lead to deterioration.
Diagnosis of pulmonary edema in cats
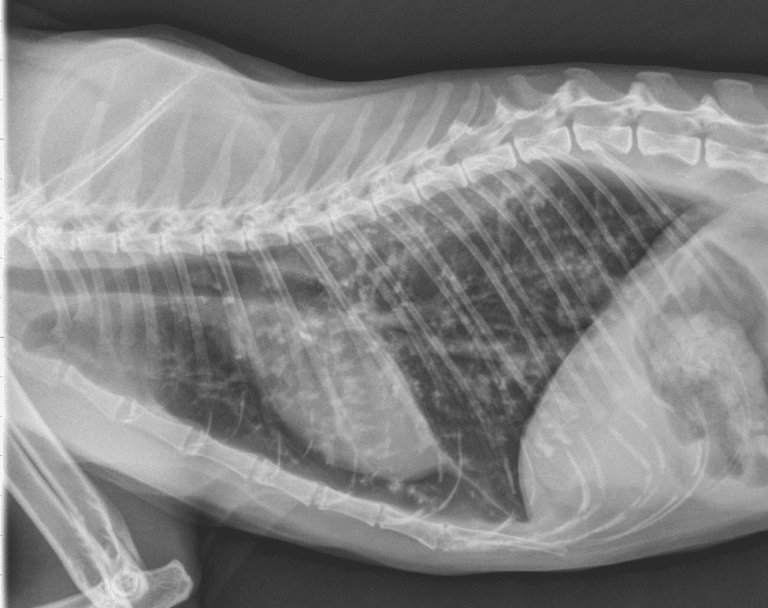
Pulmonary edema in cats and cats is diagnosed with a chest x-ray. In the presence of pathology, direct and lateral projections show a distinct blackout in the lung area. If the edema is cardiogenic, the image shows an increase in cardiac tissue.
In parallel, the doctor conducts a survey, specifying the duration of the onset of symptoms, the nuances of nutrition, living conditions, and so on. The veterinarian examines the animal, listens to breathing with a stethoscope, determines the heart rate. In addition to x-rays, a specialist can prescribe diagnostic procedures:
- blood tests, urine tests (general, biochemical);
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- ECG;
- pleural puncture.
According to the results of the examination and examination, the cat will be prescribed appropriate treatment – at home or in a hospital.
Cat chest x-ray
Treatment
If the cat’s condition is critical, he will be given first aid without waiting for the examination data. This may be drug therapy in the form of injections, the imposition of an oxygen mask. As a rule, the drugs used quickly relieve swelling and restore the animal’s breathing. If the cat is acting restless or aggressive, she will be given an injection of a sedative.
It is unacceptable to forcibly lay a cat, give her water or food. An animal in this state must be provided with complete rest, therefore the owner himself must keep a balanced attitude.
The direction of treatment depends on the severity of pulmonary edema, as well as on the factor that provoked the pathology. The complex of treatment, as a rule, includes diuretic drugs (you can’t give it yourself at home!), oxygen therapy using a special oxygen pillow. In some cases, they resort to artificial ventilation of the lungs or placing the cat in a pressure chamber, and sometimes urgent surgery is required.
Treatment of the disease that led to breathing problems is carried out only after the symptoms of pulmonary edema have been eliminated, and the animal’s condition has returned to normal. Since there are many reasons, there is no single treatment regimen. In this case, drugs are prescribed both to eliminate the provoking factor and to prevent recurrent attacks.
An animal with pulmonary edema needs constant monitoring, so it is advisable to place it in a hospital for a while. Periodic listening to the heart, monitoring the state of blood, breathing, regular medication according to the prescribed scheme – all this increases the chances of a full recovery. If necessary, the doctor will make an anesthetic injection, give a decongestant, a heart remedy.
Possible complications
Most often, complications of pulmonary edema in cats develop in small and older cats, as their immune system is not strong enough. Possible negative consequences include:
- pneumonia;
- heart failure;
- acidosis (increased acidity of the blood);
- pulmonary fibrosis (scarring of lung tissue);
- emphysema of the lungs;
- sepsis.
If the owner of the cat turns to the doctor too late, the death of the animal is inevitable. Swelling leads to cardiogenic shock or airway obstruction.
Forecast
To give any forecast, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the factor that led to pulmonary edema. If it is a non-cardiogenic cause, it is easier to manage, so the prognosis is more favorable. In the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system, a favorable outcome should be predicted with caution. Even with full compliance with the recommendations of the doctor, the likelihood of relapse remains high. In addition, the heredity of the pet, the characteristics of the body, psyche, living conditions and other factors are of great importance.
preventive measures
Of course, we cannot fight genetics, and we are not able to prevent the development of hereditary pathologies or predispositions. However, it is in our power to prevent possible complications. To do this, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- monitor the fat content in the cat’s diet, prevent overeating, the development of obesity;
- avoid cases of hypothermia of the animal;
- take environmental safety measures for the pet (do not give the opportunity to get injured);
- vaccinate according to the schedule;
- avoid stressful situations as much as possible;
- store substances hazardous to the health of the cat in a place inaccessible to him;
- regularly bring your pet to the clinic for preventive examinations, especially if he has a predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system that cannot be cured.
In addition, it is important to always have the necessary medicines on hand for first aid if the cat is at risk.





