Polycystic kidney and ovary in a cat
Contents
Polycystic kidney disease
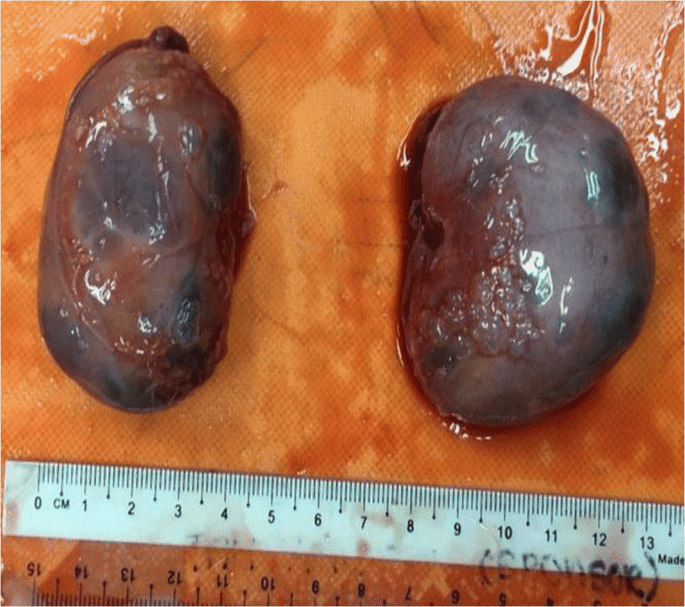
In a cat that suffers from polycystic kidney disease, changes in the structure of the organ occur in utero; with the development of the body, cystic formations increase in size and gradually destroy the kidney tissue. As a result, the structure of the organ changes and the functional ability of the kidney is impaired, which leads to dysfunction. In this case, cystic formations can affect both one and both kidneys at the same time.
Most often, thoroughbred animals suffer from this disease: Persians, British, Scottish Fold, Abyssinian cats and Maine Coons.
Symptoms
Until a certain point, the disease is asymptomatic. The first signs to look out for are decreased appetite, polydipsia (thirst), cachexia (exhaustion), lethargy, and apathy. With the greatest accuracy, only a veterinarian can diagnose polycystic disease, having carried out all the necessary diagnostic procedures.
The main visual method that allows you to immediately make a diagnosis is ultrasonography. With the help of ultrasound, polycystic disease can be detected in a kitten as early as four weeks of age. The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) genetic test is also informative, it allows you to identify a cat’s genetic predisposition to polycystic kidney disease.
Unfortunately, in most cases, the diagnosis of “polycystic” is a death sentence for a cat. This disease shortens the animal’s lifespan, although some cats live quite a long time despite this ailment.
Treatment of polycystic kidney disease
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure a pet from polycystic kidney disease. Therapy is aimed at prolonging the life of the pet, and the sooner treatment is started, the longer the cat will live. Thanks to the treatment, you can extend her life by several years.
The treatment of polycystic disease depends on the clinical manifestations of the disease and the results of diagnostic tests. Each patient in a veterinary clinic should have an individual approach. The main signs against the background of impaired renal function may be anemia, hypertension, damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Polycystic ovary
According to doctors, the etiological factor in the development of this disease can be:
Unrealized sexual instinct;
The result of the use of hormonal drugs;
Reminant ovary syndrome;
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
At risk are Persians, British and Siamese cats. Symptoms of the disease can be blurred, so the owner needs to pay attention to the following signs: sexual activity more than four times a year, rare or too long estrus. In the last stage of the development of the disease, an increase in the size of the abdomen, a violation of the act of defecation can be noted.
How is this dangerous?
The main leading symptom of polycystic disease is that the cat is constantly in a state of sexual activity, and the timing and duration of estrus change. Cysts that reach large sizes compress other organs: the liver, intestines, uterus, disrupting their normal functioning. In addition, ovarian dysfunction can provoke the development of purulent inflammation of the uterus.
Treatment of polycystic ovary
The way to solve the problem is surgery. The rest of the therapy is considered ineffective. To protect the animal from illness, doctors recommend not using hormonal drugs, and if the cat is not involved in breeding, then it is best to sterilize it.
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
July 9 2017
Updated: 21 May 2022