parrot gout
Contents
What is gout (uric acid diathesis) in parrots?
Gout, or uric acid diathesis, appears when kidney function is impaired, when uric acid accumulates in the body of a parrot in organs, tissues and blood. The kidneys in the body of a bird play a crucial role, because when their function is impaired, the concentration of uric acid rises, and it is deposited wherever blood circulation occurs in the form of calcium and sodium crystals. These crystals can cause blockage of the ureters and cloaca, resulting in retention of urine, which in turn, as one option, causes urea poisoning. In this case, fatal outcomes are also possible.

Symptoms of gout (uric acid diathesis) in parrots
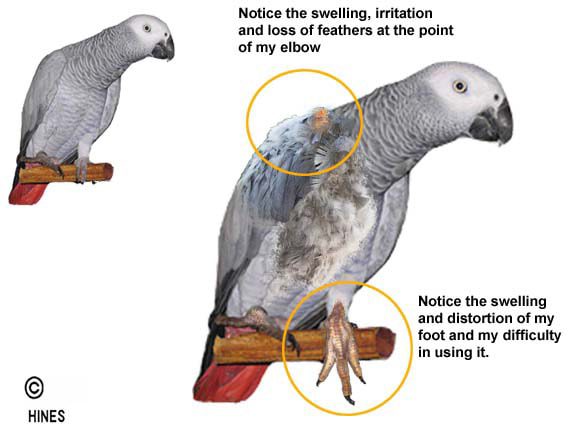
Most often, the disease is almost asymptomatic. Nodules appear around the joints, which swell and cause severe pain to the bird. The parrot gets tired quickly, does not hold well on the perch, can peck at the cloaca and pluck out feathers. A characteristic feature of gout is the alternation of opposite states: lethargy and vigor, lack of appetite and its excessive manifestation, in any state the bird experiences constant thirst and drinks a lot. Distinguish articular and visceral a form of gout (uric acid diathesis) in parrots. Articular is easier to diagnose than visceral, flowing with specific signs. In the articular form, the joints swell, the temperature rises locally, the movements of the parrot are constrained. In the visceral form of gout, salts are deposited on the surface of the internal organs in the form of a thin coating of deposits, as well as in the thickness of the organs in the form of white foci. A white mucous mass appears in the ureters, and stones form from salts. The diagnosis can be made by x-ray examination. The pictures usually clearly show salt deposits in the bird’s kidneys.
How does gout (uric acid diathesis) occur in parrots?
The disease can be divided into several stages:
- Asymptomatic increase in the content of uric acid in the blood.
- Acute gouty inflammation of the joints.
- remission stage. It can last quite a long time, even up to several years.
- Chronic deposits in the joints.
Why does gout (uric acid diathesis) occur in parrots?
Let’s look at why gout occurs in parrots. The most common cause is the wrong diet in poultry (an excess of protein and a lack of vitamin A). Also, infections and the use of antibiotics can cause kidney problems and, as a result, lead to gout.
How to treat gout (uric acid diathesis) in parrots?
Unfortunately, there is practically no drug treatment. To alleviate the condition, the parrot is prescribed a protein-free diet. The diet includes greens (alfalfa, clover), cornmeal, cherries, sweet cherries, and vitamin A. Sucrose is added to the water, which enhances the excretion of water by the kidneys and prevents uric acid salts from being deposited in the future. Nodules must be opened surgically, this will cause instant relief in the bird, however, new nodules may appear again. For a sick bird, you need to equip a cage so that the parrot experiences less pain. Use thick or flat perches that need to be wrapped in a soft cloth, water and food should be in close access. Remember that the disease is easier to prevent than to cure! Do not feed the bird unsuitable food, use only special balanced feeds.





