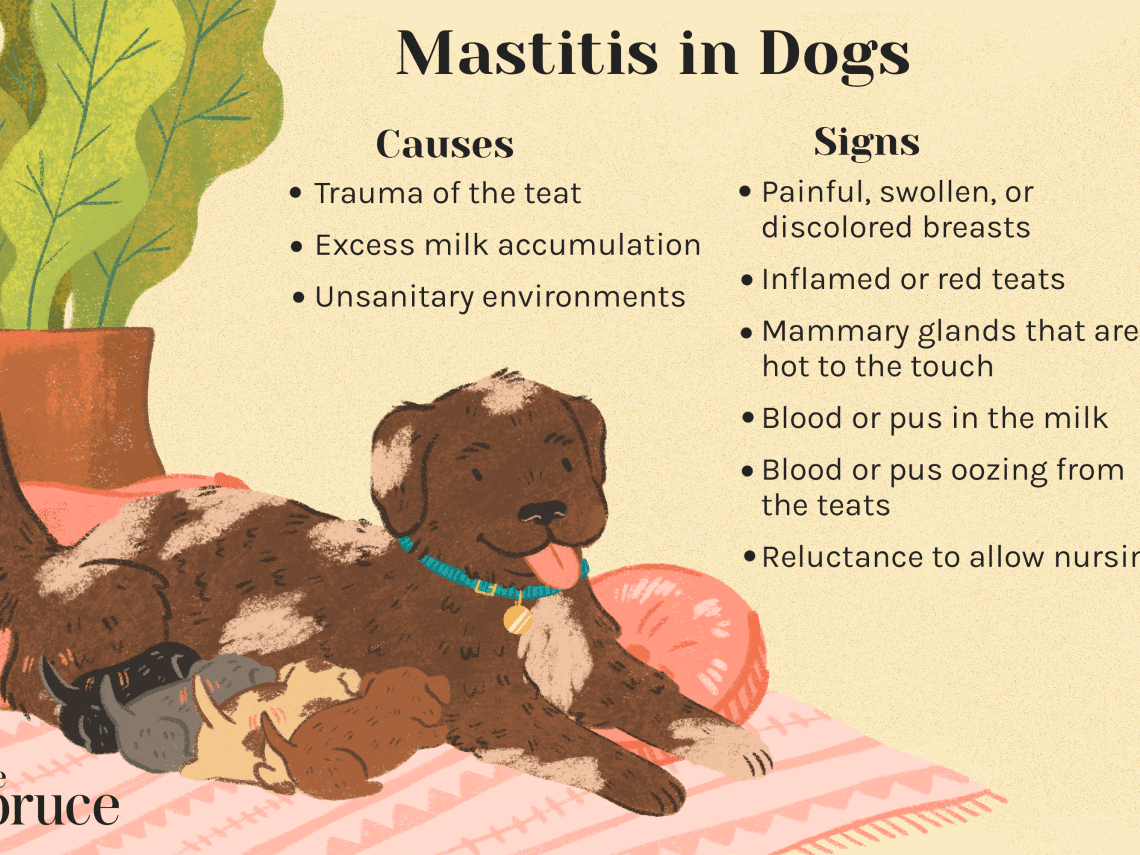
Mastitis in a dog – information, symptoms, treatment
Contents
Mastitis classification
Depending on the degree of damage to the mammary glands, the following forms of mastitis in dogs are distinguished.
- Serous. Yellowish watery discharge with inclusions in the form of flakes. Swelling of the gland, increased local temperature. There is no pain, or it is expressed slightly. It develops mainly after childbirth. Leads to lack of nutrition for puppies.
- Catarrhal. Characterized by blockage of the excretory ducts with curdled sour milk. Characteristic selections are transparent. Often occurs after estrus, regardless of whether the dog has given birth or not. Nodules are felt in the gland, which disappear after decantation (in nursing). Pain is mild.
- Hemorrhagic. Redness is clearly visible on the surface of the dog’s mammary gland. Characterized by severe pain, high body temperature. This form of mastitis is often the result of the above mentioned types of disease.
- Purulent. The discharge is cloudy, with a bad smell. Pain syndrome, severe redness and swelling of the gland are clearly expressed.
- fibrinous. Milk protein coagulates directly in the gland, so a liquid with white threads is released from the nipple. During palpation, a sound like a crunch is heard. In parallel, the dog’s lymph nodes become inflamed; pronounced pain. This form is typical for bitches over 6 years of age.
- Abscessing. Consequence of purulent mastitis. If the formed abscess ruptures, the animal may die from sepsis.
- Phlegmonous. It is also a consequence of an untreated purulent form. As a rule, all glands of the dog are involved in the pathology. There is no lactation. As in the previous case, it threatens blood poisoning.
- Gangrenous. The skin gradually acquires a bluish tint. The tissues of the gland undergo decomposition, necrosis. The body of the animal is severely intoxicated. Possible death.
In addition, mastitis in dogs can be lactational, associated with milk production, and non-lactation, which develops due to infection or injury to the glands. It should be noted that the disease is observed not only in females, but also in males.
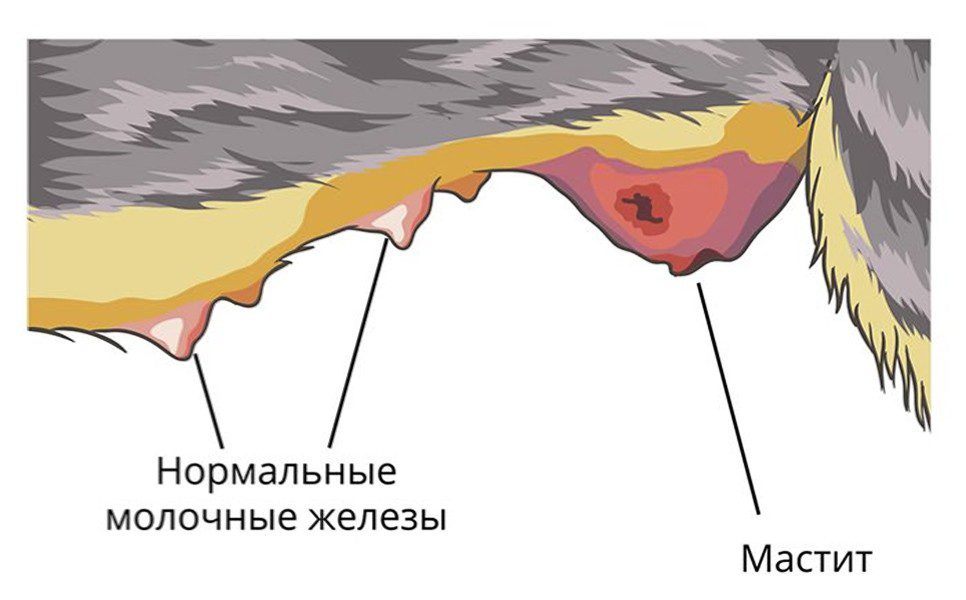
Causes of mastitis in dogs
Among the factors that provoke mastitis in dogs, note:
- infection;
- injuries of the glands, nipples (during a fall, impact, cuts);
- diseases of the reproductive organs (pyometra, endometritis);
- prolonged hypothermia, overheating;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives;
- “empty” estrus;
- injury to the mammary gland by puppies (claws, teeth);
- surgical intervention.
Separately, it should be noted a false pregnancy as a hormonal failure. In this case, abundant milk production in the absence of the possibility of feeding and pumping can lead to an inflammatory process. The same occurs in a dog that has given birth in several cases:
- few puppies in the litter;
- puppies ignoring nipples;
- early weaning from the mother.
As a result, milk stagnates, the gland thickens, the ducts are compressed – lactostasis develops, which provokes the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. Mastitis in spayed and nulliparous animals is rare, and non-neutered and frequently parous animals are at risk.
How pathology manifests itself
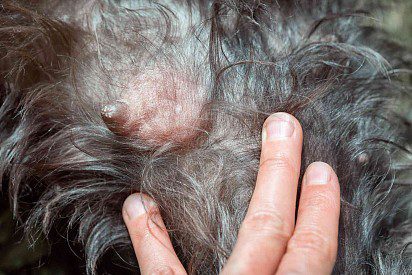
Photo of mastitis in a dog
The main sign of mastitis in dogs that you need to pay attention to is the nature of the discharge from the mammary glands (color, texture, presence of inclusions, smell). They can be greenish or yellowish in color, contain impurities in the form of flakes, threads, clots of mucus, pus or blood. In case of any deviation of the type of milk from the norm, you should contact your veterinarian.
In parallel, the following symptoms may occur:
- swelling of the gland, an increase in size;
- the mother pushes the puppies away, does not allow them to feed, which indicates pain;
- nipple inflamed, reddened, cracked;
- the skin of the mammary gland is red, burgundy, cyanotic;
- enlarged lymph nodes located nearby;
- elevated body temperature, febrile state.
Also, the dog may develop apathy, weakness, drowsiness, severe thirst. The pet refuses to eat, can be aggressive towards puppies, not allowing them to feed. In this case, babies need to be transferred to artificial feeding.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the mammary glands
Before treating mastitis, the doctor will examine the dog, collect an anamnesis. Blood tests (general and biochemical) and ultrasound diagnostics will also be required. To determine the pathogen, a PCR test of secretions from the gland may be prescribed. It is imperative to differentiate mastitis with other pathologies, for example, mastopathy.
Treatment of mastitis in dogs
The veterinarian determines the direction of treatment based on the results of the examination. If catarrhal or serous mastitis is diagnosed, the animal can be treated at home. Other forms of the disease, most often, are treated in a hospital, but this depends on the stage of the pathology, the condition of the dog, the presence of complications and other factors.
Medication
The basis of therapy is the use of antibacterial drugs. The doctor determines the duration of the intake and the type of antibiotic in accordance with the characteristics of the dog, the test data.
For the symptomatic treatment of mastitis, drugs of the following groups can be prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory;
- anesthetics;
- immunomodulatory;
- diuretic.
With mastitis in a dog or dog that is in a period of sexual dormancy, the mammary glands are treated with sprays with an antimicrobial active ingredient.
If during the diagnostic process a malignant tumor of the mammary gland was detected in a dog, they decide on the use of chemotherapy or surgery.
Operative intervention
Surgery is prescribed for dogs with advanced forms of mastitis: abscessing, gangrenous, phlegmonous. Opening of pathological cavities is performed under general anesthesia. If the process has not gone too far, the wound is washed from purulent contents, treated with drugs and sutured. With extensive damage, the gland is removed partially or completely. Postoperative care consists in drying the wounds with special powders. Instead of a bandage that the dog will take off one way or another, sprays are used that form a special protective film on the incision surface.
Mastitis, which develops during false pregnancy, requires special attention. In case of repeated cases of pathology, experts recommend sterilization of the animal – after the main drug treatment or during the operation.
Do’s and Don’ts at Home
If mastitis is suspected, especially in a nursing dog, it is unacceptable to warm up or massage the mammary gland at home before the diagnosis, to try to express milk if there are any inclusions in it. Without knowing exactly what form of the disease develops, the owner, by his actions, can cause serious complications.
In the event of a false pregnancy or lactostasis caused by the absence of puppies (or other reasons), the pet can be transferred to a low-calorie diet, eliminating food that stimulates milk production.
If mastitis occurs in a mild form, according to the testimony of a veterinarian, a massage of the mammary glands is performed. It is performed alternately with each gland, in directions: from the body to the nipple and clockwise, with rubbing movements and with light pressure. Massage is done, as a rule, up to three times a day for 3-5 minutes.
Ointments, creams, herbal preparations, folk recipes can be applied to the mammary glands of a dog. However, you should first consult with your veterinarian.
Possible complications of mastitis
With the rapid development of the disease, in case of a late visit to a specialist, the dog may experience complications of mastitis:
- infectious-toxic shock;
- blood poisoning;
- pyometra;
- benign tumors that can later become malignant;
- loss of ability to reproduce;
- inflammation of the spinal cord.
Puppies that feed on the milk of mothers with mastitis may develop digestive tract diseases and intestinal disorders. In advanced cases, this leads to the death of offspring.
Can a dog with mastitis feed puppies
What to do with babies if a lactating dog has mastitis? Feeding puppies with breast milk is possible if a serous or catarrhal form of the disease is diagnosed. In other cases, feeding can cause poisoning and death of babies, therefore, if impurities are found in milk, the offspring are isolated.
If it is impossible to place the puppies in another place, the dog’s mammary glands are bandaged (not tight) to prevent puppies from accessing them. The same is done in the case when mastitis has developed on one or two glands – only they are bandaged, and healthy offspring are allowed (according to the condition of the dog). Taping diseased glands or nipples is not recommended, since the patch needs to be re-glued for treatment, which can cause additional pain for the pet.
As an alternative to dog milk, special industrial mixes can be used. Cow’s, goat’s or regular pasteurized milk can lead to intestinal upset in puppies.
Preventive measures
The development of mastitis in a dog can be avoided with the help of simple preventive measures:
- avoid hypothermia or overheating of the dog, especially during pregnancy, lactation;
- avoid injuries to the mammary glands, and if they occur, contact a specialist;
- maintain cleanliness at the location of the animal, regularly change the bedding;
- adhere to the vaccination schedule;
- timely treat the pet for infectious diseases;
- if further breeding is not expected, spay the dog as soon as possible;
- monitor the condition of the claws of puppies, cut them, starting from a week of age;
- avoid contact of the pet with sick animals;
- maintain immunity, provide good nutrition, rich in vitamins;
- if the dog does not have enough milk, supplement the puppies artificially (malnourished, they become restless, scratch and bite the mammary glands);
- in case of false pregnancy or loss of offspring at home, the glands are lubricated with camphor oil and pulled with a bandage, a restriction on liquid, meat and dairy products is introduced into the diet;
- in lactating dogs, it is necessary to regularly examine the mammary glands, if suspicious phenomena (swelling, redness) are found, contact the veterinarian immediately;
- exclude hormonal contraceptives.
And most importantly – do not forget about the attentive and loving attitude, which will not only give the pet strength in a difficult period for her, but also strengthen the immune system.