Keeping clawed and dwarf frogs in an aquarium
Frogs are kept in the aquarium quite often. On sale, you can most often see clawed and dwarf frogs. How to keep these interesting animals?
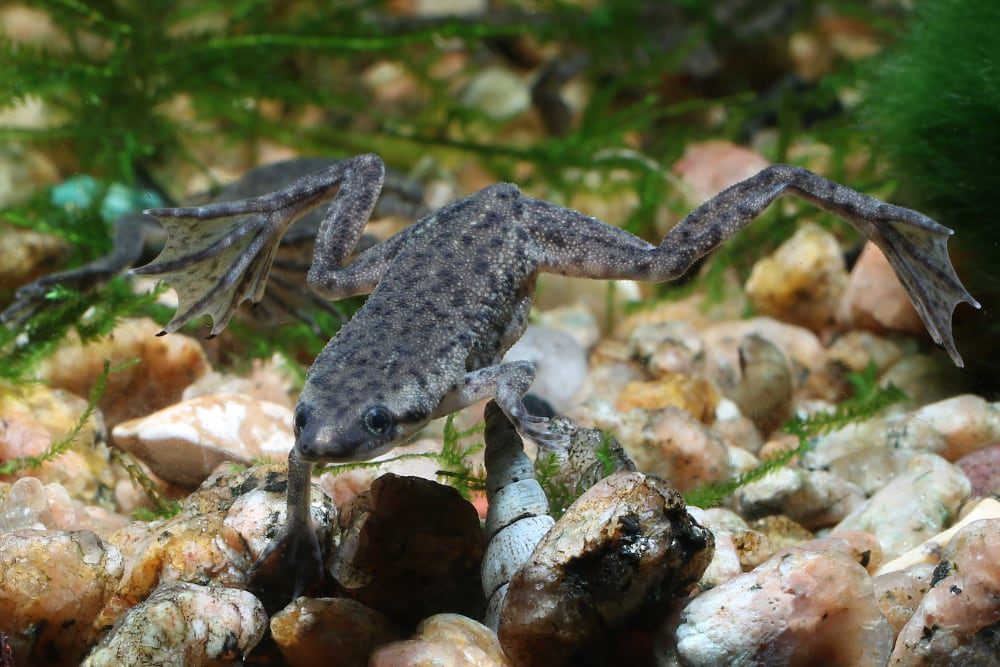
Clawed frog, xenopus
Spur frogs (Xenopus laevis) are amphibians of the pip family. A fairly large, up to 12 cm, strong-built frog, with a flattened head and small round eyes. The upper jaw has a row of small teeth, the lower jaw has no teeth. The hind legs are long and powerful, with long fingers and membranes, three fingers are equipped with sharp claws, it is on this basis that the frog is called clawed. The front paws have 4 toes and are not webbed. On the side there is a lateral line, like in fish – a sensitive organ that perceives the movement and vibrations of the surrounding water, for orientation and hunting. The color of the natural form of the clawed frog is dark – the back is from olive green to dark brown in color, in aquariums they contain both natural-colored frogs, but more often – pinkish and yellowish, and almost white albinos. The optimal volume of the aquarium for keeping the clawed frog is ~30 liters per individual. Clawed frogs are sensitive to nitrite and ammonia in the water, but they produce a lot of waste, so a filter should be installed in the aquarium, aquarium cleaning should be regular – cleaning the soil with a siphon and water changes. Frogs do not like flow, so it is advisable to install various flow dividers on the filter. Frogs eat anything that fits in their mouths, so the bottom of the tank needs to be very large so it won’t fit in their mouths, or you can get away with no bottom at all by placing a few large rocks and shelters on the bottom. Plants in frog aquariums are usually dug up or torn up, more often plants are installed artificial, or rigid, such as anubias planted in pots. It is possible to use floating plants – pistia, nayas, elodea, hornwort, cladophora balls. Clawed frogs should not be settled with other animals and fish, for larger fish or aquatic turtles the frog will become prey, and everything that is proportionate to the frog or smaller will become its prey. Clawed frogs are predators, in nature they feed on small fish and invertebrates and everything that fits into their mouths. You can offer bloodworms, shrimp, fish cut into small pieces or strips (any low-fat varieties), small thawed or live fish, crickets, earthworms. There are also specialized foods for frogs, such as Tetra ReptoFrog Granules, a complete food for aquatic frogs and newts. It is important not to overfeed the clawed frog, as they are prone to obesity. Young frogs are fed daily, and adults – two to three times a week. Do not feed frogs with oily fish, meat and tubifex. Reproduction – after artificial wintering: a gradual decrease in temperature for 1-3 weeks, and after – a gradual increase to the usual 18-25 ° C. Clawed frogs are very prolific – the number of eggs laid by the female can reach several thousand. Tadpoles at first look like small catfish, but they develop quickly and leave the eggs after two days, when the yolk sac dissolves, they switch to pulmonary breathing, then you need to start feeding them. Like all tadpoles, they are filter feeders, and the food for them should be small, dusty. For feeding tadpoles, brine shrimp nauplii, algae, scalded and finely chopped nettles and lettuce, frozen food – cyclops and powdered food for fry are used. After 2,5 – 3 months, the tadpoles turn into adult frogs, the metamorphosis itself lasts about 20 days.
Dwarf frog, hymenochirus
Hymenochirus (Hymenochirus boettgeri) is also from the pip family. A very small frog 3,5-4 cm. length. The physique is graceful and slender, slightly flattened, the paws are thin, with membranes on both the hind and front paws, the muzzle is pointed and slightly snub-nosed. The skin is fine-grained, gray or brownish in color, with small dark spots, the abdomen is light. Quite rare are albinos from almost white to golden color. An aquarium for dwarf frogs can be 5-10 liters or more, covered with a lid (glass, mesh) on top. The soil should be larger than the frog’s head. The ground, decorative elements and shelters should be smooth and not sharp, without small holes and passages so that the inhabitants of the aquarium do not get hurt or stuck. These frogs practically do not spoil the plants, but they can dig them out, so it is advisable to either plant the plants in pots, or use plants with large hard leaves and a powerful root system, cladophora, large mosses, as well as floating plants, frogs can hide and lean in them, floating up to the surface for air. Dwarf frogs molt as they grow, shedding their skin and eating it often, this should not be prevented. Hymenochirus skin is delicate, they do not tolerate hard water, chlorine and other chemicals, which must be considered when treating fish or fertilizing plants. Also, do not take the frogs in your hands and keep them out of the water; if necessary, remove the frogs from the aquarium, it is better to use a net and another container of water from the same aquarium. Hymenochiruses can feed on small daphnia, coretra, pieces of fish, medium-sized or chopped bloodworms, chopped shrimp and earthworms, and food for frogs. The sizes of the pieces must be small in order to fit into the tiny mouth of the hymenochirus, it cannot chew and tear off the pieces, swallowing the food whole. They feed dwarf frogs every 2-3 days, when kept together with fish, you need to make sure that she gets food – due to her slowness, the frog may not have time to eat. But it is also harmful for them to overeat – it is fraught with obesity and diseases, in a normal, well-fed state, the frog still remains slightly flattened. The reproduction of hymenochiruses is carried out in a separate spawning area with a water level of at least 10 cm, usually about 10-15 cm, the water temperature rises to 28 ° C, the length of daylight hours increases, and provide a full and varied diet. The singing of males resembles the quiet chirping of grasshoppers. At the moment of mating, the male holds the female by the waist, and they rise in the water in a vertical spiral, on the surface the female spawns in a transparent gelatinous membrane. The eggs are tiny, about 1 mm in diameter. Caviar should either be left in the spawning area and the frogs removed, or the eggs should be transferred to another container. After 1-2 days, small larvae appear, for the first few days they hang near the surface of the water, on glass or lie on the leaves of aquatic plants. They start feeding tadpoles when they begin to swim, they are fed with infusoria, brine shrimp nauplii, cyclops and live daphnia at least four times a day. After 4-6 weeks, the tadpoles complete their metamorphosis and become frogs about 1,5 cm long. Hymenochiruses become sexually mature by 1 year. Hymenochiruses can be kept with medium-sized and peaceful fish: corridors, tetras, rasboras, as well as snails and shrimps. But it must be taken into account that the fish should not be smaller than the frog’s head, since the frog may attempt to eat it, and not too big to be able to eat the frog itself.