Jade in dogs: treatment and symptoms

Contents
About nephritis in dogs
The kidneys are a pair of organs located in the abdominal cavity. Their functions are extremely important and varied. They are the body’s filter, removing unnecessary substances in the urine that are formed in the process of life.
They are also involved in maintaining water and electrolyte balance, pressure regulation, hematopoiesis.
Nephritis is an inflammation of the kidney tissue, which can begin in different parts of it, but gradually can lead to damage to the entire organ. And, accordingly, to the violation of his work.
The causes of nephritis are varied: intoxication, viral and bacterial pathogens, endocrine diseases, tumor processes, as well as diseases of other organs and their systems.
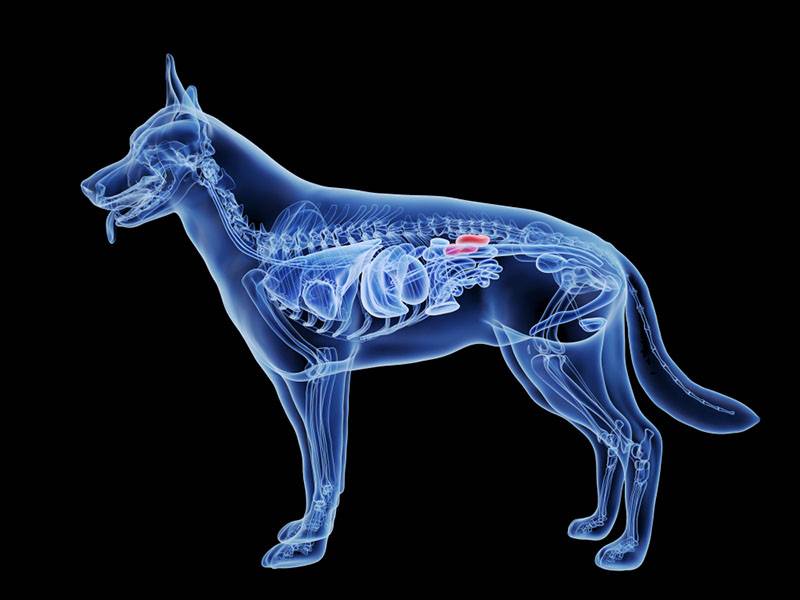
Types of disease
According to the nature of the flow, it is customary to distinguish:
Acute nephritis. It develops rapidly under the influence of various factors: infections, toxins. Also, the causes may be other serious conditions and diseases: sepsis, blood loss, cardiac pathology, etc.
One important cause of acute kidney disease in dogs is leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can damage the kidneys and liver. This disease is
zooanthroponosisAn animal-to-human disease.
Chronic nephritis can develop in a dog as a consequence of an acute lesion if a significant part of the kidney tissue has lost its function. Also, chronic kidney damage can occur against the background of other pathologies of the urinary tract: urolithiasis, cystitis, prostatitis, etc. Chronic nephritis can be the result of hereditary diseases, for example, Fanconi syndrome in Basenji or amyloidosis in Sharpei.
According to which part of the organ the pathological process develops, the following types of nephritis can be distinguished:
pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the renal pelvis and parenchyma of the kidney. The cause of the disease is most often a bacterial infection.
glomerulonephritis. Damage to the vascular glomeruli of the kidneys – their filtering system. It develops for various reasons: infections, toxins,
autoimmuneWhen the immune system attacks healthy tissue in the body disease.
Interstitial (tubulointerstitial) nephritis. The inflammatory process in this case affects the system of tubules of the kidney and the tissues surrounding them.

Symptoms of nephritis
An unpleasant feature of nephritis in dogs is the absence of symptoms in the early stages of the disease and in its mild course.
Acute nephritis is often accompanied by nonspecific symptoms: fever, vomiting, refusal to feed. In severe kidney damage, there may be a decrease in urine production up to its complete absence.
If acute nephritis has developed against the background of another pathology (sepsis, bleeding, etc.), the symptoms of nephritis may not be noticed and attributed to the underlying disease.
In the chronic course of the disease, symptoms do not appear until the kidneys are able to adequately participate in the process of filtration, maintaining water and electrolyte balance, and pressure. When most of the kidney tissue becomes non-functional, the following symptoms develop: increased thirst and urination, decreased appetite, weight, activity, vomiting, constipation, anemia, increased pressure.

Diagnosis of the disease
Various diagnostic methods are used to confirm nephritis in dogs.
Analysis of urine. Needed to evaluate kidney function and signs of inflammation. With nephritis, the density of urine decreases, cells appear in the sediment, lining the kidneys from the inside.
To exclude the loss of protein through the kidneys, for example, with glomerulonephritis, the protein / creatinine ratio in the urine is measured.
With pyelonephritis, urine culture for microflora may be required for a more accurate selection of an antibiotic.
Biochemical analysis of blood. A healthy kidney adequately removes the waste products of the body: urea and creatinine. With nephritis, their level in the blood rises. The level of glucose, phosphorus, electrolytes, and albumin is also measured in the blood.
General clinical blood test. Helps to identify signs of inflammation and anemia, which often develops with chronic kidney damage.
Ultrasound examination. It will show what the kidney looks like, whether there are any changes in its structure, exclude neoplasms, stones and other pathological inclusions in the organ.
Tonometry. It is mandatory for those animals in which it is suspected
hypertensionIncrease in pressure – a common complication of a chronic type of disease.
In addition to the above studies, others may be required: tests for leptospirosis (antibody levels in the blood, urine PCR), genetic testing if a hereditary disease is suspected,
biopsyTaking a piece of tissue for research kidneys, etc.
Treating Jade in Dogs
Treatment may be directed to a specific pathogen, such as in the case of leptospirosis, or it may consist of maintenance therapy designed to eliminate and prevent the consequences of nephritis in a dog.
Bacterial nephritis requires an antibiotic. Ideally, it is collected by urine culture. An antibiotic is also needed in the treatment of leptospirosis.
In acute nephritis, it is important to understand what caused the damage to the kidneys.
Sometimes the cause of acute nephritis cannot be corrected, such as with toxic damage. In such cases, the animal needs hemodialysis. With this procedure, a special apparatus filters the blood instead of the kidneys, giving them the opportunity to recover. Equipment for hemodialysis is complex and expensive and is available only in a few selected clinics in the country.
In the chronic course of the disease, therapy is reduced to supporting the body.
Infusions of solutions with electrolytes, food additives that remove excess phosphorus are used. Hypertension requires antihypertensive drugs
proteinuriaLoss of protein through the kidneys in the urine – drugs that reduce protein loss.
A special diet and vitamin preparations may also be prescribed. If the dog develops anemia, iron supplements and Erythropoietin are used.
The task of therapy in the chronic course of the disease is to maintain a good quality of life for the animal.
This photo contains material that people may find unpleasant
See photos
Prevention of nephritis
Vaccination, including against leptospirosis.
Treatment for ectoparasites. In regions where ixodid ticks are common, they are treated from the first thaw to the first snow without interruption.
Timely treatment of diseases of the urinary system, as well as prostatitis in males and metroendometritis, vaginitis in females.
A dog can get poisoned not only from household toxins (insectoacaricides, rodent repellents, household chemicals, etc.), but also when eating onions, garlic, raisins (grapes).

Summary
Nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys that can develop in dogs for various reasons: toxins, infections, diseases of other organs and their systems.
According to the development of the disease, acute and chronic processes can be distinguished.
The symptoms of nephritis are often non-specific. In acute nephritis, vomiting, apathy, decreased appetite, and fever may appear.
Chronic disease has no symptoms as long as the kidneys are able to eliminate toxins, maintain water balance and pressure. With a significant damage to the kidney tissue, increased thirst and urination, a decrease in appetite and body weight, and vomiting develop.
When diagnosing nephritis, urine, blood tests, and ultrasound are performed. Sometimes specific studies are required: analysis for leptospirosis, urine culture, genetic testing, etc.
Treatment for nephritis may focus on addressing the cause, such as bacteria. Acute nephritis in a dog may require hemodialysis. In chronic therapy, therapy is needed to maintain a good quality of life in an animal with reduced renal function.
Sources:
J. Elliot, G. Groer “Nephrology and urology of dogs and cats”, 2014
McIntyre D.K., Drobats K., Haskings S., Saxon W. “Emergency and small animal intensive care”, 2018
Craig E. Greene Infectious diseases of the dog and cat, 2012
October 12 2022
Updated: October 12, 2022