Indoor plants dangerous for pets.

Pets do not know which plants are useful and which are deadly for them, so the owner’s task is to know dangerous plants and protect pets from them. Often plants that are dangerous to pets are also dangerous to children. Before buying each new plant, if there are small children or pets in the house, it is necessary to study whether it is poisonous.
Contents
Araceae (Araceae)
The poisonous juice of plants of this family contains the amino acid asparagine and calcium oxalate crystals, causes swelling of the larynx and oral mucosa, burning and blisters on the mucous membrane, respiratory arrest, and if it gets into the eyes, conjunctivitis and irreversible changes in the cornea, blindness; allergic dermatitis; disruption of the kidneys and heart.
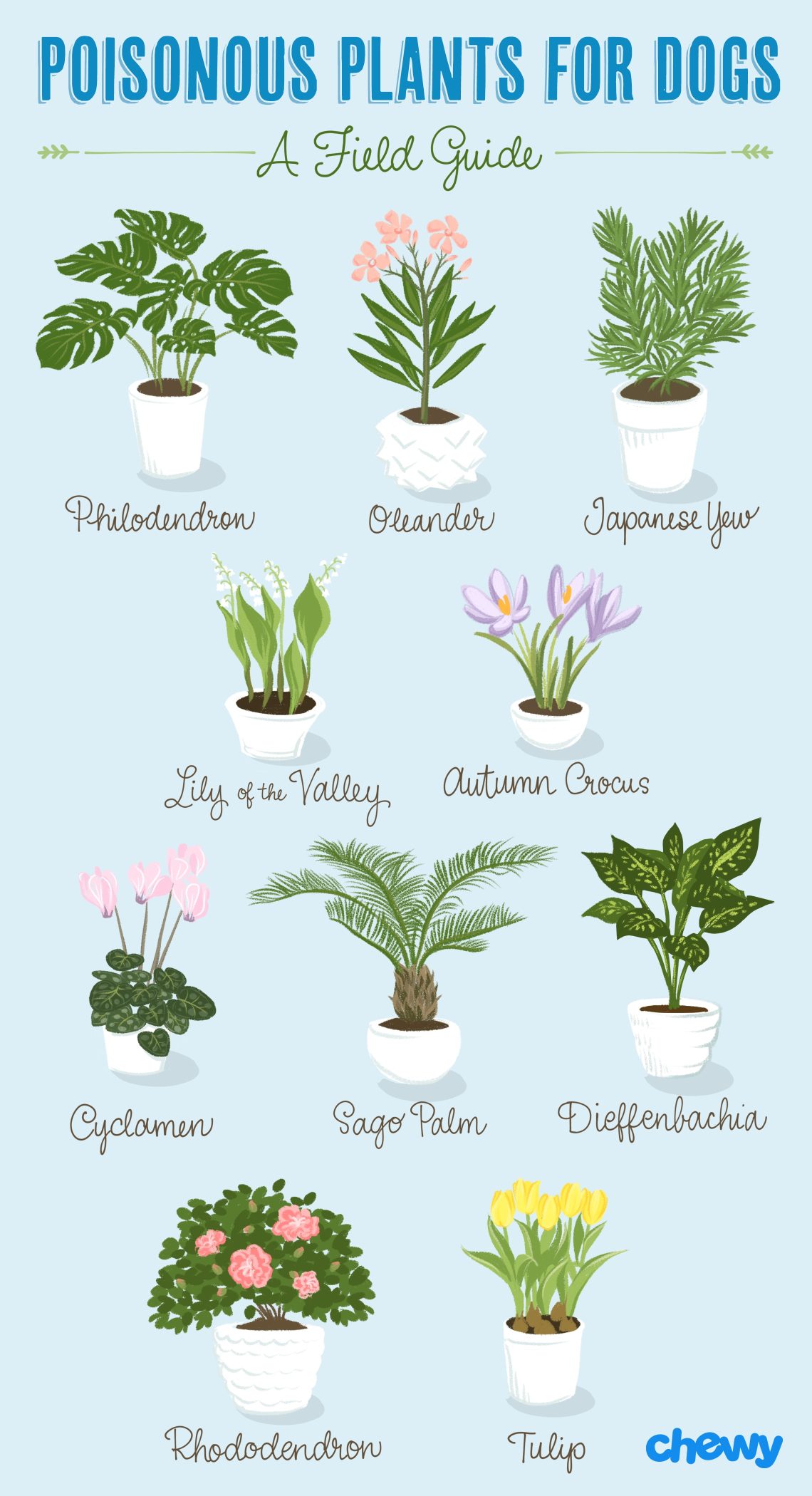
- Dieffenbachia (Dieffenbachia).
- Monstera (Monstera)
- Anthurium (Anthurium)
- Spathiphyllum (Spathiphyllum)
- Caladium
- Philodendron (Philodendron)
- Pineapple (Alocasia)
- Aglaonema (Aglaonema)
- Calla (Zantedeschia) or Spotted Arum (Arum maculatum)
- Zamioculcas (Dollar Tree) (Zamioculcas)
- Сингониум (Syngonium)
Araliaceae (Araliaceae)
Juice and leaves contain hederin saponin, various toxic glycosides and alkaloids, cause irritation of the mucous and gastrointestinal tract, depression of the heart muscle and can cause respiratory arrest.
- Hedéra (ivy) (Hedéra)
- Japanese Fatsia (Fatsia japonica)
- Polyscias (Polyscias)
- Shefflera (Shefflera)
- Fatshedera (Fatshedera)
Kutrovye (Apocynaceae)
Toxins have a nerve-paralytic effect, depress the work of the heart and lungs, and visual impairment.
- Oleander (Nerium oleander)
- Pachypodium (Pachypodium)
- Adenium obesum (Desert rose) (Adenium obesum)
- Mandevilla (Mandevilla) or Dipladenia (Dipladenia)
Colchicums (Colchicaceae)
Contains the alkaloid colchicine. Cause a violation of blood clotting, severe kidney damage.
- Gloriosa (Gloriosa)
- Colchicum (colchicum, autumn crocus) (Colchicum)
Solanaceae (Solanaceae)
The green parts of these plants contain the alkaloids solanine, some atropine and scopolamine, therefore, when ingested, they can cause vomiting, salivation, clouding of consciousness, hallucinations, impaired vision, breathing, heart function, and paralysis.
- Solandra (Solandra)
- Solanum (Solanum capiscastrum, Solanum pseudocapsicum)
- Brovallia (Browallia)
- Datura or Datura (Datura)
- Belladonna (Atropa belladonna)
- Black henbane (Hyoscyamus niger)
Including physalis berries, potatoes and eggplant
Heather (Ericaceae)
Contain glycoside andromedotoxin, causes poisoning when ingested. Poisonous nectar of flowers and leaf juice causes CNS depression, heart failure, eating disorders, nasal discharge, profuse salivation.
- Azalea (Rhododendron / Azalea).
Hydrangea (Hydrangeaceae)
Contains cyanide, causes severe abdominal pain, severe indigestion, vomiting and diarrhea. In some cases, tremors, disorders of the heart, lungs and kidneys.
- Hydrangea (lat. Hydrangea)
Amaryllis (Amaryllis)
Contain the alkaloid lycorine, causes abdominal pain, vomiting, salivation, diarrhea, in large doses – tremor, paralysis, general collapse (acute vascular insufficiency, a sharp drop in vascular tone or a rapid decrease in the mass of circulating blood, which leads to a decrease in venous flow to the heart, drop in arterial and venous pressure, hypoxia of the brain and inhibition of the vital functions of the body). Bulbs are the most dangerous. Rodents are at particular risk.
- Amaryllis (Amaryllis)
- Hippeastrum
- Zephyranthes
- Eucharis (Eucharis)
- Valotta (Valotta)
- Clívia
Primula (Primuláceae)
This family includes cyclamens and primroses, which contain the saponin cyclamine, which causes pain in the oral cavity and larynx, mucosal burns, and difficulty breathing.
- Cyclamen (Cyclamen)
- Primula (Prímula)
Euphorbia or Euphorbia (Euphorbiaceae)
They contain euphorbin, the poisoning of which proceeds in a very severe form, causing burns and ulcers of the oral cavity and pharynx that do not heal for a long time, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes (up to temporary blindness), dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract with impaired nervous regulation, allergic dermatitis.
- Poinsettia or Euphorbia is beautiful, “Christmas star” (Euphorbia pulcherrima).
- Croton or Codiaeum (Codiaeum).
- Milk thistle, or milk thistle “crown of thorns” (Euphorbia Milii)
- Milk thistle (Euphorbia tirucalli)
- Acalypha or “bald tail” (Acalypha)
- Castor bean (Ricinus communis). Beans are especially dangerous.
- Jatropha (Jatropha)
cut flowers
Some cut flowers, and even the water they stand in, can be dangerous to pets. Poisonous daffodils, snowdrops, irises, chrysanthemums, callas, lilies, tulips, hyacinths, lilies of the valley, lilacs, peonies, lupins, ranunculi, delphiniums, aquilegia, foxglove, periwinkle, asparagus, gypsophila. Therefore, in no case should you allow a cat or dog to gnaw on plants from a bouquet, as well as drink water from a vase.
What to do with poisoning?
In case of poisoning, it is necessary to remove poisonous particles from the fur, skin and mucous membranes of the animal as soon as possible, rinse with plenty of water, if it is suspected that the animal has swallowed a piece of the plant, induce vomiting, give activated charcoal and urgently contact a veterinarian. It is advisable to take a piece of the plant with you so that the doctor can determine the type of toxin and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Dangerous plants should be removed from the house, or pets should be kept away from them. You can place strong-smelling objects on the windowsill (citrus peel, spray with anti-growth spray), or rustling foil. For an alternative, offer your pet a specially grown grass: oats, wheat, rye, barley, catnip, bluegrass.