How to determine the breed of a dog
Contents
Breed, phenotype, mestizo or “nobleman” – who is who in the dog world
The official confirmation of the purity of the animal is its pedigree. Without it, any dog, even if it fully fits into the standards of cynological associations, does not have the right to breed status.
Pedigree – a card in which the following information is noted: nicknames of the puppy and his parents, show titles and ratings received by the litter producers during their life, sex and date of birth of the puppy, stigma, nicknames of ancestors (minimum 3 generations).
It is also not worth recording a dog without a pedigree as a pooch, because for pets with an appropriate standard (and sometimes ideal) exterior, breeders have a separate name – a phenotype. The main difference between a phenotypic pet and a pedigree pet is unformed documents. Moreover, a dog can have ideal ancestors in terms of the gene pool, but for some reason they were not exhibited and did not receive the right to breed.
Puppies born as a result of mating of two different breeds are mestizos. There are two subcategories of mestizos – born in nature, as well as under the influence of man (intentional crossing of breeds). An important nuance: officially only a dog from manufacturers with documents of origin can be called a mestizo.
A mongrel is already a mix of three or more breeds. Moreover, the ancestors of the animal can be purebred individuals, and mestizos, and other mongrels. Formally, the “noble brand” can even be put on puppies, one of whose parents is a purebred with a pedigree, and the second is an average inhabitant of city streets.
How to find out the breed of a dog
The presence of a brand / chip greatly simplifies the work, since a dog with such a “passport” can always be attributed to a specialist who easily reads data from existing marks. With unchip “tails” the situation is more complicated. Of course, no one forbids handing over a dog to a cynologist who will conduct an examination and then identify one or more breed groups that dominate the animal’s phenotype. But almost always the error of such an experiment will be too large.
According to statistics, only 27 dog handlers out of 100 succeed in correctly identifying the breeds that donated their genes to a mestizo animal (we are talking, of course, about a visual assessment).
From the complexities of “identification”, a natural question arises: why find out the breed of a dog at all, if without a pedigree it will never become a star of exhibitions and dog shows? Breeders explain this by the fact that, knowing the genetic base of a pet, it is much easier to monitor its health. Namely: to reveal predisposition to hereditary diseases. As an example, brachycephalic ocular and obstructive respiratory syndrome commonly affects breeds with short muzzles (brachycephals), as well as their closest relatives, and very rarely, representatives of other canine clans.
How to find out the breed of a puppy
The younger the puppy, the less likely it is to successfully determine its breed. Violated proportions, color changes, uneven growth, the appearance of spots on the coat (Dalmatians) – all these phenomena, inevitable for puppies, only slow down the process. So if you take a pet without documents, take its age-related transformations calmly – it is impossible to predict what a baby bought “from hands” will grow into. Relatively reliably, the breed of a dog is determined from 6 months, although the cynologists themselves consider the one-year-old age of the animal to be optimal.
How to determine the breed of an adult dog by external signs
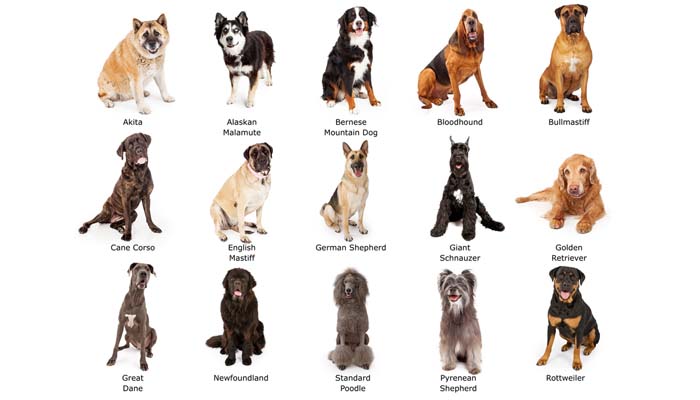
It is better to analyze exterior traits in aggregate, referring to a reference book or breed standard. But keep in mind that with the “nobles” in the nth generation, this principle will not work – too dense a mix of genes is present in their phenotype. But in a situation with mestizos, the chances of a successful “identification” are quite high.
By height and weight
The dog world has its giants, middlings and dwarfs. RKF identifies 3 main types of rocks in accordance with the dimensions of their representatives.
Large
Dogs with a height of 60 cm at the withers and a body weight of 25-30 kg. Outstanding representatives: East European Shepherd Dog, Briard, Maremma-Abruzzo Shepherd Dog, American Bulldog, Doberman, Caucasian Shepherd Dog, Black Russian Terrier, Giant Schnauzer, Alaskan Malamute, etc.
All large dog breeds
average
Medium dogs are dogs from 40 to 60 cm at the withers with a weight in the range of 12-25 kg. Some breeds classified by the RKF as medium: French Bulldog, Lhasa Apso, Russian Spaniel, Pharaoh Hound, Chow Chow, East Siberian Laika, Welsh Terrier, Border Collie, American Stafford, Bull Terrier, Thai Ridgeback, Beagle, etc.
All medium dog breeds
Small
Among small breeds, three large subgroups are distinguished: small dogs proper (height – up to 40 cm; weight – up to 10-12 kg), dwarf (height at the withers – up to 35 cm; body weight – up to 5 kg), toi (height – not more than 28 cm; weight – within 2 kg). Typical “babies”: Miniature Pinscher, Yorkshire Terrier, Mexican Hairless Dog, Belgian Griffon, Pug, Chinese Crested Dog, Russian Toy Terrier, Chihuahua, Maltese, Petit Brabancon, Papillon, Japanese Chin, Tibetan Spaniel, Coton de Tulear, Manchester Terrier etc.
All small dog breeds
By type of ears
The size, setting and shape of the ear cloth are the most important breed characteristics that can tell a lot about the pet’s “roots”.
Erect, set at a strong inclination forward ears:
Large erect ears of a classic triangular shape:

Laid back in a calm state and semi-raised in an alert:

Scottish Shepherd (collie)


Erect, slightly separated ears with a rounded bat-shaped tip:



American Hairless Terrier
Widely set, semi-lowered:

Small ears in the shape of regular triangles:
Ears hanging down or hanging forward, and also close to the cheeks:
Ears set high – the base of the ear is located above the line of the eyes:
Low-set ears – the base of the hearing organs at or below the line of the eyes:


Basset Artesian Norman
A medium-sized ear, tilted forward, with the tip covering the ear funnel and visually resembling a pocket flap:

Long, free-hanging ears along the cheekbones:


Cavalier King Charles Spaniel


Rose ears – slightly raised and wrapped to the sides according to the principle of a rose bud:


In addition to the shape and set, the ears may differ in the presence / absence of decorating feathers. Breeds that cannot be confused due to this feature: papillon, Russian long-haired toy terrier, briar.
Along the length of the muzzle
A long bridge of the nose in dogs does not always mean a first-class sniffer. Although, to a greater extent, such an anatomical feature is inherent precisely in representatives of hunting clans.
Breeds with long snouts:







Scottish Shepherd (collie)





And of course, do not forget about the representatives of the “polar” canine family – brachycephals. So if your puppy has a short or flattened muzzle, it is likely that in his genetic code were noted:
alapaha bulldog;
пагль;
Tibetan spaniel;


















Life hack for those interested: when determining the breed of a dog by the length of the muzzle, do not forget about the shape of the back of the nose. As an example: the muzzles of the bull terrier and the Afghan hound are almost the same length, but visually they are very different.
The shape and size of the tail
Tails in the form of a light corkscrew are characteristic of Chow Chow, Pug and Akita Inu. The tail-flagpole, standing straight, is an identifying sign of beagles. The hook-shaped shape with a slightly raised tip is a pedigree chip of Briards and Pyrenean Shepherds. The rat tail, like that of the Irish Water Spaniel, is a powerful, woolly base and a thin tip covered with sparse hairs. The Labrador Retriever has the so-called otter tail: thick at the base, tapering towards the tip and flattened below.
Bull Terriers are owners of horizontal tails, which are also called rods. An identification feature is a shape resembling a bee sting. The ring at the tip of the tail for most breeds is considered a serious conformation defect, but not for the Afghan Hound, for which such a “design” is a reference characteristic. Crescent tails usually belong to Siberian Huskies. Squirrel tails, sharply bent forward, are typical of the Pekingese.
According to the length and structure of the coat
The type of coat will also significantly narrow the range of breed search. Cynologists distinguish 6 main varieties of dog “clothes”:
- wild type – elongated hair on the neck, body, tail and short on the paws and head;
- short-haired – uniform smooth coat throughout the body with a minimum amount of undercoat or without it;
- wire-haired – coarse, wiry or spindle-shaped hair, forming a protective chain mail on the body of the animal;
- long-haired – the coat is silky, often hanging in a fringe, it can be either smooth or curly.
Within the main wool types, there are subspecies.
Hairless dogs – Chinese Crested, Xoloitzcuintle, American Hairless Terrier, Ecuadorian Hairless, Abyssinian Sand Terrier, Peruvian Inca Orchid, Deerhound (not officially recognized by cynological associations), Manchurian Hairless.



American Hairless Terrier
smooth-haired – Great Dane, Doberman, Dalmatian, Cane Corso, Boxer, Ca de Bo, Italian Greyhound, Pharaoh Hound, etc.
Individuals with folded skin – Sharpei, Neapolitan Mastiff, Pug.
Longhaired with little undercoat – Japanese Chin.

Long-haired with abundant undercoat – Pekingese.
Animals with corded or matted hair – bullets, komondor, bergama shepherd.

Wire-haired with a short type of cover – smooth-haired fox terrier, Hungarian vizsla.
Coarse coat of medium length – standard schnauzer, Irish terrier.


Dogs with curly coarse hair – Airedale Terrier, Welsh Terrier.


Individuals with short curly hair – Curly Coated Retriever.
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog is considered a typical owner of a wild-type coat. Also, cynologists distinguish an additional subtype, which includes broad-haired dogs with soft and extremely thick hair (bobtails).
By color
The easiest way to determine the breed in dogs with rare types of colors. For example, it is common knowledge that the merle color is almost always the Bull Terrier, Pit Bull, Aussie and Pembroke Welsh Corgi. If you see a creature with all its appearance resembling a Cavalier King Charles Spaniel, but with a pearly white coat, decorated with chestnut marks, then with a probability of 99,9% you have a Blenheim in front of you.
Curious fact: since color types are not always a harmless game of genes, some of them are prohibited from breeding. In particular, a taboo on breeding experiments has been established for albino individuals, as well as dogs of the Isabella suit. There are also a number of restrictions on merle colors, although not for all breeds.
Character and temperament: we determine the breed by behavior
The method, characterized by cynologists as the most unreliable, also sometimes works. Especially if the dog has pronounced habits of representatives of the intended breed. If the pet proved to be a real digger, it is possible that he was just lucky with terrier genes. Those who like to “graze” all horned and tailed ones that are in sight are distinguished by the instincts of shepherd dogs – border collies, shelties, corgis.
The descendants of hunting dogs will systematically poison the existence of all the surrounding cats, as well as poultry, if any. Fans of mice, rats and other rodents are, as a rule, dachshunds, ratlicks, cairn and jack russell terriers, as well as miniature schnauzers. St. Bernards, Golden Retrievers, Pugs, Papillons, Poodles and Labradors are always willing to “baby” and tinker with your children. If you come across a frank “silent man”, it is likely that representatives of little barking breeds were noted in his ancestors – Basenji, American Akita, Shiba Inu, Rhodesian Ridgeback, Afghan Hound, Greyhound.
Genetic Code: Pedigree Establishment Through Genetic Testing
In Russia, DNA testing of dogs is offered by several laboratories at once. The most popular procedures for cynologists are a test to determine the degree of relationship and establish a genetic profile. Typically, such studies serve as insurance against unscrupulous breeders. Before buying a puppy without documents, you can send the biomaterial of the animal and its parents to the laboratory (in agreement with the seller) to make sure that you are offered a pet from exactly the manufacturers that were shown.