Guinea pig tumor and abscess – treatment of bumps, sores, growths on the body

Guinea pigs have deservedly become popular pets for their friendly disposition and unpretentiousness in maintenance. The most comfortable care conditions are not able to protect your beloved rodent from various infectious and non-contagious diseases. A common problem in guinea pigs is the formation of abscesses and oncological neoplasms. They can be under the skin or in internal organs. In the absence of timely treatment, tumors can cause the death of a pet.
Contents
tumors in guinea pigs
Oncology is considered one of the most common pathologies in guinea pigs older than 5 years. It often leads to death. Neoplasms in furry rodents are due to heredity, genetic predisposition, and frequent stress. Obesity and the use of foods containing preservatives and dyes in the animal’s diet may play a role. Bumps in a guinea pig can appear anywhere on the body, head, mucous membranes and internal organs. Neoplasms are benign and malignant.
Benign tumors are characterized by the formation of a connective tissue septum that prevents the growth of pathological cells into healthy tissues. With the intensive growth of the sore, there is a strong compression of the surrounding tissues and organs, which leads to the complete immobilization of the animal. With timely treatment, this type of tumor is successfully treated surgically.
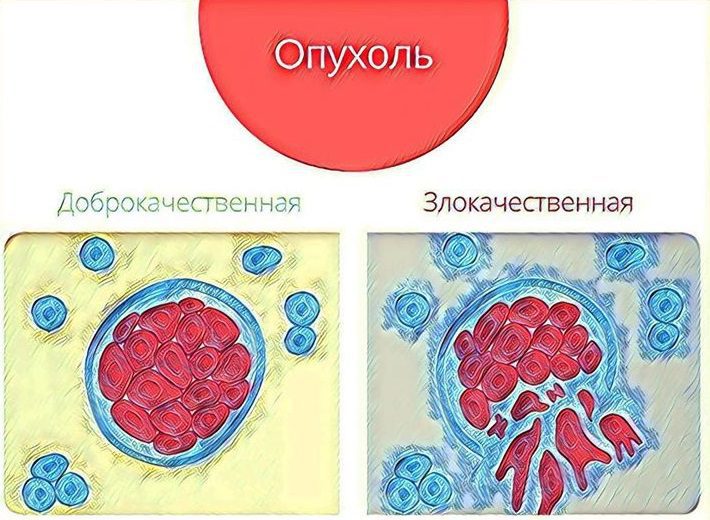
Malignant neoplasms are characterized by the germination of pathological cells in healthy tissues and the formation of multiple metastases in internal organs. Cancer of the guinea pig is an indication for euthanasia, you can leave the guinea pig to live out its term with quality care, nutrition and constant use of painkillers.
In guinea pigs, neoplasms can most often be found on the following parts of the body.
Breast tumors
Pathological degeneration of mammary gland cells occurs in males and females at a respectable age. A tumor in a guinea pig on the abdomen is most often benign; in pathology, a dense bump is found in the lower abdomen, not attached to the subcutaneous tissue.
Breast cancer is characterized by:
- edema;
- strong fixation of the neoplasm with soft tissues;
- the formation of fistulas and abscesses.
Tumor on the neck of a guinea pig
It can be an abscess, an inflamed lymph node, or lymphosarcoma, a malignant tumor. Sometimes the swelling is due to an enlarged thyroid gland. To determine the nature of the neoplasm, you must contact the veterinary clinic.
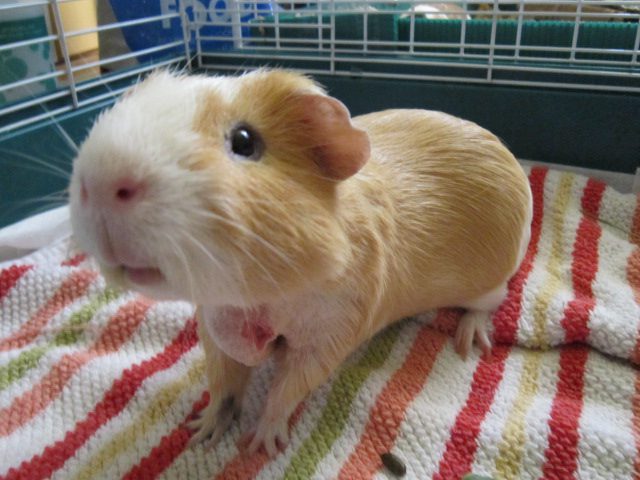

Tumor in guinea pig on side and back
It indicates the development of neoplasms in the internal organs. Such neoplasms are most often malignant. A bump on the side can be a symptom of lung, colon, liver, spleen, or kidney cancer.
Pathology manifests itself:
- lethargy of the animal;
- lack of appetite;
- the appearance of bloody discharge from the urethra, mouth, anus and loop.
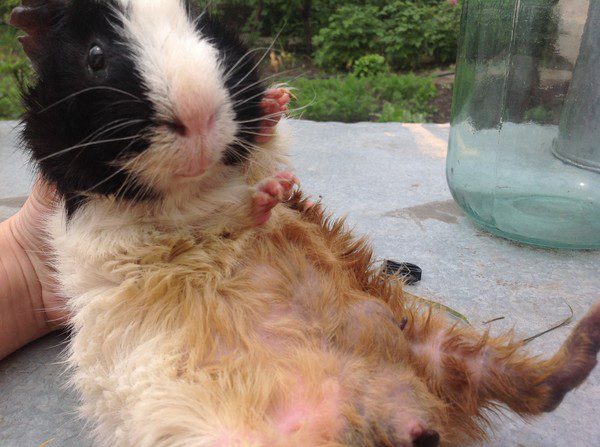
Tumors on the skin
They are benign neoplasms of the skin and subcutaneous tissue; in guinea pigs, they are most often found on the priest and genitals. If a male has swollen testicles, you should contact the veterinary clinic as soon as possible. Large testicles may indicate puberty, the presence of a hair ring, or subcutaneous neoplasms that require urgent surgical intervention.
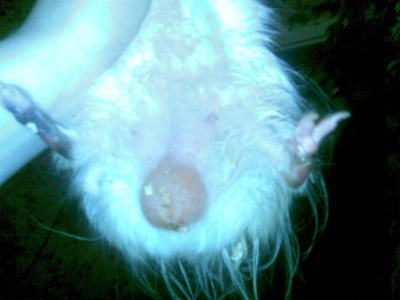
Tumors on the cheek in guinea pigs
They can be benign or malignant neoplasms. The owner may notice that the pet’s cheek is swollen, a dense tubercle or bone growth is palpated. Often the animal loses its appetite and becomes aggressive.
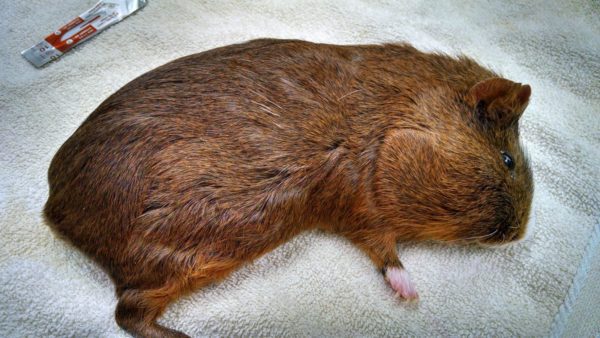
bone tumors
Manifested by thickening of the limbs and ribs, in guinea pigs, osteosarcomas are most common – malignant neoplasms. In the absence of metastases in the internal organs, specialists sometimes resort to amputation of the damaged limb.
Connective tissue tumors
Lipomas or wen in guinea pigs are benign neoplasms that are found in the form of dense bumps under the skin. In the absence of growth and causing discomfort to the animal, doctors recommend not to touch the oncological growths.
Rapid growth or impaired motor activity due to an increase in the size of the wen are indications for surgical removal of the neoplasm.
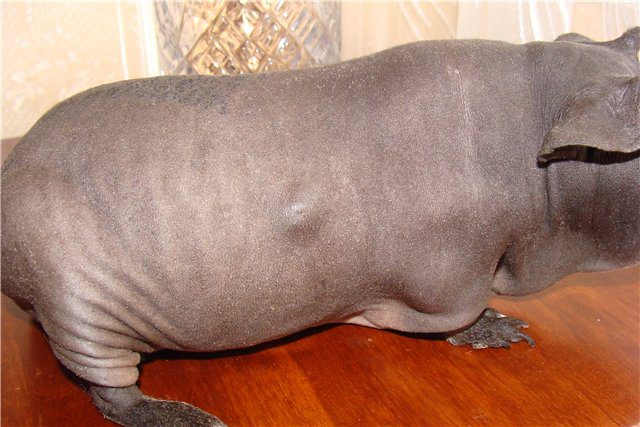

If swelling is found on the body of a pet, it is urgent to contact a veterinary clinic. After a cytological examination of the biomaterial, the specialist will decide on the nature and appropriateness of the treatment.
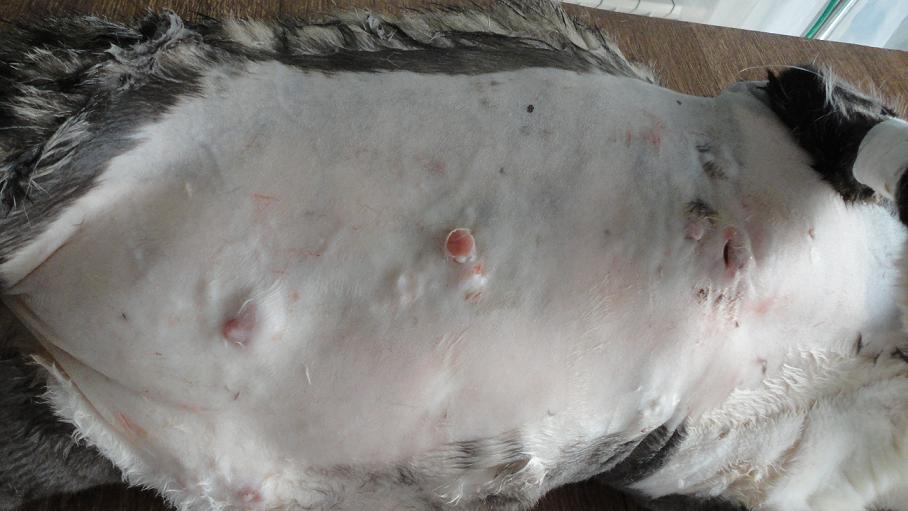
Abscess in a guinea pig
Swellings on the body of a guinea pig can be abscesses that form when the integrity of the skin is damaged as a result of injuries, fights with relatives, or the penetration of pathological microflora from nearby foci of inflammation in infectious and non-communicable diseases. Ulcers are localized in the internal organs, muscles, dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
External abscesses occur when pathogenic microbes penetrate the skin. A protective capsule is formed around damaged tissues, preventing the spread of the inflammatory process to healthy tissues. In the initial stage of the abscess, the formation of a red, painful lump is observed. As it matures, it thickens and turns into a cone-shaped swelling filled with pus. The capsule breaks through on its own or is opened in a veterinary clinic, then the abscess cavity is cleaned and the wound heals.
With improper treatment of an abscess at home, the bumps grow inward. This leads to a breakthrough of the abscess into healthy tissues. Pathogenic microflora penetrates into the bloodstream, which is fraught with the development of sepsis and the death of the animal.
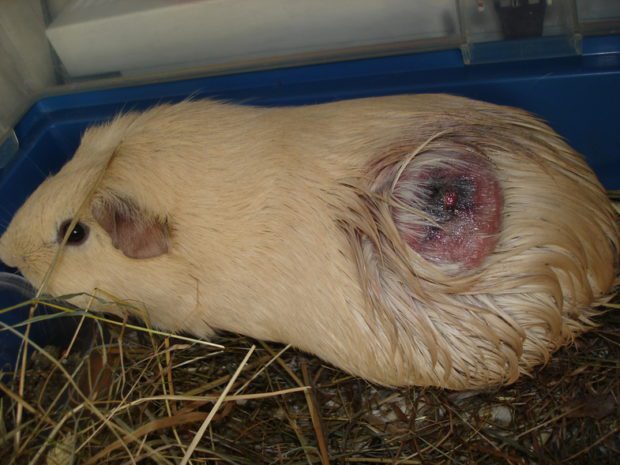
Small abscesses in guinea pigs can be treated on their own. To accelerate the maturation of the abscess, an iodine mesh is used on the affected area. Sometimes bandages are applied with Vishnevsky’s ointment. After opening the abscess, it is necessary to wash the wound daily with a solution of chlorhexidine, followed by the application of anti-inflammatory ointments to the wound surface until the skin is completely healed.
Abscesses in the neck, teeth, muzzle and large abscesses are to be removed in a veterinary clinic using local anesthesia, suturing and postoperative wound treatment. Before surgery, a pet examination, a puncture of the swelling and a cytological examination of the punctate are mandatory.
What to do if a guinea pig has a bump on its body? You need to contact the veterinarian as soon as possible. It will determine the nature of the pathological growth and prescribe treatment. With benign tumors and abscesses, the prognosis is most often favorable; guinea pig cancer cannot be cured. The earlier a comprehensive examination of a pet is carried out, the more likely it is to save the life of a family pet.
Video: surgery to remove a tumor in a guinea pig
Treatment of abscesses and tumors in guinea pigs
2.8 (55.29%) 17 votes