Guinea pig teeth: structure, diseases, loss and solution of possible problems (photo)

Guinea pigs are funny smart rodents that are born with 20 sharp teeth, which the animal needs to grind rough food and maintain the normal life of a pet. A guinea pig’s teeth constantly grow throughout its life, so it is imperative to use roughage in the animal’s diet to grind teeth properly.
Coarse feed includes hay and tree branches. For information on how to choose the right hay and which branches are suitable for guinea pigs, read our materials “Hay for Guinea Pigs” and “What Branches Can Be Given to Guinea Pigs”.
Dental problems in pets occur when the conditions of feeding and keeping at home are violated, as well as jaw injuries. All dental diseases negatively affect the growth and general health of a furry animal.
Contents
How many teeth does a guinea pig have
Most people don’t know how many teeth a guinea pig has. Many people mistakenly believe that furry rodents have only 4 massive front incisors. In fact, the animals still have back teeth for grinding food. Guinea pigs have the same number of white teeth on the lower and upper jaws: 2 long incisors and 8 cheek teeth – a pair of premolars and three pairs of molars, in total there should be 20 teeth in the oral cavity of a healthy animal. A healthy guinea pig should have teeth of varying lengths. The teeth of the lower jaw are 1,5 times longer than the similar teeth of the upper jaw.
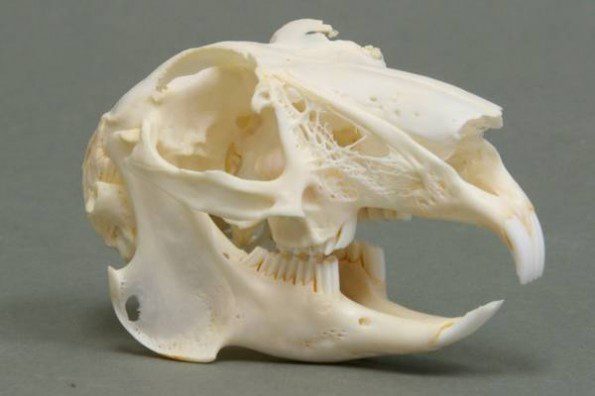
The physiological norm for a domestic rodent is the absence of fangs, the toothless space between the incisors and premolars is called a diastema, this tooth structure is characteristic of guinea pigs and chinchillas.
Features of the structure of the jaws and teeth of a guinea pig
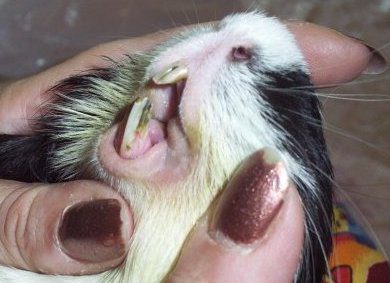
The incisors of guinea pigs are very massive, the size of the lower front teeth is larger than the upper ones. The lower incisors are convex while the upper front teeth are slightly concave. With the right bite, the incisors should not close. There is space between them vertically and horizontally. Tooth enamel covers the front teeth only from the outside. Due to this, there is a constant abrasion of the teeth from the inner surface and the formation of the necessary cutting surface of the incisors.
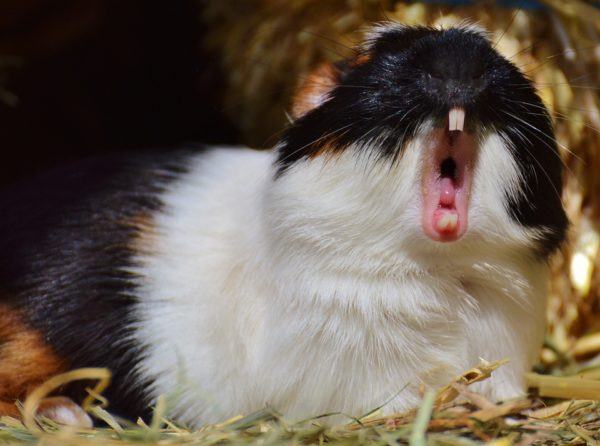

Guinea pig cheek teeth have a slightly bumpy or wrinkled surface. A distinctive feature of indigenous pets is the constant growth of not only crowns, but also roots or “reserve crowns”, since the true roots of teeth in guinea pigs are absent.
The lower jaw of guinea pigs is a kind of knife. It moves forward, backward and to the side, which is necessary for cutting off hard food. The upper jaw works as a dispenser, it bites off the portion of food necessary for one time.
With the right diet, all teeth grind down and grow evenly, so additional care for the teeth of a fluffy pet is not required.
Symptoms of dental disease in guinea pigs
A pet with dental problems is deprived of the opportunity to eat normally, which has an extremely negative effect on his health.
Weight loss to a critical value is deadly for a small animal.
You can determine the presence of dental pathologies in a guinea pig by the characteristic symptoms:
- the animal drools profusely, the hair on the muzzle gets wet as a result of a physiological increase in the amount of saliva due to a violation of the ability to chew food and the lack of closing of the oral cavity due to regrown teeth;
- the guinea pig does not eat solid food, sorts out food for a long time, tries to eat softer food, can completely refuse food, even favorite treats, which is fraught with weight loss and the development of anorexia;
- a small animal chews pieces of food for a long time, trying to grind food with one side of the jaw; Sometimes part of the food falls out of the mouth or the animal spits out too solid food on its own;
- the pet cannot bite off a piece of a solid vegetable or fruit, when treated with treats, it runs up to food, but does not eat it;
- a fluffy pet is rapidly losing weight, which can be determined by visual inspection and elementary weighing of the animal;
- diarrhea or constipation that develops when there is a violation of chewing and swallowing food;
- malocclusion, which is manifested by the complete closure of the incisors, the overlapping of the teeth, the protrusion or grinding of the teeth at an angle;
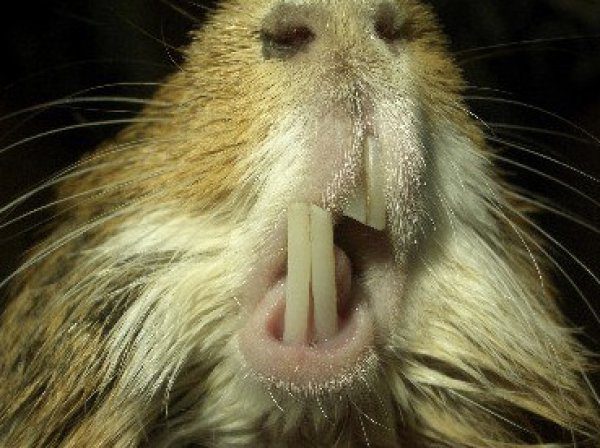

- the content of blood streaks in saliva as a result of damage to the oral mucosa by the sharp edges of overgrown crowns;
- mucous or purulent discharge from the nose and eyes when the roots of the teeth grow into the sinuses or soft tissues near the eyes;
- swelling of the eyes and an increase in the eyeball due to the formation of maxillary abscesses, asymmetry of the muzzle and dense swelling on the lower jaw with mandibular abscesses;
- rupture, fistulas on the cheeks with penetrating injuries of the mucous membrane with regrown teeth.
IMPORTANT!!! Dental disease in guinea pigs is an occasion for an urgent visit to the veterinarian.
Causes of dental problems in guinea pigs
Dental pathologies in furry rodents can be provoked by:
- imbalance in the diet, predominant feeding with soft compound feed, lack of hay and roughage, deprive the teeth of the natural physical activity necessary for their proper erasure;
- hereditary pathologies and congenital malocclusion;
- injuries of the teeth on the cage or the floor during a fall, as a result of which the jaw is displaced, the teeth are deformed, which is fraught with the formation of malocclusion, facial abscesses, fluxes and stomatitis;
- chronic systemic pathologies in which the animal refuses to feed, resulting in the growth of teeth;
- autoimmune diseases;
- lack of calcium and vitamin C;
- eating hay treated with herbicides or fluoride preparations.
Common Dental Pathologies in Guinea Pigs
The most common types of dental disease in guinea pigs are:
Tooth injuries
Guinea pigs often break their teeth when falling, trying to gnaw through the bars of the cage, and fighting with relatives. If a pet has a broken tooth, a possible cause may be a lack of calcium salts and vitamin C in the body of a small animal. In a situation where the teeth are partially broken off without damaging the crown, you need to ensure that the opposite teeth do not injure the oral mucosa in order to avoid the development of stomatitis.
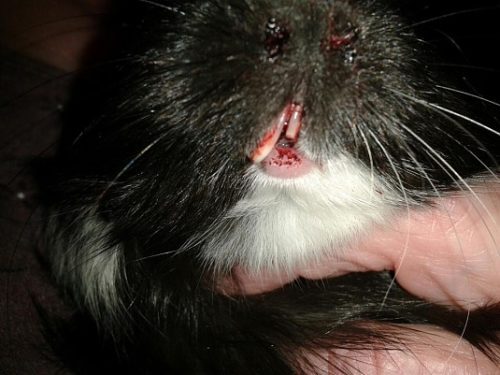
It is urgent to contact a veterinary clinic for cutting teeth if:
- the tooth broke at the root;
- jagged sharp fragments remained;
- there is gingival bleeding;
- the guinea pig broke its upper teeth;
- there is bad breath.
In order for the teeth to grow back correctly, the procedure for grinding and grinding the teeth must be done in a veterinary clinic using painkillers.
From the diet of the animal after this procedure, it is recommended to exclude roughage and grain. If a guinea pig does not eat anything after cutting its teeth, you can feed a small animal from a syringe without a needle with grated fruits, vegetables and root crops. With frequent breakage of teeth, it is necessary to additionally introduce feeds rich in calcium and ascorbic acid into the diet.
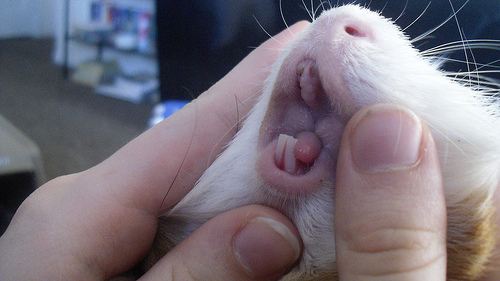
Tooth loss
If a guinea pig has lost its top tooth, there is no cause for concern. A domestic rodent periodically loses its teeth.
Loss and loosening of no more than two teeth is a physiological norm.
New teeth grow within 2-3 weeks, in young animals up to a year old, all milk teeth fall out. Loss of teeth is accompanied by a decrease in appetite, therefore, for the period of growing a new tooth, all roughage and grains are excluded from the diet of a beloved pet, fruits and vegetables are given in a frayed form. If a guinea pig’s upper teeth fell out at the same time as the lower teeth, that is, more than 3 teeth are lost, you should contact a veterinary clinic. A similar situation can be observed with a lack of calcium salts and inflammation of the gums.
Malocclusion
Malocclusion in a guinea pig is a violation of the bite due to the pathological regrowth of the front teeth. Sometimes there is an increased growth of the anterior and cheek teeth. The disease is caused by a violation of the feeding regimen, hereditary or infectious diseases.
Overgrown incisors in guinea pigs look very long and protruding. There is a displacement of the jaw and asymmetry of the muzzle. In pathology, there is an active growth of the lower molars with the sharp edges of the posterior teeth growing into the tongue. The upper molars grow towards the cheeks, which leads to the development of stomatitis and the formation of abscesses, flux, fistulas and perforation of the cheeks. The mouth of the rodent does not close, the animal is not able to eat. In pathology, there is profuse salivation, sometimes with streaks of blood, exhaustion.

Treatment of the disease is carried out in a veterinary clinic. After examining the oral cavity and radiographic examination, therapeutic measures are prescribed.
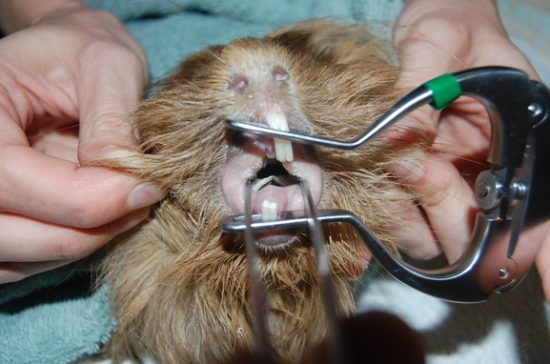
To eliminate stomatitis, irrigation of the oral cavity of the guinea pig with solutions of antiseptics and decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs is used. The flux is opened surgically. Overgrown teeth are grinded and polished with the use of anesthesia.
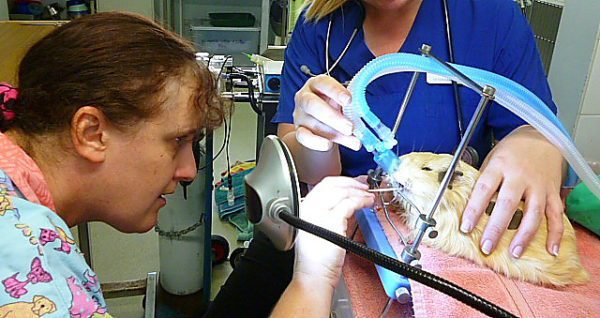
An elastic bandage is used to restore the jaw muscles.
Elongation of the roots of the teeth
The roots of teeth in guinea pigs are considered to be the reserve or subgingival part of the crown, which, when pathologically elongated, grows into soft tissues, causing damage to the eyes or sinuses. The disease is characterized by severe soreness, lack of appetite, progressive emaciation, mucous or purulent discharge from the nose and eyes, the formation of dense swelling on the jaws of the animal, fluxes, an increase in the orbit of the eye, and the asymmetry of the muzzle of the animal.
Treatment of pathology after studying the radiographic images of the jaws involves cutting overgrown crowns. As a result, there is a physiological reduction of the roots of the teeth. In advanced cases, the removal of a diseased tooth is indicated.
Prevention of dental disease in guinea pigs
Dental problems in a pet can be prevented by following simple preventive measures:
- the diet of guinea pigs should be balanced, mostly consisting of roughage and hay. Treats, juicy and soft foods are given in doses. It is forbidden to feed a pet from a human table;
- animals must be purchased from conscientious breeders who exclude from breeding rodents with congenital dental diseases;
- it is necessary to properly equip the cage to avoid falling and injury to a small animal;
- it is not allowed to keep aggressive pets together;
- pregnant females and young animals should receive a sufficient amount of foods rich in calcium, vitamins C and D;
- weigh the animal once a week so as not to miss critical weight loss;
- at the first symptoms of dental pathologies – refusal of food, salivation and rapid weight loss, it is urgent to contact a veterinary clinic.
Feed and care for guinea pigs properly. A balanced diet and the attentive attitude of a loving owner can protect pets from unpleasant dental pathologies.
Description and diseases of the teeth of guinea pigs
4 (80%) 8 votes