Frustration in dogs
Frustration (translated from Latin as “failure”, “deceit”, “vain expectation”) is a mental state that occurs in a living being in a situation where this being cannot satisfy its need.

The state of frustration occurs when a living being cannot achieve its goals or fulfill a desire. Barriers can be both external (circumstances) and intrapersonal.
In other words, we are talking about frustration when our desires do not match our capabilities.
Frustration is experienced by both humans and other creatures, including dogs.
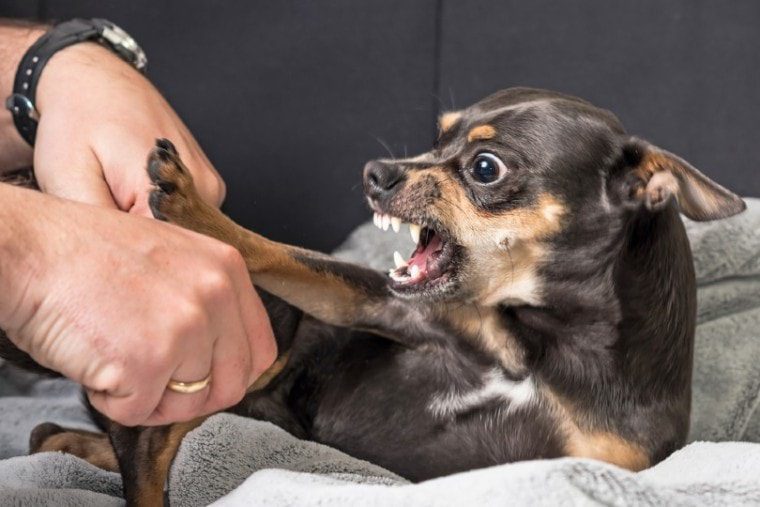
The state of frustration is associated with a wide range of negative emotions: disappointment, irritation, anxiety, despair, anger. And a prolonged state of frustration can cause distress and have a negative impact on well-being. Including causing behavioral problems, such as cowardice or aggression.
Let’s take an example. The dog sees its relatives, really wants to play with them, but for some reason cannot satisfy this need (for example, the owner keeps it on a leash). She is overexcited, excessive excitement causes an excess of energy that needs to be released. If the dog can’t blow off steam, the arousal causes frustration, which in turn triggers the problem behavior. As a result, the dog may begin to bark and lunge at other dogs or chew on the leash. Or it can result in redirected aggression when the dog bites the owner.
To help your dog cope with frustration, you must first ensure that basic needs are met, as well as teaching him to “keep himself in his paws” and relax through self-control games and relaxation protocols.
You can learn more about raising and training dogs with humane methods by using our video courses.