Foam from the mouth of a dog – causes and what to do?

Contents
Causes of foaming from the mouth in a dog
The reasons for this phenomenon can be both physiologically normal and pathological, that is, characteristic of a disease and posing a threat to the dog’s body.
Physiologically normal
Severe, prolonged hunger. Due to a prolonged lack of food, an increased amount of gastric juice is secreted in the animal’s stomach – this can provoke the release of contents into the esophagus and the animal spitting up a foamy liquid.
Rapid consumption of large portions of food after a long fast.
Wool or grass clods, which, when accumulated, are removed by abundant secretion of gastric juice. The content in this case will take on the color of pollution – green, brown or black.
Eating specific substances with a strong irritating taste – bitter, sour, pungent. Usually such a reaction is observed as a response to taking drugs.
Exposure to external stimuli, bringing the pet into a state of stress, contributes to the active release of saliva, which, in contact with oxygen, becomes foamy.
Small foreign objects in the mouth, which the body of the animal tries to remove through copious amounts of saliva.
Nausea is possible in pregnant bitches (mostly dwarf breeds) in the morning.
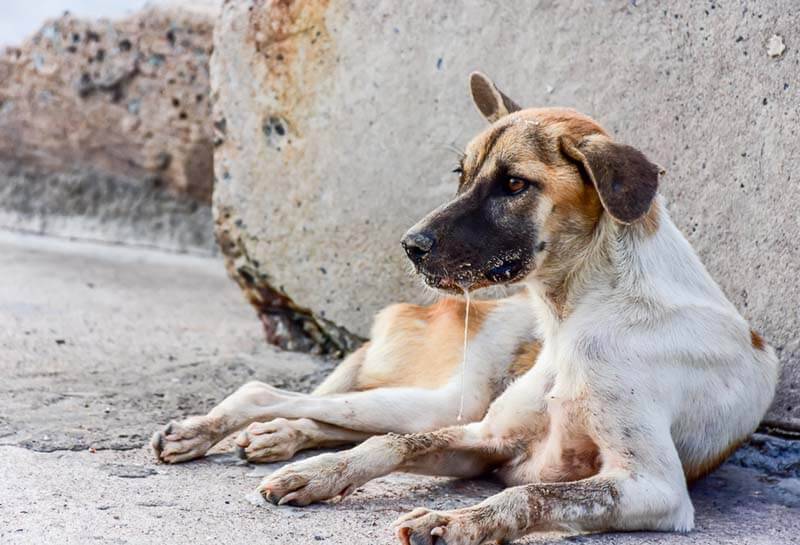

When sick
Viral diseases – rabies, canine distemper, Aujeszky’s disease, tracheobronchitis. All these conditions require the immediate intervention of a veterinarian and are dangerous for both the animal and the human. If the character of your pet has changed in a short time, his mouth is foaming and there is a fear of water or light, isolate the animal from yourself and immediately call the veterinary service.
Oncology. A neoplasm in the lumen of the esophagus, pharynx, or oral cavity can cause similar conditions. Foam may be contaminated with blood.
Trauma and inflammation in the oral cavity. In case of trauma to the oral mucosa with sharp mechanical objects – chips, bones, splinters – more saliva begins to be produced to protect against harmful bacteria. Inflammation of the gums, teeth, the presence of tartar can also contribute to active salivation. Saliva in this case is most often offensive.
Diseases of the liver and kidneys. Yellow or dark green foam from the mouth of a dog can be released in case of liver or kidney disease, as a manifestation of intoxication and nausea.
Pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Foamy discharge from the oral cavity after excitement or increased physical exertion may indicate a pathology of the cardiovascular system and incipient pulmonary edema. This situation requires urgent medical attention.
Poisoning by neurogenic (acting on nerve cells) toxins and epileptic seizures. If a dog has profuse foaming and convulsions from the mouth, this may indicate poisoning of the body with toxic substances, including treatment preparations against external and internal parasites. This condition also requires emergency intervention. Epileptic seizures may be accompanied by a copious flow of foam or saliva from the mouth.
Acute allergic condition. In a situation with acute allergies, in addition to current reactions in the form of swollen lymph nodes, vomiting, diarrhea or itching, vomiting may occur. In this case, the dog actively exudes white foam and saliva from the mouth.
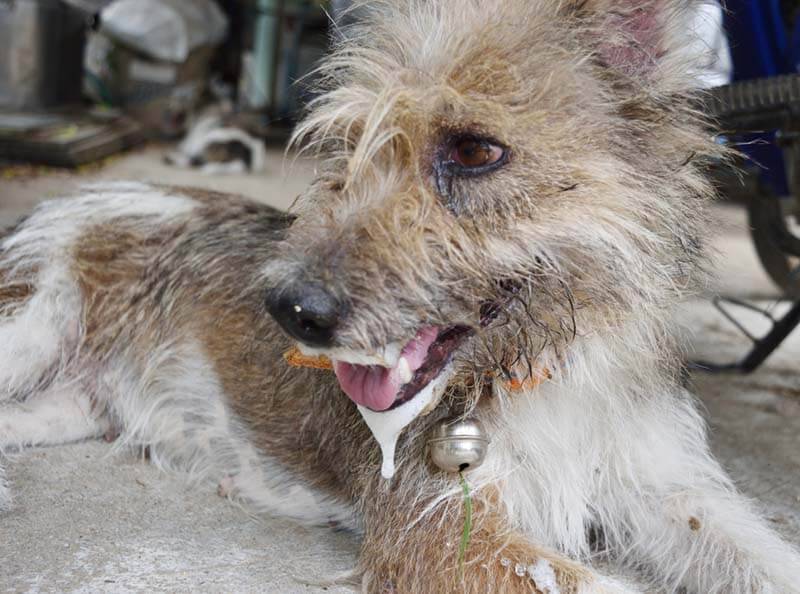

Additional symptoms
Thus, an abundant outflow of foam can be accompanied by:
convulsions;
lack of appetite;
vomiting;
outflow of blood from the oral cavity;
offensive odor from the mouth.
First aid
The first step is to understand whether in this case there is a danger directly to humans. In no case should you approach a dog that has foamed at the mouth if this animal is homeless or not vaccinated against rabies. It is better to immediately contact the state veterinary institution. Such dogs are quarantined, tracked by specialists in order to avoid infecting other animals and people with a dangerous disease. Control over a dangerous disease – rabies.
If the affected dog has been vaccinated against rabies and there is no history (history compiled according to the owner) of biting by wild animals, the pet can be given first aid, since in this case nothing threatens human health. It must be laid on its side on a flat surface, covered with a blanket or blanket. In no case should you tilt your head back to avoid inhaling the contents of the oral cavity into the respiratory tract.
Only a doctor can help a dog in an attack, so it must be transported to the clinic as soon as possible. For a specialist, it is worth recording a video of what is happening.
It is not worth fixing or holding the animal in an attack – at the time of convulsions, it does not control its body, often does not realize what is happening around, may not recognize the owner and unknowingly injure a person.
If the pet is conscious, expiration can be removed with a soft cloth to avoid wetting the coat and a possible decrease in body temperature.
In the clinic, it is important to undergo a complete examination to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe therapy.

Puppies foaming at the mouth
Foam flows from the baby’s mouth, what could be the reason?
This condition in a puppy can be caused by the same reasons as in adult dogs: a long period of hunger, poisoning, neoplasms, epileptic seizures, and even poisoning with neurogenic toxins. The difference is the increased rate of development of pathological processes in the animal’s body. This means that you need to go to the doctor as soon as possible.
The baby may also need a heating pad with warm water when transporting – it is more difficult to maintain the puppy’s body temperature. In case of malaise, pressure drop, sugar level – it immediately falls.

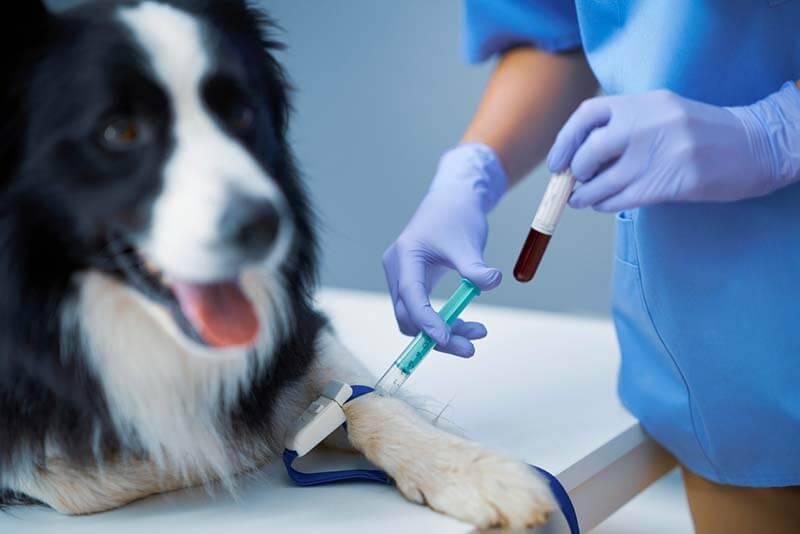
Diagnostics
Complete blood count – a general analysis indicating the presence and nature of the inflammatory process, indications for blood transfusion or emergency infusion (resuscitation) therapy.
Blood chemistry. This analysis is mandatory on an empty stomach – 6-8 hours of hunger – and shows the state of the organs – the liver, kidneys, heart, indicates emergency conditions of the animal that require immediate intervention.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and heart – control of visual changes in the dog’s organs.
Analysis for electrolytes – this indicator indicates the salt composition of the blood, which makes it possible to select saline solutions for a dropper.
Laryngo-, esophago-, gastroscopy – visual examination of the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract – endoscopic examination.
Selection of a biopsy of altered parts of organs – further histology and cytology (cell analysis) of the material – the establishment of the type of tumor or inflammatory process.
X-ray of the skull, upper and lower jaws of the animal – if there is a need for tooth extraction – determination of the condition of the tooth, differentiation of altered teeth from healthy ones.
PCR, ELISA, ICA studies of animal materials for viral infections – canine distemper, adenovirus infection and others.
CT, MRI examination of the head, neck, chest of the animal, if necessary, in the control of soft tissue formation that causes pathological changes.
Treatment
For a dog with convulsions and bites from wild animals, not vaccinated against rabies, quarantine at a state veterinary institution, monitoring the condition and maintaining safety for surrounding doctors, owners, and other animals is recommended.
Foam at the dog’s mouth and convulsions may indicate poisoning, epilepsy, neurogenic viral infections. In this case, it is recommended:
introduction of the animal into drug sleep;
the use of possible antidotes (antidotes);
use of anticonvulsants or antiepileptic drugs;
maintenance therapy in the form of antiemetics, painkillers, decongestants, the introduction of saline solutions, etc.;
stabilization of the condition in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. Such patients require constant high-quality monitoring: control of pressure, brain performance, sugar levels, the state of the abdominal and thoracic cavities.
For diseases of the cardiovascular system, you need:
diuretic therapy, which provides a decrease in pressure in the vessels and, accordingly, effusion (excess) of fluid in the lungs
oxygen therapy – an animal with pulmonary edema experiences a catastrophic lack of oxygen, which affects the performance of the whole organism. Doctors will make up for this deficit.
the dog needs a round-the-clock hospital and monitoring: x-rays and ultrasound of the chest in dynamics, temperature control, selection of the dosage of a diuretic drug.
With prolonged hunger in puppies of dogs of dwarf breeds, it is necessary:
introduction of antiemetic therapy (if necessary);
feeding – they begin to give food in small portions, gradually increasing them to standard ones as the condition of the animal stabilizes.
Neoplasms, injuries requiring surgical interventions, inflammation of the teeth, gums require:
surgical excision of education;
removal of affected teeth with subsequent treatment of wound cavities;
antibacterial therapy and antiseptic treatment, which reduces the level of pathological (disturbed) microflora. Accordingly, swelling and allows you to subsequently select a full-fledged informative cytology or histology of the affected tissues;
chemotherapy (strictly after receiving the result of histology, it is selected according to the type of tumor process that affected the dog).
The allergic condition is corrected with antihistamine (against allergies) drugs, steroid hormones (depending on the severity and severity of the condition).

Prevention of causes
Timely high-quality vaccination saves the animal from neurogenic viral diseases, including rabies.
Periodic examination of the animal by specialists and monitoring of its condition makes it possible to detect the disease at an early stage of development – thus, it will be easier for the pet to help.
Annual cleaning with ultrasound and polishing of teeth, treatments with gels, sprays, the use of special additives in water allow you to maintain the health of teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
The absence of bones, sharp toys and other items in the diet saves the dog from injuries and perforation (breaks) of the soft tissues of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus.
High-quality care for the animal on a walk, care of the walking area help to prevent the dog from eating toxic drugs, substances and solutions.
A consultation with a veterinary specialist allows you to gain knowledge on caring for a young, adult and aged animal, monitor its feeding (multiplicity, composition and quality of the diet). Thus, it is possible to provide for food intolerance, exacerbation of inflammation of the pancreas, liver, kidneys or hungry vomiting, nausea.

Summary
The expiration of foam from the mouth of a dog, both in a state of convulsions and without, requires a doctor’s examination, diagnosis and hospitalization.
The causes of this condition can be both physiological (prolonged hunger, agitation, bitter preparations, etc.), and pathological (poisoning, viral infection, neoplasm of the oral cavity, and even stomatitis)
Diagnosis is very important and has a wide range of studies: blood tests, x-rays, CT or MRI, ultrasound studies, histology and others. It is selected based on the results of the examination of the animal.
Treatment involves a qualitative selection of therapy and drugs, taking into account the established diagnosis, and may include: surgery, treatments, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and even antihistamines.
Prevention of this condition includes vaccination, careful selection of feeding norms, supervision during walks, preventive examinations and examinations.
Answers to frequently asked questions
January 31 2022
Updated: January 31, 2022