Eosinophilic granuloma complex in cats
Contents
What is an eosinophilic granuloma complex?
Eosinophilic granuloma complex (EG) is a type of skin and mucosal lesion, most often the oral cavity, in cats. It can be expressed in three forms: indolent ulcer, linear granuloma and eosinophilic plaque. It is characterized by the accumulation in certain areas of eosinophils – a type of leukocyte that protects the body from parasites and is involved in the development of allergic reactions. Any cat can develop, regardless of age and breed.
How different forms of CEG manifest themselves
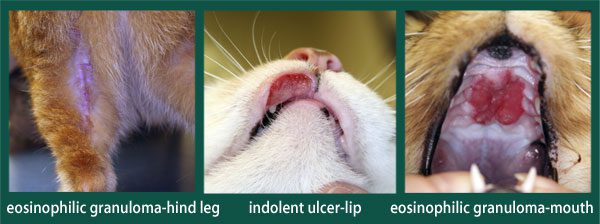
- Indolent ulcer. It occurs on the mucous membrane of the mouth, manifested by an increase in the size of the upper or lower lip, erosion of the mucous membrane, turning into an ulcer. With the development of the disease, it can affect the nose and skin of the muzzle. The peculiarity is that these lesions are painless.
- Granuloma. Manifested in the oral cavity in the form of whitish nodules on the tongue, in the sky, may have erosion or ulcers, foci of necrosis. The linear shape of the EG appears as strands on the inside of the hind legs, which protrude above the skin surface. Linear granuloma is accompanied by itching and baldness. The cat can be very worried, constantly licking.
- Plaques. They can occur on any part of the body and mucous membranes. Protrude above the surface of the skin, may have a pink, weeping appearance. Single or multiple, rounded and irregular, flat. When a secondary infection is attached, pyoderma, papules, pustules, purulent inflammation, and even areas of necrosis may additionally occur.
Causes of granulomas
The exact cause of the eosinophilic granuloma complex is unknown. Often lesions are idiopathic. There is reason to believe that allergies, in particular the reaction to flea, midge, mosquito bites, may cause CEG. Atopic dermatitis can also be accompanied by ulcers, plaques of an eosinophilic nature. Food hypersensitivity and intolerance. Hypersensitivity, also known as a food allergy, is extremely rare, indicating that the cat is allergic to some type of food protein. In what amount the allergen enters the body – it does not matter, even if it is a small crumb, a reaction may occur, including with the appearance of one or more forms of eosinophilic granuloma. With intolerance, which occurs when exposed to a certain amount of a substance, symptoms quickly appear and quickly disappear. That is, in this case, the occurrence of plaque, ulcers or linear lesions is unlikely.
Differential diagnoses
Usually the picture for all manifestations of eosinophilic granuloma is characteristic. But it is still worth confirming the diagnosis in order to prescribe the right treatment. It is necessary to distinguish the complex from such diseases as:
- Calicivirus, feline leukemia
- Fungal lesions
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Pyoderma
- Neoplasia
- Burns and injuries
- Immune-mediated diseases
- Diseases of the oral cavity
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made comprehensively on the basis of anamnestic data given by the owner, based on the results of the examination and diagnostic procedures. If you know why the cat might have a problem, then be sure to tell the doctor about it. By eliminating this factor as soon as possible, you will save your pet from CEG. If the cause is unknown, or the diagnosis is in doubt, then the material is taken for cytological examination. For example, an indolent ulcer can be confused with signs of calicivirosis in cats, with the only difference being that with this viral infection, the ulcers look less intimidating, but are very painful. Imprint smears are usually not informative, they can only show a picture of superficial pyoderma, so a fine needle biopsy should be taken. The glass with the obtained cells is sent to the laboratory for diagnostics. A large number of eosinophils are found in the material, which gives us reason to speak of an eosinophilic granuloma complex. If, after a cytological examination, the doctor or the owners have questions that it may still be not an eosinophilic granuloma complex, but some other disease, or if the treatment does not work, then in this case the material is sent for histological examination. Treatment Treatment depends on the cause of the eosinophilic granuloma. Therapy must be taken seriously. A granuloma can return to its original state if the cause is not removed. Of course, if it is not an idiopathic condition, then symptomatic treatment is used. Treatment consists of taking hormones or immunosuppressants for two weeks, such as Prednisolone. When the owners cannot comply with the doctor’s prescription, give a tablet 1 or 2 times a day, then injections of the drug can be used, but it is not recommended to use long-acting glucocorticosteroids, one injection of which lasts two weeks. This is due to the unpredictability of the duration and intensity of the drug’s effect. The duration of therapy is about two weeks. If you have to use the drug for longer, then the course of hormones is canceled smoothly and strictly under the supervision of a doctor. But, again, this usually does not happen if the owners follow all the recommendations properly. Additionally, therapy may include antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets or ointments. The most important thing is to be patient and follow the doctor’s prescriptions, then you will definitely help your pet.