Endometritis in dogs: symptoms and treatment
Preventing the development of pathology by sterilizing a pet is the right decision if mating and the birth of puppies are not planned. Since endometritis in a dog leads to a number of complications, it is worth understanding what symptoms indicate the disease and what treatment is offered by veterinarians.

Contents
Causes of endometritis in dogs
The main factor provoking endometritis is an endocrine disorder that increases the level of estrogen in the blood of a pet. This pathology leads to the transformation of the walls of blood vessels. The presence of pathogenic organisms in the uterus causes damage to the endometrium. Therefore, the second factor is a viral-bacterial infection that triggers inflammatory processes with intoxication of the dog’s body. Vaginitis, diseases of the genital organs, the genitourinary system can cause the disease.
Other factors affecting the pathology:
- false pregnancy (pregnancy), which is difficult twice a year, accompanied by severe swelling of the nipples, an increase in the abdomen, weight gain and the appearance of milk;
- injuries of the reproductive system, ruptures and erosion on the walls of the uterus, if the dog bore large puppies, various pathologies during childbirth;
- after childbirth, a poorly contracting uterus is not completely cleared, which can lead to infection;
- death of puppies at the time of childbirth or in the womb, incomplete excretion or resorption of the fetus, infection during childbirth with non-sterile devices;
- acute and chronic diseases of internal organs of infectious and parasitic etiology;
- transmission of infection from male to female during mating. Endometritis will manifest itself after the penetration of infection from the vagina into the uterine cavity of the dog.
Veterinarians note the factors contributing to the development of pathology: the lack of important biological elements in the dog’s body during the period of bearing puppies, insufficient physical activity during pregnancy.

Symptoms of the disease
Endometritis in dogs can have a variety of symptoms, depending on the severity of the infection, and varies from mild to acute and hyperacute.
There are acute and chronic forms of endometritis.
Acute includes endometritis and metritis, complicated by infection in females who have just given birth. As the name implies, this form is transient, and therefore should be especially monitored by the owner for symptoms.
You should contact your veterinarian if you experience:
- purulent, bloody (sometimes black or brown) discharge of a thick consistency from a loop with a putrid, pungent odor;
- pain on palpation of the abdominal cavity, the abdomen is visually enlarged;
- an increase in body temperature above 40,5 ° C;
- thirst, loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea;
- apathy, general depression, drowsiness, refusal to play, walk.
In the initial phase, endometritis may not be felt due to its small localization. As long as it does not lead to tissue destruction and intoxication of the body, metabolic processes are preserved.
If the dog has recently given birth and is breastfeeding, symptoms of decreased milk production or refusal to feed puppies may indicate the need to call the veterinarian. Similarly, if 1-1,5 months have passed since the last estrus, but discharge from the loop or other warning signs are noticeable, the owner should also schedule a visit to the veterinarian.

The chronic form of endometritis occurs if the dog has not been fully treated for the acute form or there is a hormonal imbalance. It differs from the acute form by mild symptoms, lethargy and “floating” clinical manifestations. This form can last for several months. Affected dogs give birth to weak or dead puppies with symptoms of sepsis. With the development of the disease, purulent discharge from the loop appears. In the future, with a decrease in immunity, the state may transition into an acute and even purulent phase, which is dangerous for the pet.
The main symptoms of chronic endometritis include:
- violation of the estrus cycle – its duration, time intervals from one to another,
- weight loss,
- at birth, puppies are weak, with pathologies, often die immediately after birth.
Endometritis diagnostics
To establish the causes of the disease, the method of differential diagnosis is used, in which the clinical condition of the diseased is confirmed by laboratory tests. The veterinarian will need data on estrus, childbirth, operations, information on alarming symptoms from the owner. An important factor is the description of secretions from the loop. They can be photographed so as not to forget the details, to clarify the frequency, color, consistency.

After a general examination, an ultrasound examination of the state of the uterus and its walls is performed, the presence of neoplasms – cysts and tumors is detected.
Laboratory studies include:
- general clinical blood test,
- blood chemistry,
- general urine analysis,
- analysis of vaginal discharge.
During the clinical examination, the veterinarian collects exudate released from the uterus in order to identify the causative agent of the infection. Bacterial culture on nutrient media is necessary to determine the infection.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the veterinarian develops an individual treatment regimen.

Endometritis treatment
Endometritis in a dog is not easy to treat: the disease is insidious by the transience of acute phases. Therapy is selected depending on the results of the studies, the stage of endometritis, the clinical condition of the dog and conditionally consists of three phases.
Antimicrobial therapy consists in prescribing broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Symptomatic therapy eliminates signs of intoxication. For this, drugs are prescribed aimed at restoring the water-salt balance (for example, intravenous droppers of glucose solutions and Ringer-Locke). They are needed if the dog has a large fluid loss due to diarrhea or vomiting. At a high temperature, the pet is shown antipyretic drugs.
To increase the body’s resistance, a course of immunomodulators is needed.
Advanced endometritis in dogs can be treated with surgery. This happens when the body does not respond to conservative therapy; the doctor decides on a surgical intervention, during which the uterus and appendages are removed. The operation is indicated if there is a high risk of rupture of internal organs due to accumulated pus. In the postoperative period, a complex of rehabilitation therapy will be needed.
The success of treatment depends on a number of factors, among which the age of the dog, the presence of chronic diseases of the internal organs and the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys are of no small importance.

disease prevention
Prevention of endometritis is to minimize the causes that provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
From the first estrus, it is important to record in a separate journal or pet’s veterinary book the dates of the beginning and end of the cycle, the complexity of the course, childbirth or other operations.
Responsible approach to the process of mating and childbirth. At this time, the uterus is open, the endometrium is thickened, the environment is vulnerable to any pathogenic microorganisms. During childbirth, it is necessary to call a veterinarian at home, in order to avoid injury: cervical ruptures, cracks. The owner must observe hygiene: wash hands, treat them with an antiseptic, use only sterile instruments and wipes.
A balanced diet is essential for a healthy dog. But it is especially important to adhere to full feeding during the period of gestation and lactation.
If the owner does not plan to breed, sterilization is recommended for the pet.
Timely vaccination and antiparasitic treatments will save the dog from possible infections that have a direct effect on the reproductive organs and can contribute to endometritis.
It is important to monitor where the dog walks, with whom he communicates, how clean the walking area is. Particular attention should be paid to this during estrus: you should try to walk in quiet places, away from walking other dogs.
The owner should pay attention to the mood of the pet in order to monitor possible changes in hormonal levels. With careful attention, the chance of serious consequences is minimal, so the basis for disease prevention is attention and care for the animal.

Possible complications
With the progression of the disease, the infection spreads into the fallopian tubes, penetrates into the deeper layers of the uterus, triggering irreversible processes in the dog’s body. Complications with advanced endometritis can be infertility, sepsis, or even the death of a pet.
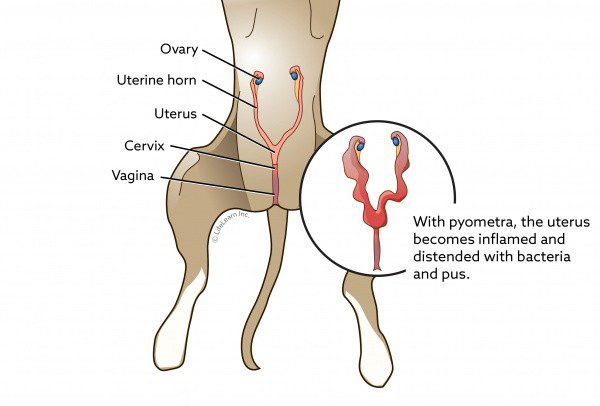
Pyometra (or purulent endometritis) is an acute inflammation of the uterus or fallopian tubes. This serious disease is referred to as postpartum complications. Pyometra often has a hyperacute course, affecting the lining of the uterus. Its difference is purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor. Due to the rapid infection process, this form is characterized by intoxication and a sharp increase in the dog’s body temperature. This pathology is extremely dangerous for the life of the dog and requires emergency surgical intervention.
Peritonitis is an acute inflammation of the serous membrane, which can develop against the background of endometritis. This is a serious complication that requires urgent treatment of endometritis in a dog, since the life of a pet goes by the clock.
With an open cervix, catarrhal endometritis develops. Turbid discharge with mucus and pus appears from the loop. The dog is restless, often licks itself under the tail.

With a closed uterus, latent endometritis progresses. Allocations cannot go outside, which complicates the diagnosis. But they are present and accumulate in the uterine cavity, which leads to its stretching and threatens with serious ruptures and blood poisoning. It can be seen that the female’s abdomen sags, on palpation it is painful in the uterus.
Sepsis (or blood poisoning) can be a complication of endometritis. The infection spreads from the uterus throughout the body, in the absence of urgent treatment can cause the death of a pet.
The consequences for even treated dogs are not simple. There are complications in the form of renal failure, which can become chronic; as a result of processes in the uterus, its size increases, other internal organs are displaced and, as a result, their functions are impaired. If you ignore this stage of endometritis, uterine rupture may occur, peritonitis may occur, which, unfortunately, often ends in the death of the dog.
The chronic form of endometritis is insidious in that already cured endometritis appears again and again with a latent course and symptoms. Even after a successful operation and subsequent treatment, there is a risk of complications. Preventing endometritis in dogs is easier than fighting the disease, so you should not lose your vigilance: with alarming symptoms, it is better to consult a veterinarian.
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
July 7 2020
Updated: February 13, 2021