Elderly dog: care rules
“Old dogs are as comfortable as old shoes.
They are a little frayed and frayed around the edges,
but they don’t squeeze anywhere. ”
Bonnie Wilcox
Unfortunately, the years do not spare our faithful friends, and they age much faster than we would like. I am the owner of such an elderly dog. It would seem that once a young and frisky dog in the morning it starts to get up harder, walk less. Sleeping more and not frolicking. Even the view is changing, it becomes much wiser and deeper … Photo: pixabay.com
Photo: pixabay.com
Contents
How to properly care for an older dog
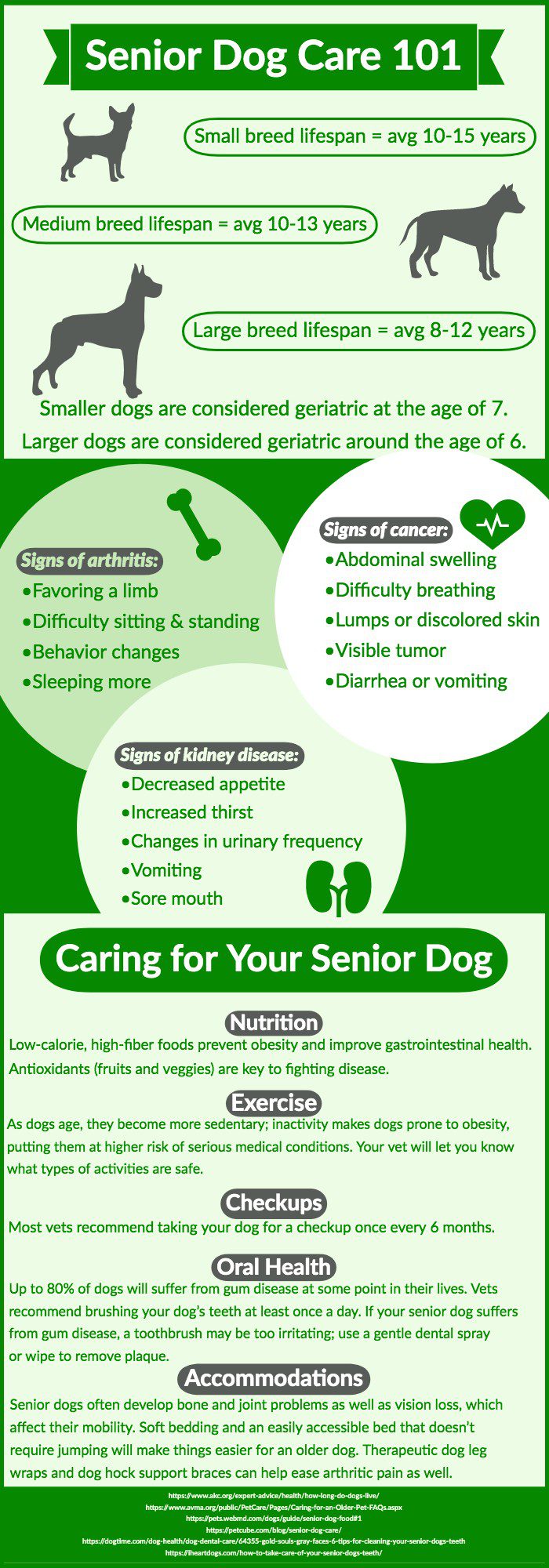
You have many years of mutual friendship and devotion behind you, and do not forget that older dogs need a special approach and care. Large breeds age much earlier than small breeds, and it is in your power to make your pet’s old age brighter and happier. It is also worth noting that in most cases, the life span of sterilized and neutered animals is much higher than that of non-sterilized ones. They are less likely to develop cancer, they are not subject to hormonal disruptions.
Preventive care for an older dog
First of all, let’s talk about preventive examinations: it is advisable for older dogs to carry them out much more often than for young ones. It is advisable to do this three to four times a year. A routine checkup for an older dog is no different than a checkup for a young dog. Most dogs, especially large breeds, suffer from diseases of the musculoskeletal system in old age, and this should be given special attention. Your pet should be seen by an orthopedist twice a year.
Internal organs of an aging dog
Charmingly follow the cardiovascular system, liver and urinary system. It is important to monitor changes in the indicators of general and biochemical blood tests. Dynamics can be seen by comparing your pet’s new test results with earlier ones. Also, do not forget to conduct an ultrasound diagnosis of the abdominal cavity twice a year. This allows you to observe and evaluate the functional state of internal organs. If you notice unusual changes in your aging pet’s behavior, contact your veterinarian immediately. Photo: pixabay.com
Photo: pixabay.com
Senior dog vaccination
As in youth, an aging dog needs routine vaccinations and deworming. But in the case of an elderly dog, even deworming must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Vaccination or deworming can be canceled by a veterinarian, based on the results of tests and diagnostic measures taken.
The idea that dogs over the age of 9 are not vaccinated is a myth.
Elderly dog teeth
Older dogs often have decayed teeth, so you need to regularly examine the oral cavity and brush their teeth. Your dentist can help you with this. Even young dogs often suffer from diseases such as tartar growth and periodontal disease. This can lead to the growth of pathogenic microflora, an unpleasant odor, inflammation and loss of teeth.
Senior dog nutrition
Also be sure to watch your pet’s diet. After all, often older dogs are prone to obesity, which puts additional stress on the joints. The diet should be balanced, appropriate for age and physical activity. Be sure to introduce vitamin and mineral supplements for older dogs. But only a veterinarian can help you choose the right diet and various supplements. Do not change the diet spontaneously and do not prescribe any drugs to the dog yourself. Contact your veterinarian. Remember that any changes are stressful – what goes unnoticed for a young dog, for an elderly one can turn into unpleasant and sometimes serious consequences.
Fur of an aging pet
With age, the coat of the dog changes, as well as the fermentation of the skin. The coat becomes duller and more brittle, shedding intensifies. There may be an unpleasant odor and dermatosis of a different nature. Examine the dog’s skin daily for redness and indurations – older dogs are prone to neoplasms. Regularly brush and bathe your dog as recommended for the breed.
Exercise for an older dog
Don’t get mad if your dog can’t keep up with you on a walk. Now you have to adjust to her pace. Don’t overload your dog. Physical activity should be reasonable and based on the abilities and needs of your elderly companion. If in doubt, it is best to consult a professional. Avoid long trips and sudden climate changes – these will all become the strongest stress factors for an aging organism. And as you know, stress is destructive. Also try to avoid overheating and hypothermia – thermoregulation is disturbed in old animals. Overheating can provoke a stroke, a heart attack. Avoid traumatic situations, since any surgical manipulations are associated with a risk due to anesthesia. Anesthesia should be used only when there is a vital need for it and it cannot be dispensed with at all.
Anesthesia for an older dog is used only when the risk to the life of the animal is much higher than the risk of a side effect of anesthesia.
The main thing to remember is that a disease detected in a timely manner is treated much easier than in an advanced stage. Do not wait until it becomes bad, and do not spare the time and effort to contact a specialist at the first symptoms that alert you. Our pets have brought us a lot of bright and pleasant moments in their lives, let’s make their old age worthy.





