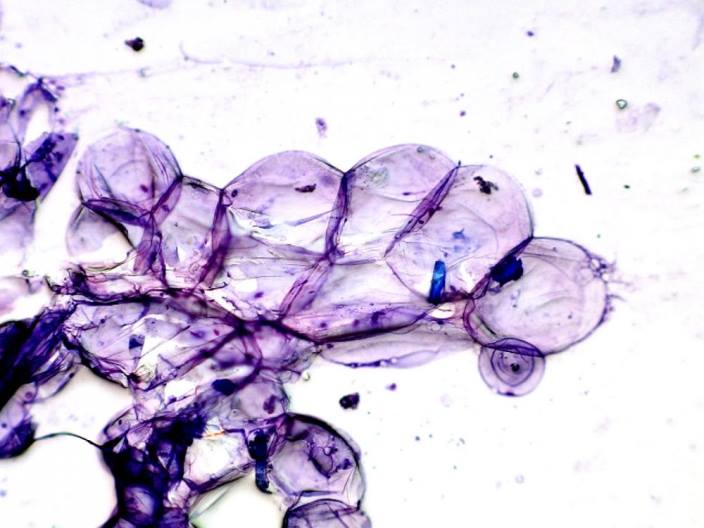
Dog fat cells
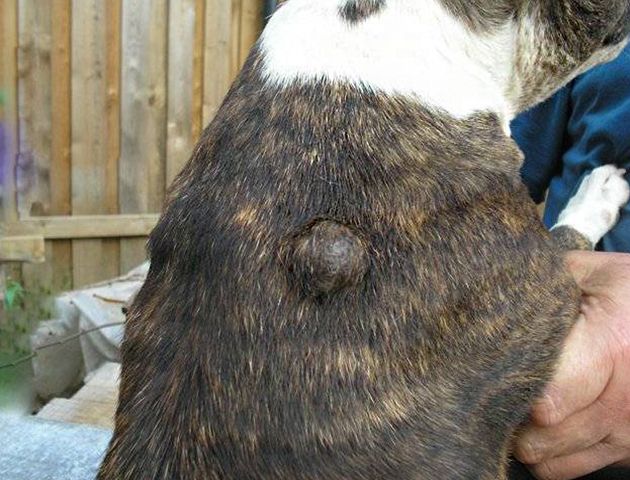
Wen or lipomas are often benign neoplasms of adipose tissue. Mostly appear in dogs of middle and older age groups, after five years. Bitches are more commonly affected than males. What to do if you find such a tumor in a dog?
features of a lipoma.
Lipomas are rounded, moderately mobile subcutaneous formations, single or multiple. Painless. Animals do not cause much concern, if they do not grow to a huge size. They are localized more often in the region of the sides, back, in the region of the sternum closer to the paws. With a prolonged process, they can interfere with the dog’s walking, creating mechanical inconvenience. Small lipomas do not undergo ulceration, unlike, for example, tumors of the mammary glands, but can be easily injured by surrounding objects and by the dog itself. Large lesions may be ulcerated. One of the varieties is an infiltration lipoma, which can damage deep-lying tissues, in this situation the treatment is more difficult. Since fat is contained not only in the subcutaneous tissue, lipomas can also occur in the internal organs, because there is also a fatty layer there. More often they are registered in a mesentery. Also, benign lipomas can degenerate into malignant fibrosarcoma. This is a dangerous condition. Atypical cells can damage many internal organs, disrupt their functioning and cause death of the animal. Benign tumors should also not be ignored, since in addition to the fact that they, reaching a gigantic size, interfere with the movement and mobility of the animal, the risk of their degeneration into malignant and metastasis increases. Also, if the formation has reached a large size, it is more difficult to carry out an operation to remove it both from a technical point of view and from the side of restoring the animal’s body. Minor surgical manipulations are naturally tolerated by dogs more easily. If you find any neoplasm on the body of a pet, it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
As with other neoplasms, the exact cause of lipomas in dogs is unknown. Predisposing factors for the appearance of these types of formations are considered genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders, inactive lifestyle, carbohydrate-rich diet, overweight.
Diagnostics
An experienced oncologist with a high degree of probability can assume a lipoma, based only on examination, palpation and personal experience. However, you should not be presumptuous, just as it makes no sense for the owners to guess whether it is a wen only by appearance or not, and try to make predictions. Valuable time may be lost if, for example, a mastocytoma is encountered. But this is a very dangerous type of tumor.
- First of all, a fine-needle biopsy of the neoplasm is performed. The resulting material is transferred to a glass slide, stained and viewed under a microscope. The method does not give a 100% result, but still the probability of specifying the type of tumor is high.
- ultrasound. It is possible to conduct a study as the formation itself in order to consider the structure: the presence of cysts, blood vessels. Ultrasound may also be required to rule out abdominal lipomas and metastasis.
- X-ray. alternative to ultrasound. You can visualize the shadows of large neoplasms in the abdominal and chest cavities.
- CT and MRI are used for a thorough cancer search, especially when there is a suspicion that the process is malignant.
- Blood tests and heart screening are required if surgery is planned.
- To accurately confirm the diagnosis, the removed tumor or part of it is sent for histological examination. With this diagnostic procedure, they look in more detail not at scattered cells, but at the structure of the altered tissue as a whole. The result of histology has to wait about 3-4 weeks.
Treatment
Surgical excision of the tumor is predominantly used. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Anesthesiologists recommend undergoing a series of tests before surgery: heart screening and blood tests. Many owners ask, what will change? The fact is that, depending on whether there are concomitant diseases of any of the organ systems, the anesthesiologist selects individually the scheme according to which anesthesia will be given, what drugs are needed, whether preparation is required before the operation or treatment after. The owner has the right to refuse additional diagnostics, but in this case, the surgical team cannot be fully responsible for the outcome of the operation. If the neoplasm is small, then the operation is fast, as is the recovery period. With an infiltration type of lipoma, it may be necessary to remove part of the muscle tissue. After surgery, you will need a short course of antibiotic therapy, suture treatment, wearing a protective collar or blanket, depending on the location of the lipoma. The age of the animal is not a contraindication for surgery. However, there are a number of reasons why surgeons may refuse, such as severe comorbidities. In this case, a decision is made about alternative methods of treatment, for example, radiation therapy. In general, with lipoma, the prognosis is favorable, relapses do not occur often. In each case, the dog should be re-examined by a doctor, as another, malignant tumor that looks like a lipoma may appear.





