
Diseases of ornamental rats, symptoms and treatment at home
Decorative rats are not only the smartest unpretentious pets, they are little devoted friends who know how to wait, empathize and have fun with their beloved owner. Fluffy pets live a relatively short time by human standards, only 2-3 years, but even during this short time period, funny animals suffer from diseases of various severity.
IMPORTANT!!! A specialist should diagnose the pathology, identify the cause and treat the rat! If a domestic rat is sick, it is advisable for the owner to urgently contact a veterinary clinic, some diseases of rats are very dangerous for humans: mycoplasmosis, rabies, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, tularemia, toxocariasis, rickettsiosis, leptospirosis, hemorrhagic fever, typhus, plague, sodoku, listeriosis.
Contents
How to understand that a rat is sick
Diseases of domestic rats often occur due to violations of the norms of feeding and maintenance, hypothermia, overheating or drafts cause colds and inflammatory diseases in intelligent animals, an imbalance in the diet and the abuse of harmful delicacies are the cause of obesity, allergies, beriberi or intestinal pathologies in pets.
Infectious diseases of rats are also common, domestic rodents can become infected with viral, fungal and parasitic diseases through care items, food or contact with infected relatives.
Often the owners of fluffy rodents have a question whether a rat can get a virus or a cold from a person. Decorative rats are bred in the laboratory, have reduced immunity and are susceptible to human respiratory viral infections. In the acute period of the disease, the owner needs to limit communication with pets, cancel walks and games, leaving only feeding and water changes for the animal.

Diseases of domestic rats can be caused by various causes and pathogens, as a result of which a different clinical picture will be observed. The owner can understand that a domestic rat is sick if a beloved rodent has characteristic symptoms common to many pathologies:
- change in appetite or complete refusal of food;
- lethargy, excessive drowsiness, unwillingness to play with the owner or other rats;
- change in color and odor of urine and feces;
- dirty genitals, the pet stops licking;
- dull and tousled hair, the formation of bald patches;
- the appearance of causeless aggression, anxiety, nervousness;
- slowness, difficulty moving;
- respiratory failure;
- unnatural postures;
- the formation of growths, bumps, swelling on the body of the animal;
- discharge from the nose, eyes, vagina, anus.
Diseases of ornamental rats and their treatment
Diseases in rats can be divided into two large groups, within which several subgroups are distinguished.
contagious diseases
They are caused by various biological pathogens (pathogenic microflora, viruses, fungi) and are divided into:
- Infectious diseases of rats;
The causative agents are bacteria, viruses, fungi, rickettsia: listeriosis, ectromelia, salmonellosis, pasteurellosis, infectious pneumonia, tularemia, rabies, tuberculosis, encephalomyelitis.
- Invasive (parasitic diseases).
They are caused by infection of the body of a domestic rat with ticks, insects, helminths and protozoa: syphacyosis, aspiculuriosis, rodentolepiasis, hymenolepiasis, coccidiosis, demodicosis, pediculosis, fleas, scabies.
Non-communicable diseases
Decorative rats develop as a result of a violation of the conditions of feeding and keeping the animal and are divided into:
- Internally;
Diseases of internal organs, blood and metabolic disorders: gastritis, enterocolitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, beriberi, oncology, allergies, anemia, cardiovascular insufficiency, ischemia, porphyrin.
- outdoor;
Diseases of the limbs, head, neck, skin, tail – wounds, pododermatitis, injuries, skin abscesses, burns, bruises, frostbite, eczema, diseases of the eyes, ears and teeth.
- Diseases of the genital area.
Endometritis, vaginitis, pyometra, miscarriage, spirochetosis.
Treatment of pathologies of decorative rats is carried out by a veterinarian after determining the diagnosis and finding out the cause of the disease, many diseases require specific therapy or the euthanasia of the infected animal.
Infectious diseases of domestic rats
Infectious diseases often found in ornamental rats include: mycoplasmosis, listeriosis, tuberculosis, infectious pneumonia, parasitic diseases.
Infectious diseases of rats
Domestic rodents often become infected with infectious diseases, sources of pathogens can be contaminated food, water, litter, insects, sick animals. These pathologies are characterized by a severe course with serious damage to the vital organs of the animal, often leading to the death of the pet. Many infectious diseases of rodents are dangerous for humans, self-treatment of rats is unacceptable and threatens with sad consequences. A timely appeal to a specialist can save the life of a small animal and protect the family of the owner of the animal from infection.
Mycoplasmosis
Most decorative rats are carriers of the causative agent of mycoplasmosis, but infection and the development of characteristic pathological changes are observed only as a result of contact with a sick animal, in violation of the conditions of feeding and keeping, hypovitaminosis and weakened immunity, in elderly individuals. Pathogenic microorganisms affect the upper and lower parts of the lungs of a rodent, forming numerous abscesses and causing the development of pneumonia, sometimes the inflammatory process affects the animal’s genitals.
Symptoms characteristic of rats: sneezing, red discharge from the nose and eyes (porphyrin), wheezing and whistling when breathing, blue mucous membranes and skin, the rat became lethargic and lies a lot. Treatment includes a course of antibiotics, hormones, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs; in advanced cases, it is impossible to save a fluffy rodent.
Rabies
Rabies in decorative rats is quite rare, it is very dangerous for humans, a pet becomes infected through saliva when bitten by a sick animal, especially while walking on the street, the most severe course of the disease is observed when biting the head or the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbnerve nodes.
The disease can proceed in violent, paralytic and abortive forms, the incubation period in bitten people and ornamental rats ranges from 2 weeks to three months.
The signs of rabies in rats develop gradually, in several stages:
- the first stage – there is apathy, photophobia, followed by aggressiveness, sharp jumps around the cage, characteristic attempts to catch non-existent flies. The rodent refuses food, salivation, vomiting, shortness of breath appear, the pet cannot swallow due to paralysis of the lower jaw. Similar symptoms of rabies in rats against the background of recent bites should alert the owner of the rodent, you must urgently contact a veterinary clinic;
- the second stage – rabies in rats manifests itself in increased aggression, the rodent bites people, animals, a cage, profuse salivation appears, paralysis of the hind limbs and throat, a drooping jaw, a lowered head and tail are characteristic. Outbursts of excessive aggression are replaced by periods of rest. The rabies virus enters the brain and the rat dies within 5-10 days. When a disease is detected in a decorative rat, the animal is euthanized, the room where the pet was kept is disinfected with ultraviolet rays and alcohol.
infectious pneumonia
The causative agents of the disease are specific viruses, domestic rodents are infected by airborne droplets, the pathological process occurs in the upper lung of a domestic rat. Pathology is manifested by characteristic symptoms: sneezing, red and mucopurulent discharge from the nose and eyes, hunched back, wheezing and whistling, the rodent breathes heavily from its sides, refuses food, the rat is lethargic, apathetic, sleeps more than usual. Sometimes there is a rapid course of the disease, due to an increased level of metabolism in rats, in advanced cases, the animal cannot be saved. Treatment is carried out with the use of antibiotics, hormones, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Papillomas in rats
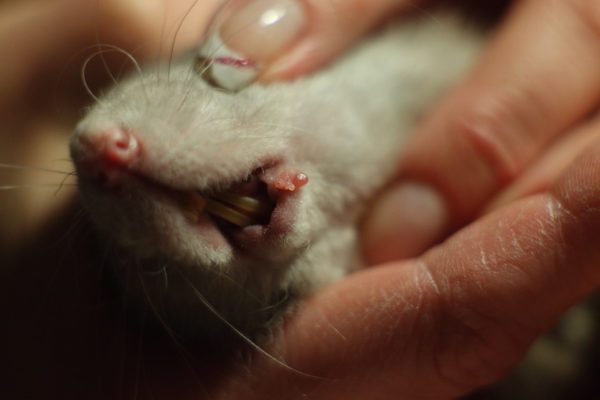
Papilloma virus in rats is manifested by the formation of small skin outgrowths on the skin, which can degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Infection occurs upon contact with a sick animal through damaged skin (wounds, cracks, scratches), the disease manifests itself only in emaciated, weakened or elderly individuals. When detected, papillomas are subject to surgical removal.
Parasitic diseases of rats
Most often, decorative rats are affected by ectoparasites – parasitic insects, infection occurs through feed, filler, clothes and hands of the owner, upon contact with sick animals, the characteristic symptoms of the disease are severe anxiety of the animal, sores on the rat’s neck, scratches and wounds on the head and shoulders fluffy rodent. For the treatment of a pet, they are treated with insecticidal sprays.
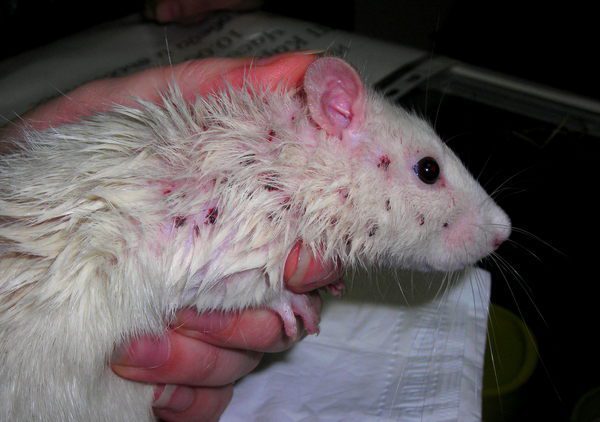
Withers and lice
Small insects, you can find adult red-brown insects or nit eggs in the form of white dandruff attached to the rodent’s fur. Lice feed on the blood of a domestic rat, lice feed on skin scales and blood, parasitism is accompanied by severe itching, and can cause the death of an animal.
Fleas
Small blood-sucking insects that can migrate between rats, dogs and cats, a sick rodent itches intensely, bites hair with its teeth, and worries. If the rat has bloody crusts on its back, this indicates a pet infection with fleas and requires immediate treatment.
pliers
Rat mites live on the skin of healthy animals, emaciated weakened animals get sick, parasitism is accompanied by itching, the rat has sores on the neck and muzzle or red-yellow growths on the ears and genitals. Some types of rat mites are dangerous to humans.
Worms
Parasites are localized in the internal organs of rats: intestines, kidneys, liver, lungs, migration of larvae causes inflammation in the affected organs, worms produce poisons that cause exhaustion and intoxication of the rodent. The owner may notice intestinal disorders in the pet, lethargy, progressive emaciation, detection of parasites in the feces. Treatment includes the use of deworming drugs.
Common Non-Contagious Diseases of Domestic Rats
Among non-communicable diseases in domestic rodents, the following are common: cancer, dental pathology, urolithiasis, intestinal disorders, obesity, allergies, coronary heart and brain disease, heart and kidney failure.
Tumors
Oncological diseases often affect adult ornamental rats older than two years, mostly females, and cause the death of a beloved pet.
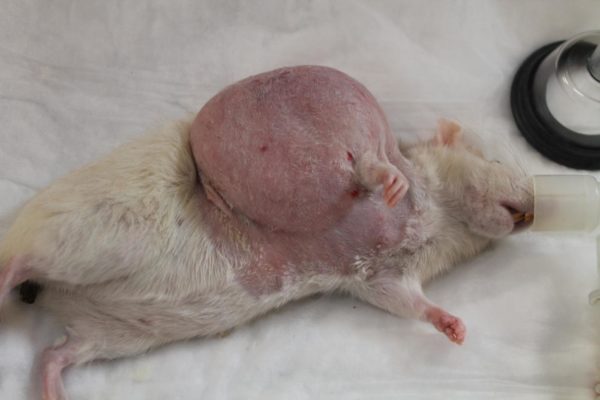
Benign neoplasms are subject to surgical removal with a favorable prognosis, rat cancer is not treated due to the formation of metastases and the germination of malignant tumor formations in healthy tissues of the animal. In ornamental rats, the following types of tumors are common:
- a tumor of the mammary glands is found as a mobile or fused lump on the abdomen;
- a swelling on the neck, on the side, under the paw or under the tail is felt like a rolling ball under the skin on the leg;
- the swelling on the muzzle looks like a swollen cheek in a pet;
- a brain tumor (BTM) is a common tumor of a benign nature with a characteristic clinical picture: the rat’s front and hind legs failed, the rodent lies with outstretched limbs, it is impossible to bend the joints;
- bone tumors are manifested by thickening of the bones of the limbs, ribs and skull, the animal is not able to move independently.
Allergy

Allergy in rats occurs quite often to the action of external stimuli, which can be filler, food and water. Allergy in domestic rats is accompanied by itching and is manifested by characteristic symptoms: active scratching of the skin, the appearance of wounds and scabs on the paws and neck, swelling of the limbs and skin behind the ears. The signs of allergy in rodents are similar to the symptoms of insect parasitism, the diagnosis of the disease and the examination of the animal should be carried out by a veterinarian. Treatment of allergies in rats involves the use of antihistamines, anti-inflammatory ointments and the exclusion of the source of the allergen: changing the filler and feed.
Rhinitis
Rhinitis in rats occurs when contact with infected animals or people (infectious rhinitis) or when conditions are violated (non-communicable rhinitis). Symptoms of infectious rhinitis in rats develop rapidly, the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, in weakened, emaciated and elderly animals, the pathology can be fatal. If the rat caught a cold, then non-contagious rhinitis occurs.
Infectious rhinitis in a rat is manifested by mucopurulent discharge from the nose, sneezing, grunting, red discharge from the nose and eyes, lethargy, an increase in the general body temperature of the animal, shortness of breath, heavy breathing and wheezing. It is necessary to treat rhinitis with a veterinary specialist using antibacterial, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs.
A cold in rats occurs when the animal is in a draft, hypothermia or sudden changes in temperature in the room, contributing factors are insufficient feeding and unsanitary conditions for keeping the rodent. If a decorative rat has a cold, a runny nose will be mucous, grunting, sneezing is observed, the animal rubs its nose with its paws. Treatment of the common cold should be started at the first symptoms of the disease, inhalations and antibacterial drugs are prescribed for sick pets, non-contagious rhinitis can cause pneumonia in a domestic rat.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea in a rat occurs as a result of a violation of the conditions of keeping and feeding a pet, against the background of stress, and diarrhea can also be due to the development of an inflammatory process in the intestines of an animal during infectious and parasitic diseases. The disease manifests itself in the rapid release of light, liquid fecal masses with an unpleasant odor; mucus and streaks of blood may be present in the feces.
The owner of the rat needs to know what to do if the rat has diarrhea in order to prevent dehydration and exhaustion of the animal. If the animal has soft feces with mucus, you can drink rice water and diluted smectite 3 times a day for three days, and also exclude prohibited foods. In the event that improvement does not occur, or the animal’s diarrhea initially proceeds with the release of a large amount of liquid foamy mass with blood and mucus, it is urgent to consult a specialist.
Conjunctivitis
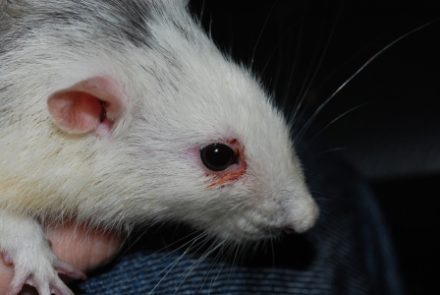
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by microtrauma or a viral infection. The disease is manifested by purulent discharge from the lacrimal canal, the eyes of animal covers, dried crusts of pus are found on the eyelids. If the rodent has an inflamed eye, it is urgent to deliver the pet to a specialist, the animal needs to wash the conjunctival sac with antiseptic solutions, put hormonal and anti-inflammatory ointments under the eyelid.
Corns (pododermatitis in rats)
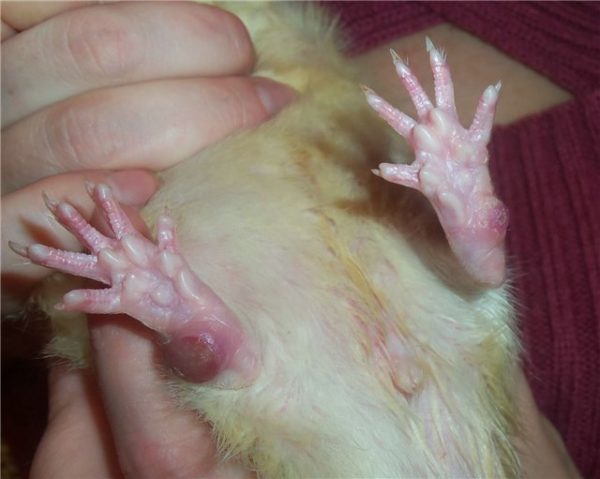
Pododermatitis in elderly or over-fed rats occurs when animals are kept on hard dry filler or in cages with slatted floors, dry skin of the feet is damaged and rounded corns are formed in rats, resembling human corns. In the future, periodic opening and suppuration of these swellings occurs, lameness and chronic irreversible processes occur in the ligamentous apparatus of the pet’s limbs. Treatment of pododermatitis should be started immediately with reddening of the feet, therapy is reduced to moisturizing the skin with oils and creams, corns are lubricated with wound healing ointments. An important preventive step is to change the conditions of keeping and feeding.
Periodontitis
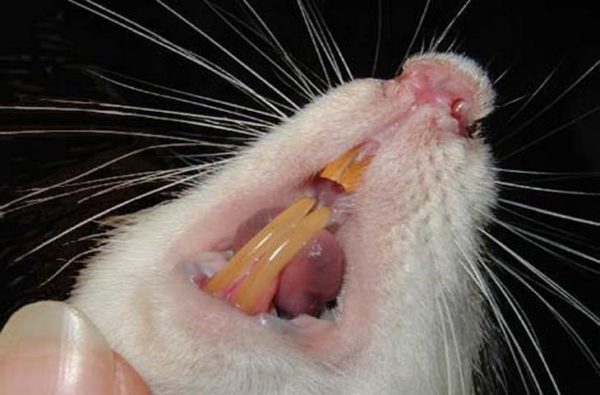
Periodontitis in rats is an inflammatory disease of the musculoskeletal apparatus of the tooth, manifested by refusal of food, bad breath, redness and bleeding of the gums, yellowness of the teeth, profuse salivation, sometimes with blood, loosening and loss of teeth, swelling of the muzzle. The disease develops in violation of the rules of feeding and maintenance, an unbalanced diet using predominantly soft food. If the rat’s teeth turn yellow, it is urgent to revise the diet, solid food cleans the tartar well, preventing the development of periodontitis. Treatment of the disease in advanced cases includes the removal of diseased teeth and tissues under local anesthesia.
Porphyrin
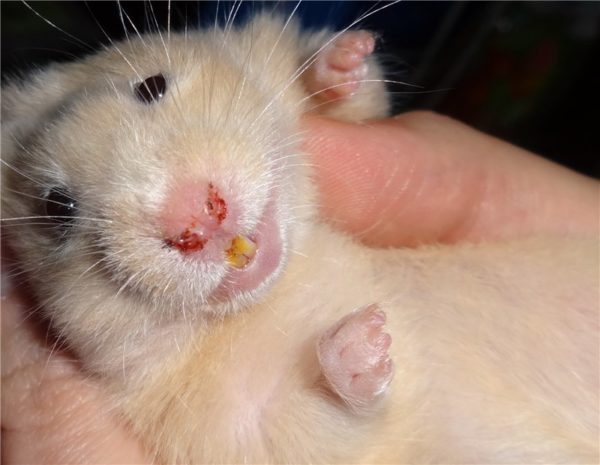

Porphyrin in ornamental rats is manifested by burgundy-red outflows of the secretion of the Garder gland from the nose and eyes, resembling dried blood in appearance. Porphyrin arises independently in case of injuries, stress, violation of the conditions of feeding and maintenance, or signals serious pathological conditions in the body: pneumonia, mycoplasmosis, oncology, tuberculosis. Treatment of porphyrin is reduced to improving the conditions of feeding, keeping, eliminating stress and symptomatic therapy.
Stroke
Stroke is a common pathology in ornamental rats, characterized by impaired cerebral circulation as a result of rupture or blockage of blood vessels in the brain. Individuals suffering from obesity, heart and kidney diseases, diabetes mellitus, and oncology are predisposed to the disease. Stroke is manifested by impaired coordination, paralysis of the limbs, blindness, respiratory failure, eye hemorrhages, the rat walks sideways, the rodent may become lethargic or aggressive. Treatment is effective in the first hours after the onset of the disease, the animal is prescribed oxygen, diuretics and antiepileptic drugs.
Abscess
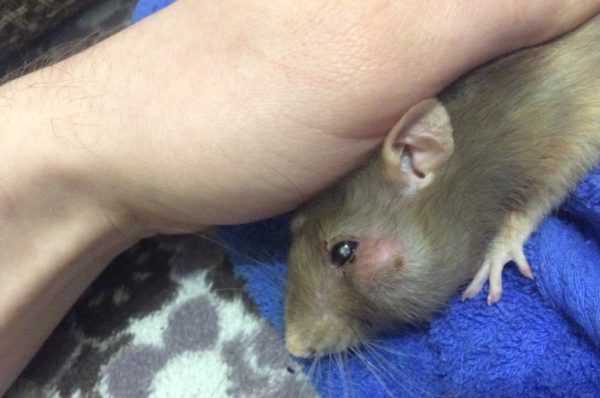
An abscess is a focal inflammation of tissues, a fairly common pathology in domestic rats that occurs when the integrity of the skin is damaged against the background of reduced immunity. An abscess is characterized by the formation of a swelling filled with pus. Treatment of the disease is carried out only by a veterinarian by surgical opening with the use of local anesthesia. Treatment at home can provoke infection of healthy tissues, sepsis and death of the pet.
Otitis
Otitis in rats is a common inflammatory disease of the ear; localization can be internal, middle or external, in the latter case, the skin of the auricle and the external auditory canal are damaged. Otitis externa and otitis media can be the result of otitis externa or caused by an infection of the upper and lower respiratory tract, otitis externa occurs as a result of damage to the skin of the auricle by sarcoptic mites, bacterial and fungal infections, against the background of eczema and dermatitis.
Otitis in a rat is manifested by pronounced symptoms: discharge from the ear with an unpleasant odor, redness and swelling of the auricle with external otitis, head tilt to the side, circling in place, the rodent rubs the ear against objects, treatment of the disease must begin immediately. The animal is prescribed a course of antibiotics, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs.
It is advisable for the owner of a decorative rat to immediately show the pet to the veterinarian when changing the behavior and appearance of the domestic rodent, as well as refusing food. It must be remembered that there are diseases of rats that are dangerous to humans, some pathologies can develop rapidly and cause the death of a beloved pet in a matter of hours. Wasting time self-medicating can be dangerous both for the life of the animal itself and for the health of all household members, especially young children.
What sick domestic rats: symptoms and treatment of common and rare diseases
3.2 (63.41%) 135 votes





