Diseases of guinea pigs: symptoms and treatment of common diseases
Guinea pigs are fluffy pets that live quite a long time compared to other domestic rodents. Lovely creatures are distinguished by good health, most of the diseases of charming animals occur as a result of violations of the conditions of feeding and keeping.
IMPORTANT!!! Domestic rodents can infect the host family with dangerous infectious diseases, therefore, an experienced rodentologist, a veterinarian specializing in diseases of domestic rodents, should determine the symptoms and treatment in each case!
Contents
- How to understand that a guinea pig is sick
- What causes guinea pigs
- Infectious diseases of guinea pigs
- Parasitic diseases of guinea pigs
- Non-communicable diseases of guinea pigs
How to understand that a guinea pig is sick
A healthy pet pleases a loving owner with a cheerful mood and willingness to play at any time, curious guinea pigs are always happy with the voice of a familiar person and their favorite treats. Signs of health are also: clean dry eyes, nose, ears and genitals, a beautiful even coat and excellent appetite.
You can determine that a guinea pig is sick by a characteristic clinical picture:
- the fluffy animal is very lethargic, depressed, tries to hide, does not respond to the caresses of the owner and the offered treats, prefers to sit still, lie down or sleep;
- a small rodent refuses food and water;
- the coat is tousled, dull, there is hair loss, areas of baldness, sometimes there are scratches, wounds and ulcers on the skin;
- the eyeball is enlarged or, conversely, there is a narrowing of the palpebral fissure, the eyes are red, swollen, lacrimation occurs;
- the guinea pig sneezes, pulls its muzzle with its paws, mucopurulent discharge flows from the nose, the hair on the muzzle and chin is stuck together, covered with crusts;
- sometimes a small animal breathes heavily, you can hear a gurgling cough, wheezing, whistles;
- litter is dry, solid or vice versa liquid, fetid, sometimes there is a complete absence of bowel movements;
- the skin of the auricle is reddened, swollen, there may be dark discharge in the ears;
- the fluffy rodent itches intensely, worries, gnaws at itself and rapidly grows bald;
- in the urine there is a visible sediment and drops of blood;
- the guinea pig moves heavily around the cage, falls on its side, sometimes there are convulsions, chaotic movements of the limbs and paralysis;
- the mouth of a beloved animal is constantly ajar, the animal squeaks when feeding, pieces of food fall out of the oral cavity and profuse salivation;
- calluses or non-healing bleeding wounds form on the pads of the limbs;
- bumps and growths are felt on the body of a pet.
It is quite problematic to cure a guinea pig at home, self-treatment is associated with the risk of aggravating the situation, developing serious complications and death. If your beloved pet is ill, it is worth entrusting the diagnosis and treatment of pathology to competent specialists.
What causes guinea pigs
Common diseases of small animals include infectious and non-communicable diseases. Infectious diseases in guinea pigs develop as a result of the defeat of the animal by pathogenic bacteria, viruses and fungi, most often individuals with reduced or undeveloped immunity are ill: young animals, elderly rodents, weakened pets. A huge role in maintaining immunity is played by high-quality feeding of funny animals, and providing the animal’s body with the necessary amount of vitamin C.

Non-contagious diseases of guinea pigs occur in charming pets in old age, in other individuals, the causes of pathologies are a banal violation of optimal feeding and maintenance conditions.
It is desirable to treat guinea pigs in a veterinary clinic, it is allowed to call a specialist at home to identify the cause and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Sometimes surgery or the use of specific drugs is necessary to save the life of a beloved animal.
Infectious diseases of guinea pigs
Regardless of the quality of care and feeding, furry pets can become infected with infectious diseases through food, water, contact with sick relatives or other pets, insect bites. Infectious pathologies proceed quite hard, and most often end in the death of a small animal. Guinea pigs can infect the host with trichophytes, microsporia, listeriosis, tuberculosis, rabies, mycoplasmosis, pediculosis, plague, toxoplasmosis. Diagnosis and treatment of infections must be carried out by a veterinarian; for many diseases, the euthanasia of a sick animal is indicated in order to avoid the spread of infection and human infection.
Plague
Fluffy animals become infected with plague through contact with sick relatives, the causative agent of the pathology is a virus. The pathology is characterized by high virulence and death of an infected pet. A sick rodent becomes lethargic and depressed, refuses to eat.
When the disease occurs characteristic neurological symptoms:
- convulsions;
- lack of coordination;
- chaotic movements or paralysis of the limbs.
What to do about guinea pig plague?
The animal must be delivered to a veterinary clinic, the diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory methods, if a pathogen is detected, the sick pet must be euthanized.
Mycoplasmosis
The disease is observed in elderly, weakened and young individuals who become infected through contact with sick relatives.
The causative agent of the pathology are pathogenic microorganisms that affect the respiratory organs of the animal with the formation of characteristic abscesses and the development of pneumonia.
Sick animal:
- refuses food and water;
- becomes lethargic and inactive;
- mucopurulent discharge from the nose and eyes, sneezing, coughing are observed;
- heavy breathing with wheezing and whistles;
- fever.
What to do with mycoplasmosis?
Treatment of a sick pet should begin with the development of the first symptoms of pathology, therapy includes a course of antibacterial, vitamin, immunostimulating, expectorant and anti-inflammatory drugs. If untreated, the fluffy animal dies after 3-5 days from the onset of the disease.
Rabies
A small animal becomes infected with rabies after being bitten by a sick animal in the head, most often this occurs while walking a pet in the external environment.
The rabies virus is dangerous to humans.
The characteristic clinical picture of the disease develops 2-12 weeks after contact with an infected animal. First, a sick guinea pig develops apathy, which is replaced by uncharacteristic bouts of arousal. The pet has salivation, vomiting, paralysis and shortness of breath. Then uncontrolled aggression occurs, during this period the fluffy animal is able to bite relatives, humans or other pets.
What to do about rabies?
At the first suspicion of the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary to urgently contact the veterinary clinic in order to avoid the spread of the disease and infection of the hosts. If the causative agent of the pathology is detected by the laboratory method, the pet must be urgently euthanized.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis
Domestic rodents become ill with a viral infection after contact with sick pets. Infection can also occur through water, food, or the skin of an animal. The infection is extremely dangerous for people. At the first symptoms of pathology, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
The disease is manifested by characteristic symptoms:
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- feed refusal;
- an increase in body temperature;
- vomiting;
- photophobia;
- convulsions and paralysis.
What to do with lymphocytic choriomeningitis?
Upon confirmation of the diagnosis, the sick animal is subject to immediate euthanasia.
Vaccination is essential to prevent guinea pig disease.
Parasitic diseases of guinea pigs
Guinea pigs have internal and external parasites, infection of small animals occurs through food, water, human clothing and contact with infected relatives or domestic animals. Parasitization of endoparasites is accompanied by severe itching, as a result of which the restless animal constantly itches, numerous wounds, scratches, eczema, and alopecia appear on the body of the furry animal. Internal parasites most commonly cause lethargy and digestive upset.
Sarcoptic mange
The disease occurs when a pet is infected with subcutaneous mites that parasitize in the Malpighian layer of the skin. Parasitic insects have chewing mouthparts for migration in subcutaneous tissues. Pets become infected through food or contact with sick pets.
When the disease is noted:
- strong anxiety of a furry animal;
- combing the body;
- the formation of cone-shaped growths and alopecia on the skin of the muzzle and limbs.
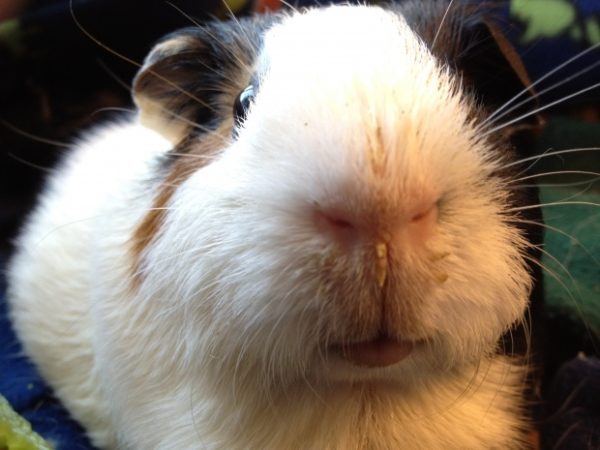

What to do with sarcoptic mange?
The diagnosis is confirmed when the pathogen is detected in a skin scraping; Stronghold drops are used for treatment according to the weight of a small pet.
Trixacarose
The causative agent of the pathology is an arachnid subcutaneous mite, which causes severe itching. The disease is also called guinea pig scabies. Infection occurs through contact with sick animals.
An infected individual has:
- lethargy;
- refusal of food and water;
- combing and gnawing the skin;
- the formation of wounds, ulcers and foci of baldness in the spine and extremities;
- abortions and loss of coordination.
In the absence of timely treatment, a pet may die from dehydration and the addition of a secondary infection.
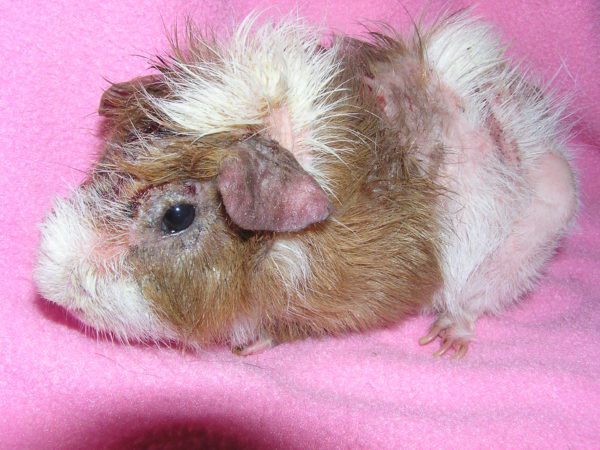

What to do with trixcarosis?
After identifying a subcutaneous tick in a skin scraping, a course of Otodectin or Ivermectin is prescribed to a sick rodent.
Vlasoyed, lice, fleas
Vlas-eaters, lice and fleas parasitize on the skin of furry pets, feeding on its blood. Lice cause pediculosis, which is dangerous for the owners of a funny animal.
Animal affected by insects:
- often itches and worries;
- loses weight;
- wounds, abscesses, scratches are found on the skin;
- adults or nits can sometimes be seen with the naked eye.

What to do in case of damage by ectoparasites?
When a pathogen is detected, the veterinarian uses drugs based on ivermectin or permethrin to treat a sick animal.
Helminthic invasions
Parasitization of nematodes and protozoa in the liver, intestines or respiratory organs of domestic rodents is accompanied by:
- lethargy;
- refusal of food;
- with pride;
- vomiting;
- shortness of breath or cough.
A vivid clinical picture is observed in weakened, elderly animals and young animals. Infection of furry animals occurs through food, water and contact with sick relatives.
What to do with the defeat of worms?
The diagnosis is confirmed by a veterinarian upon detection of pathogens in the analysis of the animal, treatment is based on the use of anthelmintic drugs.
Non-communicable diseases of guinea pigs
Most often, domestic rodents develop diseases of the respiratory, digestive and genitourinary systems, metabolic disorders, skin and oncological diseases, pathologies of the eyes and teeth, and various injuries. Non-contagious pathologies arise as a result of non-compliance with the rules of feeding and keeping furry animals.
Respiratory diseases
Rhinitis
Inflammation of the nasal mucosa in domestic rodents occurs when complication of colds or when attacked by pathogenic microbes or viruses. The disease is dangerous by the development of bronchitis and pneumonia.
A sick animal has:
- mucopurulent discharge from the nose and eyes;
- sneeze;
- lethargy;
- food refusal.
What to do with rhinitis?
Treatment of the common cold includes cleansing the nasal passages of mucus using vitamin, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and sulfanilamide drugs.
Pneumonia
Inflammation of the lungs in domestic rodents often occurs upon contact with sick relatives or in the spring-autumn period with hypothermia. Pathology is dangerous with a rapid course and death. A sick pet refuses food, coughs and sneezes, purulent discharge from the nose and eyes is observed, wheezing and whistling are heard with heavy breathing.
What to do with pneumonia?
Animal treatment is based on the use of antimicrobial and sulfanilamide drugs, anti-inflammatory, expectorant, immunomodulatory and vitamin agents.
Digestive system pathologies
Bloating
Bloating of the stomach and intestines in guinea pigs develops against the background of infectious diseases or as a result of feeding roots, wet grass, and poisonous plants to a fluffy pet. With pathology, gases resulting from fermentation accumulate in the cavity of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The disease is accompanied by severe pain. In the absence of first aid, a small animal may die.
With bloating, the pet becomes:
- lethargic and lethargic;
- refuses food and water;
- breathing heavily and grinding his teeth;
- the abdomen is greatly enlarged and makes a characteristic tympanic sound when tapped.
What to do with bloating?
Emergency assistance consists in feeding carminatives to a sick animal with a massage of the abdomen, painkillers, probiotics and a diet are prescribed to a furry animal.
Constipation
Constipation is a deadly condition for a domestic rodent, the development of pathology contributes to:
- lack of succulent feed and water in the diet of your beloved pet;
- overfeeding;
- hypodynamia and diseases of the digestive system.
Guinea pig disease manifests itself:
- absence or decrease in the amount of litter;
- refusal of food;
- anxiety;
- vomiting;
- enlargement and pain in the abdomen.
Constipation is dangerous by rupture of the intestinal wall and death.
What to do with constipation?
The treatment of the pathology consists in drinking vaseline oil to a small patient or injecting laxatives into the rectum, after alleviating the condition, a course of probiotics and a restorative diet are used.

Diarrhea
Diarrhea in funny animals develops when:
- infectious diseases;
- poisoning;
- eating spoiled, poisonous or forbidden foods.
With diarrhea, the oppressed animal:
- refuses to feed;
- lethargy is observed;
- liquid stools, sometimes with an admixture of mucus and blood.
Pathology is dangerous with a fatal outcome from dehydration.
What to do with diarrhea?
Depending on the patient’s condition, the veterinarian prescribes detoxification therapy for the animal, a course of antibacterial or sulfanilamide drugs, astringents and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Metabolic disorders
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus in guinea pigs is caused by hereditary factors, feeding forbidden foods or industrial feeds with various additives.
Pathology manifests itself:
- increased thirst;
- clouding of the cornea of the eye;
- swelling of the muzzle and limbs;
- a decrease in the amount of urine produced.
What to do with diabetes?
Treatment of pathology in pets has not been developed, a small patient is prescribed a lifelong diet.
Obesity
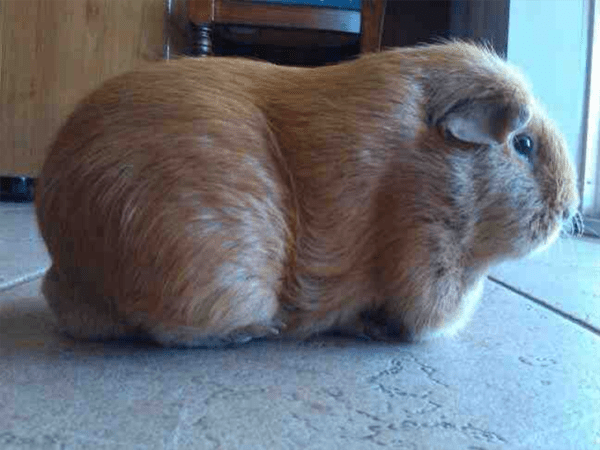

Obesity in furry animals occurs as a result of:
- physical inactivity and overfeeding of the animal;
- crowded content;
- lack of necessary physical activity;
- enough drinking water and succulent feed.
Obesity in a domestic rodent manifests itself:
- shortness of breath;
- lethargy;
- the appearance of corns on the feet;
- weight gain.
What to do with obesity?
Treatment of pathology involves the appointment of a low-calorie diet with the introduction of daily walking, depending on the patient’s condition, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, painkillers, antibacterial drugs are used.
Injuries
Guinea pigs are quite often injured after fights, falls from a height or careless handling. Animals have bruises, dislocations, open and closed fractures of the limbs and spine.
What to do if a guinea pig falls from a height?
If an injury is suspected, it is necessary to take the pet to a veterinary clinic for damage diagnosis. Dislocation successfully adjusted by a specialist at the reception. For treatment closed fracture limbs are bandaged. Open fracture is an indication for limb amputation. At spinal injury while maintaining the integrity of the spinal cord, painkillers, vitamin and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. With a rupture of the spinal cord it is recommended to euthanize the animal.

Cardiovascular diseases
Heart failure
Pathology occurs in weakened or elderly individuals, sometimes it is a complication of bronchitis.
A sick pet has:
- weight loss and activity;
- wheezing when breathing;
- dry cough;
- blue fingers;
- lack of coordination.
What to do with heart failure?
The sick animal is prescribed cardiological and vitamin preparations.
Stroke
Most often, a stroke occurs in older rodents, sometimes the cause of the pathology is severe stress. In the absence of emergency assistance, a fluffy animal can die suddenly.
With a stroke, there is:
- laying a pet on its side;
- there are convulsions, convulsive movements of the limbs;
- severe shortness of breath.
What to do with a stroke?
Emergency assistance consists in stopping a heart attack with cardiological drugs with the further appointment of drugs that improve the nutrition of the heart muscle.
Diseases of the urinary system
Urolithiasis disease
Urinary tract disease is caused by:
- hypodynamia;
- obesity;
- lack of water and succulent feed in the animal’s diet;
- overfeeding a small animal;
- feeding mainly dry granular feed.
sick animal:
- refuses to feed;
- becomes restless;
- drops of blood are observed in the urine;
- the amount of discharge decreases;
- the pet is very sensitive to touch.
What to do with urolithiasis?
The analysis is put after a laboratory study of a urine test of a small patient and an ultrasonographic examination. Depending on the size of the stones, antibiotic therapy or surgical treatment is used.
Cystitis
The cause of inflammation of the bladder in a small animal is hypothermia of a pet. A sick animal has frequent urge to urinate with a decrease or absence of urine discharge, the presence of blood in the urine.
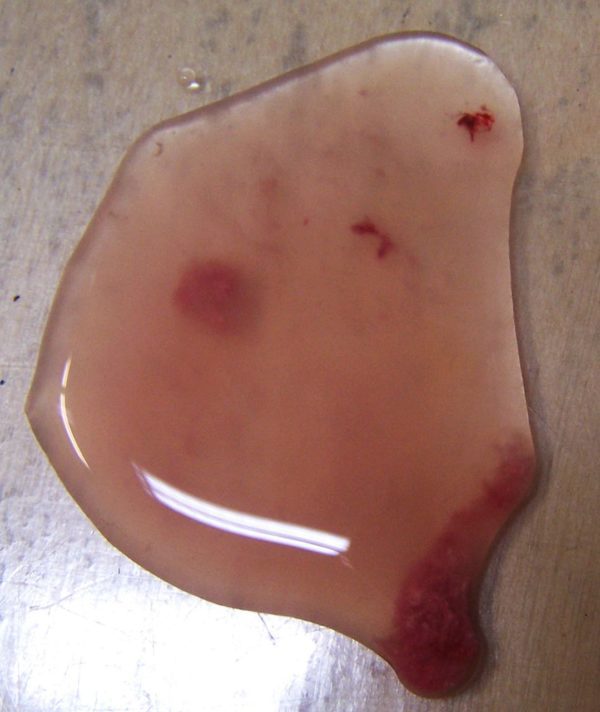
What to do with cystitis?
Treatment of a furry patient is based on the use of antibacterial, sulfonamide, diuretic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Skin pathologies
Dermatitis and the formation of hairless areas on the body of a fluffy pet are due to a number of reasons:
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- stress
- fungal diseases;
- parasitism of insects;
- allergies.
In diseases, hair loss, the appearance of alopecia, wounds, scratching, abscesses and abscesses on the skin of the animal are noted.
What to do with skin diseases?
Diagnosis of the disease should be carried out by a veterinarian, depending on the etiology of the disease, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Diseases of the ears and eyes
Conjunctivitis
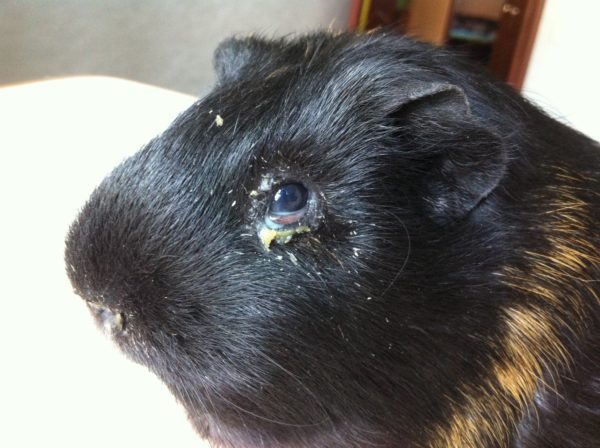
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes occurs in guinea pigs with:
- infectious diseases;
- eye injuries;
- allergies;
- ingress of a foreign body;
- lack of vitamin C.
The small animal has:
- lacrimation;
- swelling and redness of the eyes;
- adhesion of the palpebral fissure;
- accumulation of pus in the corners of the eyes.
What to do with conjunctivitis?
Therapy of diseased eyes consists in washing them with sterile saline and using anti-inflammatory drops or ointments.
Cataract
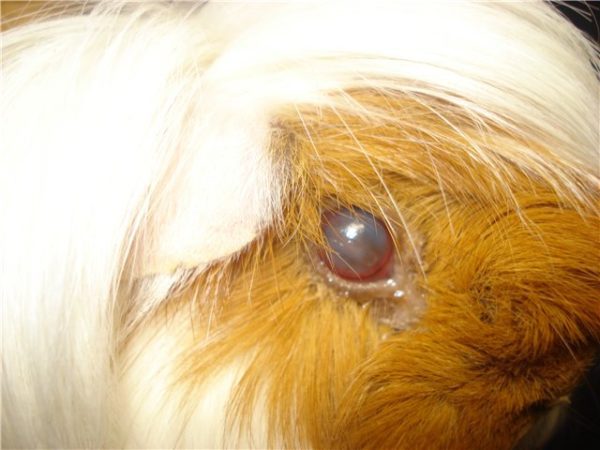
Cataracts in guinea pigs develop when:
- diabetes mellitus;
- lack of vitamins;
- injuries;
- conjunctivitis;
- congenital defects.
The animal has a complete or partial clouding of the eye.
What to do with a cataract?
Anti-inflammatory treatment is used, most often the pathology leads to blindness.
Otitis
In guinea pigs, otitis externa often occurs when:
- sarcoptosis;
- lichen;
- injuries;
- dermatitis.
Otitis media and internal are most often a complication of rhinitis and bronchitis.

Sick pet:
- rubs ear on objects;
- turns his head and itches;
- there is a dark discharge from the ear;
- swelling and redness of the ear;
- head tilt and torticollis.
What to do with otitis?
The specialist prescribes a course of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs to a small patient.
Dental diseases
Malocclusion
Incorrect bite in guinea pigs is caused by pathological regrowth of incisors or cheek teeth, as a result of improper feeding of pets, sometimes the pathology is inherited.
sick animal:
- cannot fully eat;
- there is a loss of food from a half-open mouth;
- salivation;
- emaciation
- muzzle asymmetry.
What to do with malocclusion?
Treatment of the disease consists in grinding down elongated teeth with further grinding and anti-inflammatory therapy of the oral cavity.
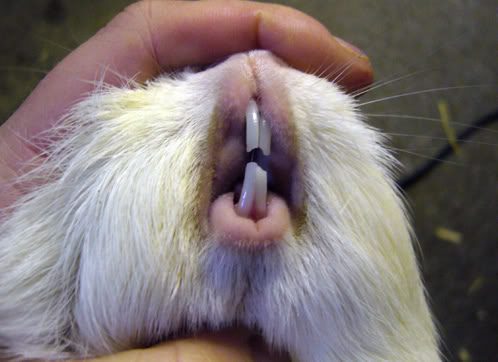
Elongation of the roots of the teeth
The disease is characterized by pathological elongation of the root part of the teeth with their ingrowth into soft tissues. The development of pathology is due to hereditary factors and violation of feeding a pet.
Depending on the affected area, a sick animal has:
- mucopurulent discharge from the nose and eyes;
- swelling;
- redness and enlargement of the eyeball;
- fluxes and growths on the jaws.
What to do when lengthening the roots?
Depending on the neglect of the disease in a veterinary clinic, crown cutting or extraction of a diseased tooth is used.
Nature has endowed funny kids with fairly good health, therefore, with proper feeding and maintenance, small animals rarely get sick at home. If your beloved pet has lethargy and refusal to feed, along with other signs of animal disease, you should urgently contact a veterinary clinic. Diseases of guinea pigs are characterized by a rapid course, sometimes, in the absence of competent therapy, a domestic animal dies within a few days, so the treatment of guinea pigs should be prescribed and monitored by a competent specialist.
Diseases of guinea pigs and their treatment
4.4 (88.82%) 34 votes





